Selina Concise Biology Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Cell – The Structure and Functions
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Biology Chapter 3 Cell – The Structure and Functions
Synopsis
• The single-celled organisms are called unicellular and if the organisms are made up of more than one cell are called multicellular.
• The simple microscope was developed by Antony Von Leeuwenhoek.
• The compound microscope was developed by Robert Hooke.
• The branch of biology which deals with the study of cells is called cytology.
• The living substance of the cell is called protoplasm.
• Examples of
(a) unicellular organisms:
- bacteria
- amoeba
- yeast
- chlamydomonas etc.
• (b) multicelluar organisms: plants like rose, neem, animals like man, hydra etc.
• Examples of different cellular shapes.
- irregular — amoeba
- oval — chlamydomonas (slipper organism)
- oblong — paramecium
- elongated — striated muscle cells
- very long or thread like — nerve fibre cells
- cubical or rectangular — plant cell
• The smallest cell — Bacterial cell
The longest cell — Nerve cells
The largest cell — Ostrich egg
• Cell theory explains
- Every living organism is made up of one or many cells.
- The structural unit of all the living organisms is the cell.
- The functional unit of all the living organisms is the cell.
- All cells arise from the pre-existing cells.
• The three scientists who contributed in the cell theory are:
- M.J. Schleiden
- Theodor Schwann
- Rudolph Virchow
• Animal cells have no cell walls.
• The cell wall is made up of cellulose which is rigid and gives shape to the cell.
• The cell wall is freely permeable while the cell membrane is semi-permeable.
• The supportive framework which helps in the distribution of various product across the cell is endoplasmic reticulum.
• Power house of the cell — Mitochondria
• Synthesise proteins — Ribosomes.
• The organelle found only in the animal cell which initiate and regulate cell division is Centrosome.
• The organelle found only in the plant cell is plastid.
Green plastids are chloroplasts
Other plastids are amyloplasts.
• Cell organelles are concerned with specific functions.
• The importance of cell division is.
- Production of new cells.
- For growth and repair.
- Replacement of the dead and worn out cells. –
- For reproduction.
• The process of fusion of sperm and an egg is called fertilisation.
• The result of fertilisation is Zygote.
Review Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statements:
(i) Identify the part which contain pigment:
(a) cell membrane
(b) plastid
(c) centrosome
(d) cell wall
(ii) The organelle that controls all activities in
(a) nucleus
(b) vacoule
(c) plastids
(d) cytoplasm
(iii) A cell that is spherical in shape is:
(a) white blood cell
(b) nerve cell
(c) red blood cell
(d) amoeba
(iv)The vacuole contains:
(a) water
(b) cell sap
(c) salts
(d) food
Question 1.
Name the scientist who invented the first microscope.
Answer :
Antony Von Leeuwenhoek.
Question 2.
Who coined the term “cell” ?
Answer :
The term “cell” was coined by Robert Hooke.
Question 3.
Briefly describe the three essential basic parts of a cell.
Answer :
The essential basic parts of a cell are:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Cell membrane — It is a very thin, delicate and flexible membrane which surrounds each cell. It is also called plasma membrane. It consists of fine pores which allow only certain molecules to pass through it and prohibit the others and therefore, due to its function, also called selectively permeable membrane.
- Cytoplasm: This is the living portion of the cell which is a semi-liquid, translucent and colourless liquid. It is the portion of the cell where major functions of the cell are carried out through various finer parts of the cell. The finer structures which are contained in this are called the cell organelles.
- Nucleus: The small spherical dark coloured body usually located in the centre of the cell. It is the most important part of the cell which regulates and co-ordinates various life processes. Its major role is during cell division. It contains hereditary factors called the genes.
Question 4.
The cell membrane is called selectively permeable. Why?
Answer :
The cell membrane of the cell is composed of fine pores through which only certain molecules of the different substances can pass into the cell. Since it allows only specific molecules to enter prohibiting the other it is referred to as Selectively Permeable.
Question 5.
State the difference between
Answer :
(i) Nucleus and nucleolus
Nucleus
- It is a cell organelle.
- It is the most important part of the cell.
- It is present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- It is bounded by a delicate nuclear membrane
Nucleolus
- It is a component of the nucleus.
- It is the most important part of the nucleus.
- It is present in the nucleoplasm.
- It does not have any such membrane around it
(ii) Cytoplasm and protoplasm
Answer :Cytoplasm
- The living portion of the cell inside the cell except the nucleus.
- It has many finer parts contained in it like golgi bodies, mitochondria etc.
Protoplasm
The living substance of a cell is called the protoplast.
It consists of two main parts
- cytolasm
- nucleus.
(iii) Cell wall and cell membrane.
Answer :
Cell wall
- It is made up of cellulose.
- It gives shape and rigidity to the plant cell.
- It is a non-living structure.
- It protects the cell from the entry of disease-causing agents, as well the underlying protoplasm against mechanical injuries.
Cell Membrane
- It is very thin, delicate and flexible.
- This allows the entry of certain molecules only, while holding back the others.
- It is living structure.
- It has fine pores in it, through which only certain substances carfpass in and out, while others cannot.
Question 6.
List the major differences between a plant cell and an animal cell.
Answer :
Plant cell
- Cell is comparatively larger with distinct outlines.
- Has a definite and rigid cell wall.
- Has negligible amount of cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm is not very dense.
- Contains plastids.
- No centrosome.
- Have prominent one or more vacuoles.
- Has simple golgi apparatus composed of units called dictyosomes.
Animal cell
- Size is small with less distinct outlines.
- Cell wall absent.
- Cytoplasm fills almost the entire cell.
- Cytoplasm is granular and relatively dense.
- Do not contain plastids
- Centrosomes are present.
- Have temporary vacuoles which are small and concerned with secretion or excretion.
- Have complex and prominent golgi apparatus.
Question 7.
Briefly discuss the importance of chromosomes to an organism.
Answer :
The most important feature of a living cell is that it can divide or reproduce of its own kind and this function is regulated by the nucleus of the cell. The nucleus in its nucleoplasm contain a network of dark stained thread like structures called chromatin fibres. These fibres during cell division become thick and ribbon like which are then called chromosomes. The chromosomes are the actual hereditary factors. These are unique for each species both in number and in character.
Human body has 46 chromosomes which occur in pairs.
They are further categorised as:
- Chromosomes specific for determining the sex of the species called the sex chromosomes.
- Other chromosomes are called autosomes.
8. Fill up the blanks with the terms given below in the box.
Pigments, wall, pre-existing, cell, vacoules
- The cell is the structural unit of all living things.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
- Animal cells have no cell wall.
- Plastids contain pigments.
- Vacoules are filled with water and dissolved substance
Question 9.
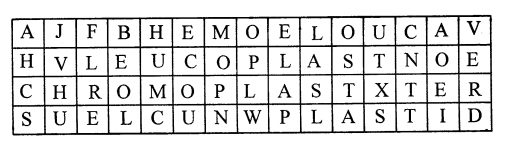
Try to find the names of four cell organells hidden in this maze, (hint: The hidden words can appear horizontally or vertically; forwards or backward or even mixed up). Write them in the lines provided. For example :
“NUCLEUS” in the last row, seven backward letters.
- Vacuole
- Leucoplast
- Chromoplast
- Nucleus, Plastid