Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 17 Symmetry
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 17 Symmetry (Including Reflection and Rotation)
Selina Publishers Concise Maths Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 17 Symmetry (Including Reflection and Rotation)POINTS TO REMEMBER
1. Symmetry : A geometrical figure is said to be symmetric about a line if on folding about that line, the two parts of the figure exactly concide each other. The given figure is symmetric about the line PQ. The line is said to be a line of symmetry or an axis of symmetry
2. Lines of symmetry of given geometrical figures :
It is not necessary that every figure under consideration will definitely have a line symmetry. If we consider different types of triangle ; we find :
1. A scalene triangle has no line of Symmetry : i.e. we can not have a line in a scalene triangle about which if the figure (triangle) is folded, the two parts of the figure will coincide.
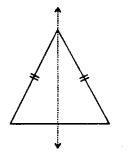
2. An isosceles triangle has only one line of symmetry. The bisector of angle of vertex which is also the perpendicular bisector of its base.
The bisectors of the angle of vertices which are also the perpendicular bisectors of its sides.
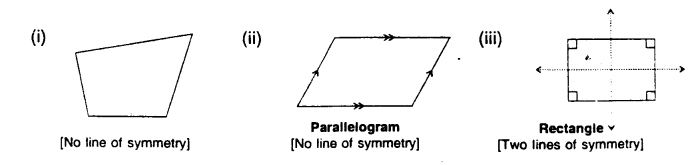
4. Line/lincs of symmetry of differed types of quadrilaterals are shown below by dotted lines :
5. In each of the following, the dotted line/lines are the line/lines of symmetry of the given figure:
6. As shown below:
(i) a circle has infinite lines of symmetry ; every line through its centre is line of symmetry’.
(ii) a semi-circle has one line of symmetry.
(iii) a quadrant (one-fourth) of a circle has one line of symmetry’ and so on.
Note : It is clear from the question numbers 4 and 5, given above that:
1. The largest number of lines of symmetry’ of a triangle is three (3).
2. The largest number of lines of symmetry of a quadrilateral is four (4).
i. e. as the number of sides in a triangle is 3 ; the largest number of lines of symmetry in it is 3 and as the number of sides in a quadrilateral is 4 ; the largest number of lines of symmetry is 4.
In the same way :
1. The largest number of lines of symmetry of a pentagon is 5, as a pentagon has 5 sides.2. The hexagon has 6 sides and so the largest number of lines of symmetry’ of a hexagon is 6.
In general, we can say, that if a polygon has n sides ; M
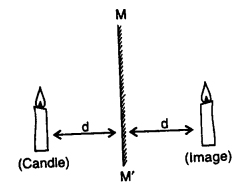
the largest number of lines of symmetry, it can have, is n.3. Reflection (Image): Tire given figure shows a candle place ‘d’ distance before a plane mirror MM’, the image of the candle is obtained in the mirror at the same distance ‘d’ behind the mirror. Geometrically, the line joining the candle (c) and its reflection c’ is (Candle) perpendicular bisector of the mirror line MM’.
4. Reflection in x-axis : Reflection if x-axis means the x-axis is considered as the plane mirror, the given point as the object and then to find its image.
Let P (x, y) be a point and. as shown in the figure, when it is reflected in x-axis to point P’; the co-ordinates of image point P’ are (x, – y).
i. e. reflection of P (x, y) in x-axis = P’ (x, – y)
In other words :Image of P (x, y) in x-axis = P’ (x, – y)
We can say, when a point (x, y) is reflected in x-axis, the sign of its second component (ordinate) changes i.e. tire sign of y changes and so the image of (x, y) in x-axis is (x, – y).
5. Reflection in y-axis : As is clear from the figure, given alongside, the reflection P (x, y) in y-axis is point P’ (- x, y).
We can say, when a point (x,y) is reflected in y-axis, the sign of its first component (abscissa) change i.e. the sign of x changes and so the image of (x, y) in y- axis is (-x,y).
6. Reflection in Origin : When a point P (x, y) is reflected in origin, the sign of both of its components change i.e. the image of P (x, y) is P’ (- x, -y) as shown along side in the figure.
Symmetry Exercise 17A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
For each figure, given below, draw the line (s) of symmetry, if possible :Write capital letters A to Z of English alphabet ; and in each case, if possible, draw the largest number of lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Line or lines of symmetry’ is possible in the following alphabets. For others alphabets it is not possible
Question 3.By drawing a free hand sketch of each of the following, draw in each case, the line (s) of symmetry,
if any:
(i) a scalene triangle
(ii) an isosceles right angled triangle
(iii) a rhombus
(iv) a kite shaped figure triangle.
(v) a rectangle
(vi) a square
(vii) an isosceles
Solution:
.
Question 4.
Draw a triangle with :
(i) no line of symmetry,
(ii) only one line of symmetry,
(iii) exactly two lines of symmetry,
(iv) exactly three lines of symmetry,
(v) more than three lines of symmetry.
In each case, if possible, represent the line/ lines of symmetry by dotted lines. Also, write the special name of the triangle drawn.
Solution:
(i) Scalene triangle : It has no line of symmetry.
(ii) Isosceles Triangle : It has one line of symmetry as shown.
(iii) It is not possible.
(iv) Equilateral Triangle : It has three lines of symmetry as shown
(v) It is not possible.
Question 5.
Draw a quadrilateral with :
(i) no line of symmetry.
(ii) only one line of symmetry.
(iii) exactly two lines of symmetry.
(iv) exactly three lines of symmetry.
(v) exactly four lines of symmetry.
(vi) more than four lines of symmetry.
In each case, if possible, represent the line/ lines of symmetry by dotted lines. Also, write the special name of the quadrilateral drawn.
Solution:
Question 6.
Construct an equilateral triangle with each side 6 cm. In the triangle drawn, draw all the possible lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 6 cm
(ii) With centres B and C and radius 6 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC
∆ ABC is the required equilateral triangle,
(iv) Draw the angle bisectors of ∠A, ∠B and ∠C.
These are the lines of symmetry which are three in numbers as the triangle is equilateral.
Question 7.
Construct a triangle ABC in which AB = AC = 5cin and BC = 5.6 cm. If possible, draw its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 5.6 cm
(ii) With centres B and C and radius 5 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
∆ ABC is an isosceles triangle.
(iv) Draw the bisector of ∠A. This is the only one line of symmetry as the triangle is an isosceles.
Question 8.
Construct a triangle PQR such that PQ = QR = 5 .5 cm and angle PQR = 90°. If possible, draw its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
∴ ∠PQR = 90°, and ∠P = ∠R
(opposite sides are equal)
∴∠P + ∠R = 90°
Hence ZP = ZR = = 45°
= 45°
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment QR = 5.5 cm
Question 9.
If possible, draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral which has exactly two lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Since the quadrilateral has exactly two lilies of symmetry
∴It must be a rectangle or a rhombus
Question 10.
A quadrilateral ABCD is symmetric about its diagonal AC. Name tire sides of this quadrilateral which are equal.
Solution:
The quadrilateral ABCD is symmetric about its diagonal AC.
∴It must be a kite shaped.
Hence side AB = AD and BC = DC.
Question 1.
In each figure, given below, find the image of the point P in the line AB :
Solution:
Steps of Construction : Fig. (i) and (ii)
(i) From P, draw a perpendicular to the given line AB meeting it at O.
(ii) Produce PO to P’ such that OP’ = PO.
P’ is the required image of P in AB.
Question 2.
In each figure, given below, find the image of the line segment AB in the line PQ :
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) From A and B, draw perpendiculars on PQ intersecting PQ at L and M.
Question 3.
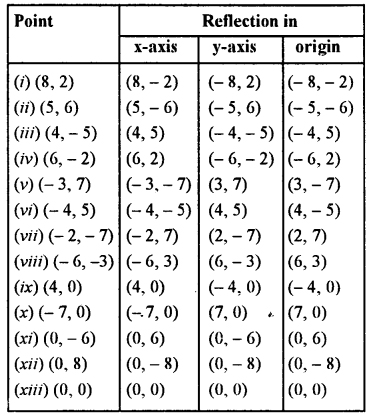
Complete the following table :
Solution:
Question 4.
(iii) the image of P (7, 3) in origin.
Solution:
(i) Image of point P (7,3) when reflected in x-axis is P’ whose co-ordinates will be (7,-3)
(ii) Image of point P’ (7,-3) when reflected in y-axis, is P” whose co-ordinates will be (- 7,-3)
(iii) The image of P (7, 3) in origin is P” whose co-ordinates are (- 7, – 3).
Question 5.
(iii) the image of A (- 5, 4) in x-axis.
Solution:
(i) Image of point A (- 5,4) when reflected in y-axis is B whose co-ordinates will be (5,4)
(ii) Image of B (5, 4) when reflected in origin is C whose co-ordinates will be (- 5, – 4)
(iii) Image of A (- 5,4) in x-axis is C whose co-ordinates are (- 5, – 4)
Question 6.
(iii) the image of P (3, – 8) in y-axis.
Solution:
(i) The image of the given point P (3, – 8) when reflected in origin is Q whose co-ordinates will be (- 3, 8).
(ii) The image of Q (- 3, 8) when reflected in x-axis is R whose co-ordinates will be (-3,-8)
(iii) Tlie image of P (3, 8) in y-axis is R whose co-ordinates are (- 3, – 8).
Question 7.
A (3, 0), B (1, 0), C (-8, 0), D (- 7, 0) and E (0, 0)
find if AB = A’ B’ ?
Solution:
The given points :
A (4, 5) and B (- 5, 4) have been marked on the graph.
A (6, 4) and B (4, – 6)
Question 12.
How many lines of symmetry does a rhombus have?
Solution:
It has two lines of symmetry.
Question 2.
What is the order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus?
Solution:
Solution:
Question 4.
Name a figure that has a line of symmetry but does not have any roational symmetry.
Solution:
(i) It has no line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 3
(ii) It has 2 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 4.

(iii) It has 2 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 2.
(iv) It has no line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 0.
(v) It has 1 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 0.
.
Question 4.
Draw a triangle with :
(i) no line of symmetry,
(ii) only one line of symmetry,
(iii) exactly two lines of symmetry,
(iv) exactly three lines of symmetry,
(v) more than three lines of symmetry.
In each case, if possible, represent the line/ lines of symmetry by dotted lines. Also, write the special name of the triangle drawn.
Solution:
(i) Scalene triangle : It has no line of symmetry.
(ii) Isosceles Triangle : It has one line of symmetry as shown.
(iii) It is not possible.
(iv) Equilateral Triangle : It has three lines of symmetry as shown
(v) It is not possible.
Question 5.
Draw a quadrilateral with :
(i) no line of symmetry.
(ii) only one line of symmetry.
(iii) exactly two lines of symmetry.
(iv) exactly three lines of symmetry.
(v) exactly four lines of symmetry.
(vi) more than four lines of symmetry.
In each case, if possible, represent the line/ lines of symmetry by dotted lines. Also, write the special name of the quadrilateral drawn.
Solution:
Construct an equilateral triangle with each side 6 cm. In the triangle drawn, draw all the possible lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 6 cm
(ii) With centres B and C and radius 6 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC
∆ ABC is the required equilateral triangle,
(iv) Draw the angle bisectors of ∠A, ∠B and ∠C.
These are the lines of symmetry which are three in numbers as the triangle is equilateral.
Question 7.
Construct a triangle ABC in which AB = AC = 5cin and BC = 5.6 cm. If possible, draw its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 5.6 cm
(ii) With centres B and C and radius 5 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
∆ ABC is an isosceles triangle.
(iv) Draw the bisector of ∠A. This is the only one line of symmetry as the triangle is an isosceles.
Question 8.
Construct a triangle PQR such that PQ = QR = 5 .5 cm and angle PQR = 90°. If possible, draw its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
∴ ∠PQR = 90°, and ∠P = ∠R
(opposite sides are equal)
∴∠P + ∠R = 90°
Hence ZP = ZR =
 = 45°
= 45°Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment QR = 5.5 cm
(ii) At Q, draw a ray making an angle of 90° and cut off QP = 5.5 cm.
(iii) Join PR.
∆PQR is an isosceles triangle.(iv) Draw the angle bisector of ∠PQR. It is the line of symmetry. Since the triangle is an isosceles.
∴It has only one line of symmetry.
If possible, draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral which has exactly two lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Since the quadrilateral has exactly two lilies of symmetry
∴It must be a rectangle or a rhombus
A quadrilateral ABCD is symmetric about its diagonal AC. Name tire sides of this quadrilateral which are equal.
Solution:
The quadrilateral ABCD is symmetric about its diagonal AC.
∴It must be a kite shaped.
Hence side AB = AD and BC = DC.
Symmetry Exercise 17B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
In each figure, given below, find the image of the point P in the line AB :
Solution:
Steps of Construction : Fig. (i) and (ii)
(i) From P, draw a perpendicular to the given line AB meeting it at O.
(ii) Produce PO to P’ such that OP’ = PO.
P’ is the required image of P in AB.
In each figure, given below, find the image of the line segment AB in the line PQ :
Steps of Construction :
(i) From A and B, draw perpendiculars on PQ intersecting PQ at L and M.
(ii) Produce AL to A’ such that AL = LA’ and produce BM to B’ such that BM = MB’ A’B’ is the image of the line segment AB in PQ.
Complete the following table :
Solution:
A point P (7,3)|is reflected in x-axis to point P’. The point P’ is further reflected in v-axis to point P” Find :
(i) the co-ordinates of P’
(ii) the co-ordinates of P”(iii) the image of P (7, 3) in origin.
Solution:
(i) Image of point P (7,3) when reflected in x-axis is P’ whose co-ordinates will be (7,-3)
(ii) Image of point P’ (7,-3) when reflected in y-axis, is P” whose co-ordinates will be (- 7,-3)
(iii) The image of P (7, 3) in origin is P” whose co-ordinates are (- 7, – 3).
Question 5.
A point A (- 5, 4) is reflected in y-axis to point B. The point B is further reflected in origin to point C. find :
(i) the co-ordinates of B
(ii) the co-ordinates of C(iii) the image of A (- 5, 4) in x-axis.
Solution:
(i) Image of point A (- 5,4) when reflected in y-axis is B whose co-ordinates will be (5,4)
(ii) Image of B (5, 4) when reflected in origin is C whose co-ordinates will be (- 5, – 4)
(iii) Image of A (- 5,4) in x-axis is C whose co-ordinates are (- 5, – 4)
Question 6.
The point P (3, – 8) is reflected in origin to point Q. The Point Q is further reflected in x-axis to point R. Find :
(i) the co-ordinates of Q
(ii) the co-ordinates of R(iii) the image of P (3, – 8) in y-axis.
Solution:
(i) The image of the given point P (3, – 8) when reflected in origin is Q whose co-ordinates will be (- 3, 8).
(ii) The image of Q (- 3, 8) when reflected in x-axis is R whose co-ordinates will be (-3,-8)
(iii) Tlie image of P (3, 8) in y-axis is R whose co-ordinates are (- 3, – 8).
Question 7.
Each of the points A (3, 0), B (7, 0), C (- 8, 0), D (- 7, 0) and E (0, 0) is reflected in x-axis to points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’ respectively. Write the co-ordinates of each of the image points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’.
Solution:
The points are given :A (3, 0), B (1, 0), C (-8, 0), D (- 7, 0) and E (0, 0)
This images will be when reflected in x-axis. A’ (3, 0), B’ (7, 0), C’ (- 8, 0) D’ (- 7, 0) and E’ (0, 0) as the given points lie on x-axis.
Question 8.
Each of the points A (0, 4), B (0, 10), C (0, – 4), D (0, – 6) and E (0, 0) is reflected in y-axis to points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’ respectively. Write the co-ordinates of each of the image points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’.
Solution:
The given pointsA (0, 4), B (0, 10), C (0, – 4), D (0, – 6) and E (0, 0) are reflected in y-axis. The co – ordinates of their images will be A’ (0, 4), B’ (0, 10), C’ (0, – 4) D’ (0, – 6) and E’ (0, 0) as they all lie on y-axis.
Each of the points A (0, 7), B (8. 0), C (0, -5), D (- 7, 0) and E (0, 0) are reflected in origin to points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’ respectively. Write the co-ordinates of each of the image points A’, B’, C’, D’ and E’.
Solution:
The points A (0, 7), B (8, 0), C (0, – 5). D (- 7.0) and E (0,0) are reflected in origin.So, the co-ordinates of their images will be A’ (0,-7), B’ (- 8, 0), C’ (0,5), D’ (7, 0) and E’ (0, 0)
Question 10.Mark points A (4, 5) and B (- 5, 4) on a graph paper. Find A’, the image of A in x-axis and B’, the image of B in x-axis.
Mark A’ and B’ also on the same graph paper.
(ii) Join AB and A’ B’ andfind if AB = A’ B’ ?
Solution:
The given points :
A (4, 5) and B (- 5, 4) have been marked on the graph.
The image of A in x-axis A (4, – 5) and image of B in x-axis is B’ (-5, -4) which have been also plotted on the same graph.
AB and A’ B’ are joined. We see that AB = A’ B’.
Question 11.
Mark points A (6, 4) and B (4, – 6) on a graph paper.Find A’, the image of A in y-axis and B’, the image of B in y-axis. Mark A’ and B’ also on the same graph paper.
Solution:
The given points areA (6, 4) and B (4, – 6)
The images of A and B is y-axis are A’ (- 6, 4) and B’ (- 4, – 6) respectively as shown in the same graph.
Mark points A (- 6, 5) and B (- 4, – 6) on a graph paper. Find A’, the image of A in origin and B’, the image of B in origin. Mark A’ and B’ also on the same graph paper. Join AB and A’ B’. Is AB = A’ B’ ?
Solution:
The given points are A (- 6, 5) and B (- 4, – 6). The images of A and B in the origin are A’ and B’ where co-ordinates are A’ (6, – 5) and B’ (4, 6) which have been plotted on the same graph.
AB and A’ B’ are joined we see that AB = A’ B’.Symmetry Exercise 17C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.How many lines of symmetry does a rhombus have?
Solution:
It has two lines of symmetry.
Question 2.
What is the order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus?
Solution:
The order of rotational symmetry can be defined as the number of times that a shape appears exactly the same during a full 360° rotation. Order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus is 2.
Question 3.
Show that each of the following figures has two lines of symmetry and a rotational.Solution:
Question 4.
Name a figure that has a line of symmetry but does not have any roational symmetry.
Solution:
Isosceles triangle has only line symmetry and no rotational symmetry.
Question 5.In each of the following figures, draw all possible lines of symmetry and also write the order of rotational symmetry:
Solution:(i) It has no line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 3
(ii) It has 2 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 4.

(iii) It has 2 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 2.
(iv) It has no line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 0.
(v) It has 1 line of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry is 0.