Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Natural Numbers and Whole Numbers
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Natural Numbers and Whole Numbers (Including Patterns)
EXERCISE 5(A)
Fill in the blanks :
(i) Smallest natural number is …………..
(ii) Smallest whole number is …………
(iii) Largest natural number is …………
(iv) Largest whole number is ………..
(v) All natural numbers are …………
(vi) All whole numbers are not …………
(vii) Successor of 4099 is …………..
(viii) Predecessor of 4330 is …………….
Solution:
(i) Smallest natural number is 1
(ii) Smallest whole number is 0
(iii) Largest natural number is can not be obtained
(iv) Largest whole number is can not be obtained
(v) All natural numbers are whole numbers
(vi) All whole numbers are not natural numbers
(vii) Successor of 4099 is 4099 + 1 = 4100
(viii) Predecessor of 4330 is 4330 – 1 = 4329
Question 2.
Represent the following whole numbers on a number line :
0, 3, 5, 8, 10
Solution:
Number line used to represent whole numbers 0, 3, 5, 8, 10 is as given below:
Question 3.
State, true or false :
(i) Whole number are closed for addition.
(ii) If a and b are any two whole numbers, then a + b is not a whole number.
(iii) If a and b are any two whole numbers, then a + b = b + a
(iv) 0 + 18= 18 + 0
(v) Addition of whole numbers is associative.
(vi) 10 + 12 + 16 = (10 + 12) + 16 = 10 + (12 + 16)
Solution:
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) True
(v) True
(vi) True
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) 54 + 234 = 234 + …………
(ii) 332 + 497 = ………… + 332
(iii) 286 + 0 = ………..
(iv) 286 x 1 = ……….
(v) a + (b + c) = (a + ………) + c
Solution:
(i) 54 + 234 = 234 + 54
(ii) 332 + 497 = 497 + 332
(iii) 286 + 0 = 286
(iv) 286 x 1 = 286
(v) a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
Question 5.
By re-arranging the given numbers, evaluate :
(i) 237 + 308 + 163
(ii) 162 + 253 +338 + 47
(iii) 21 + 22 + 23 + 24 + 25 + 75 + 76 + 77 + 78 + 79
(iv) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 596 + 597 + 598 + 599
Solution:
(i) 237 + 308 + 163
= (237 + 163) + 308 (by associative law)
= 400 + 308 = 708
(ii) 162 + 253 + 338 + 47
= (162 + 338) + (253 + 47) (By associative law)
= 500 + 300 = 800
(iii) 21 + 22 + 23 + 24 + 25 + 75 + 76 + 77 + 78 + 79
= (21 + 79) + (22 + 78) + (23 + 77) + (24 + 76) + (25 + 75) (By associative law)
= 100 + 100+ 100+ 100 + 100 = 500
(iv) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 596 + 597 + 598 + 599
= (1 + 599) + (2 + 598) + (3 + 597) + (4 + 596) (By associative law)
= 600 + 600 + 600 + 600 = 2400
Question 6.
Is a + b + c = a + (b + c) = (b + a) + c ?
Solution:
Yes, because any set of three whole numbers if the sum of any two whole numbers is added to the third whole number, then whatever be their order, the sum will remain same.
Question 7.
Which property of addition is satisfied by :
(i) 8 + 7 = 15
(ii) 3+ (5 + 4) = (3 + 5)+ 4
(iii) 8 x (8 + 0) = 8 x 8 + 8 x 0
(iv) (7 + 6) x 10 = 7 x 10 + 6 x 10
(v) (15 – 12) x 18 = 15 x 18 – 12 x 18
(vi) 16 + 0= 16
(vii) 23 + (-23) = 0
Solution:
(i) 8 + 7=15
The property used as closure property satisfied by 15.
(ii) 3+ (5 + 4) = (3 + 5)+ 4 3 +(5+ 4) = 3 + 9=12 and (3+ 5)+ 4 = 8 + 4=12
The property used as Associative law of addition satisfied by 12.
(iii) 8 x (8 + 0) = 8 x 8 + 8 x 0
8 x (8 + 0) = 8 x 8 = 64
and 8 x 8 + 8 x 0 = 64 + 0 = 64
The property used as Distributive property over addition satisfied by 64.
(iv) (7 + 6) x 10 = 7 x 10 + 6 x 10 (7 + 6) x 10= 13 x 10= 130
and 7 x 10 + 6 x 10 = 70 + 60 = 130
The property used as Distributive over addition satisfied by 130.
(v) (15 – 12) x 18= 15 x 18- 12 x 18 (15 – 12) x 18 = 3 x 18 = 54
and 15 x 18 – 12 x 18 = 270 – 216 = 54
The property used as Distributive over subtraction satisfied by 54.
(vi) 16 + 0=16
The property used as Existence of identity satisfied by 16
(vii) 23 + (-23) = 0
The property used as Additive inverse satisfied by 0.
Question 8.
State, True or False :
(i) The sum of two odd numbers is an odd number.
(ii) The sum of two odd numbers is an even number.
(iii) The sum of two even numbers is an even number.
(iv) The sum of two even numbers is an odd number.
(v) The sum of an even number and an odd number is odd number.
(vi) Every whole number is a natural number.
(vii) Every natural number is a whole number.
(viii) Every whole number + 0 = The whole number itself.
(ix) Every whole number x 1 = The whole number itself.
(x) Commutativity and associativity are properties of natural numbers and whole numbers both.
(xi) Commutativity and associativity are properties of addition for natural numbers and whole numbers both.
(xii) If x is a whole number then -x is also a whole number.
Solution:
(i) False.
The sum of two odd numbers is an even number.
(ii) True.
(iii) True.
(iv) False.
The sum of two even numbers is an even number.
(v) True.
(vi) False.
Every natural number is a whole number.
(vii) True.
(viii) True.
(ix) True.
(x) True.
(xi) True.
(xii) True.
EXERCISE 5(B)
Question 1.
Consider two whole numbers a and b such that a is greater than b.
(i) Is a – b a whole number ? Is this result always true ?
(ii) b-a a whole number ? Is this result always true ?
Solution:
Let us take a as 2 and has 1
(i) a – b = 2 – 1 = 1,
Yes, a – b is a whole number and the result will always remain the same.
(ii) b – a = 1 – 2 = -1
No, a – b can never be a whole number. Yes, the result always be true.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) 8 – 0 = ……….. and 0 – 8 = ……….
8 – 0 ≠ 0 – 8, this shows subtraction of whole numbers is not ………..
(ii) 5 – 10 = ………., which is not a …………
=> Subtraction of ……….. is not closed.
(iii) 7 – 18 = ……….. and (7 – 18) – 5 = …………..
18 – 5 = …………. and (7 – 18) – 5 = ………….
Is (7 – 18) – 5 = 7 – (18 – 5) ?
=> Subtraction of whose numbers is not ………….
Solution:
(i) 8 – 0 = 8 and 0 – 8 = -8
8 – 0 & 0 – 8, this shows subtraction of whole numbers is not commutative
(ii) 5 – 10 = -5, which is not a whole number
=> Subtraction of whole numbers is not associative.
(iii) 7 – 18 = -11 and (7 – 18) – 5 = -16
18 – 5 = 13 and (7 – 18) – 5 = -6
Is (7 – 18) – 5 = 7 – (18 – 5) = ?
No, (7- 18) – 5 ≠ 7 – (18 – 5)
=> Subtraction of whole number is not associative.
Question 3.
Write the identify number, if possible for subtraction.
Solution:
It is not possible to identify the number.
Question 4.
Write the inverse, if possible for subtraction of whole numbers ?
Solution:
The inverse does not exit.
Question 5.
12 x (9 – 6) = ………….. = ………….
12 x 9 – 12 x 6 = …………. = …………….
Is 12 x (9 – 6) = 12 x 9 – 12 x 6 ? ………….
Is this type of result always true ? ……………
Name the property used here …………..
Solution:
12 x (9-6)= 12 x 3 = 36
12 x 9- 12 x 6 = 108 – 72 = 36
Is 12 x (9 – 6) = 12 x 9 – 12 x 6 ? =
Is this type of result always true ? Yes
Name the property used here Distributive property.
Question 6.
(16 – 8) x 24 = ………….. = …………..
16 x 24 – 8 x 24 = …….. – ……….. = ………..
Is (16 – 8) x 24 = 16 x 24 – 8 x 24 ? …………..
Is the type of result always true ? ………….
Name the property used here ………………
Solution:
(16 – 8) x 24 = 8 x 24 = 192
16 x 24 – 8 x 24 = 384 – 192 = 192
Is (16 – 8) x 24 = 16 x 24 – 8 x 24 ? Yes.
Is the type of result always true ? Yes
Name the property used here Distributivity.
EXERCISE 5(C)
Fill in the blanks :
(i) 42 x o = ……….
(ii) 592 x 1 = ………..
(iii) 328 x 573 = ……….. x 328
(iv) 229 x ………… = 578 x 229
(v) 32 x 15 = 32 x 6 + 32 x 7 + 32 x ……….
(vi) 23 x 56 = 20 x 56 + ……… x 56
(vii) 83 x 54 + 83 x 16 = 83 x ( ……….. ) = 83 x ………….. = …………
(viii) 98 x 273 – 75 x 273 = ( …………. ) x 273 = ………… x 273
Solution:
(i) 42 x 0 = 0
(By closure property 0)
(ii) 592 x 1 = 592
(By closure property 1)
(iii) 328 x 573 = 573 x 328
(By commutative law of multiplication)
(iv) 229 x 578 = 578 x 229
(By commutative law of multiplication)
(v) 32 x 15 = 32 x 6 + 32 x 7 + 32 x 2
(By commutative law of multiplication)
(vi) 23 x 56 = 20 x 56 + 3 x 56
(By Distributive law of multiplication)
(vii) 83 x 54 + 83 x 16 = 83 x (54 + 16) = 83 x 70 = 5810
(viii) 98 x 273 – 75 x 273 = (98 – 75) x 273 = 23 x 273
Question 2.
By re-arranging the given numbers, evaluate :
(i) 2 x 487 x 50
(ii) 25 x 444 x 4
(iii) 225 x 20 x 50 x 4
Solution:
(i) 2 x 487 x 50
2 x 50=100
2 x 487 x 50 = (2 x 50) x 487 = 100 x 487 = 48700
(ii) 25 x 444 x 4
25 x 4 = 100
25 x 444 x 4 = (25 x 4) x 444 = 100 x 444 = 444000
(iii) 225 x 20 x 50 x 4
= (225 x 4) x (20 x 50) = 900 x 1000 = 900, 000
Question 3.
Use distributive law to evaluate :
(i) 984 x 102
(ii) 385 x 1004
(iii) 446 x 10002
Solution:
(i) 984 x 102
= 984 x (100 + 2)
= 984 x 100 x 984 x 2
= 98400 + 1968 = 100,368
(ii) 385 x 1004
= 385 x (1000 + 4)
= 385 x 1000 x 385 x 4
= 385000 + 1540 = 386540
(iii) 446 x 10002
= 446 x (10000 + 2)
= 446 x 10000 x 446 x 2
= 4460000 + 892 = 4460892
Question 4.
Evaluate using properties :
(i) 548 x 98
(ii) 924 x 988
(iii) 3023 x 723
Solution:
(i) 548 x 98
= (500 + 40 + 8) x 98
= 500 x 98 + 40 x 98 + 8 x 98
= 49000 + 3920 + 784 = 53704
(ii) 924 x 988
= (900 + 20 + 4) x 988
= 900 x 988 + 20 x 988 + 4 x 988
= 889200 + 19760 + 3952 = 912912
(iii) 3023 x 723
= (3000 + 20 + 3) x 723
= 3000 x 723 + 20 x 723 + 3 x 723
= 2169000 + 14460 + 2169 = 2185629
Question 5.
Evaluate using properties :
(i) 679 x 8 + 679 x 2
(ii) 284 x 12 – 284 x 2
(iii) 55873 x 94 + 55873 x 6
(iv) 7984 x 15 – 7984 x 5
(v) 8324 x 1945 – 8324 x 945
(vi) 3333 x 987 + 13 x 3333
Solution:
(i) 679 x 8 + 679 x 2
= 679 x (8 + 2) (using distributivity)
= 679 x 10 = 6790
(ii) 284 x 12-284 x 2
= 284 x (12-2) (using distributivity)
= 284 x 10 = 2840
(iii) 55873 x 94 + 55873 x 6
= 55873 x (94 + 6) (using distributivity)
= 55873 x 100 = 5587300
(iv) 7984 x 15 – 7984 x 5
= 7984 x (15 – 5) (using distributivity)
= 7984 x 10 = 79840
(v) 8324 x 1.945 – 8324 x 945
= 8324 x (1945 – 945) (using distributivity)
= 8324 x 1000 = 8324000
(vi) 3333 x 987 + 13 x 3333
= 3333 x (987 + 13) (using distributivity)
= 3333 x 1000 = 3333000
Question 6.
Find the product of the :
(i) greatest number of three digits and smallest number of five digits.
(ii) greatest number of four digits and the greatest number of three digits.
Solution:
(i) Greatest number of three digits = 999
and Smallest number of five digits = 10000
Required product = 999 x 10000 = 9990000
(ii) Greatest number of four digits = 9999
and Greatest number of three digits = 999
Required product = 9999 x 999
= 9999 x (1000 – 1)
= 9999 x 1000 – 9999 x 1 (using distributivity)
= (10000- 1) x 1000 – (10000- 1) x 1
= 10000 x 1000 – 1 x 1000 – 10000 + 1
= 10000000 – 1000 – 10000 + 1
= 10000001 – 11000
= 9989001
Question 7.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) (437 + 3) x (400 – 3) = 397 x ……….
(ii) 66 + 44 + 22 = 11 x (………..) = 11 x ……….
Solution:
(i) (437 + 3) x (400 – 3) = 397 x 440
(ii) 66 + 44 + 22 = 11 x (6 + 4 + 2) = 11 x 12 = 132
Question 8.
Evaluate :
(i) 355 x 18
(ii) 6214 x 12
(iii) 15 x 49372
(iv) 9999 x 8
Solution:
(ï) 355 x 18
(300 + 50 + 5) x 18
300 x 18 + 50 x 18 + 5 x 18
= 5400 + 900 + 90
= 6390
(ii) 6214 x 12
=(6000 + 200 + 10 + 4) x 12
=6000 x 12+ 200 x 12 + 10 x 12 +4 x 12
= 72000 + 2400 + 120 + 48
= 74568
(iii) 15 x 49372
= 15 x (40000 + 9000 + 300 + 70 + 2)
= 15 x 40000 + 15 x 9000 + 15 x 300+ 15 x 70 + 15 x 2
= 600000 + 135000 + 4500 + 1050 + 30
= 740580
(iv) 9999 x 8
= (9000 + 900 + 90 + 9) x 8
=9000 x 8+900 x 8 + 90 x 8 + 9 x 8
= 72000 + 7200 + 720 + 72
= 79992
EXERCISE 5(D)
Question 1.
Show that :
(i) division of whole numbers is not closed
(ii) any whole number divided by 1, always gives the number itself.
(iii) every non-zero whole number divided by itself gives 1 (one).
(iv) zero divided by any non-zero number is zero only.
(v) a whole number divided by 0 is not defined.
For each part, given above, give an example.
Solution:
(i) For example
5 and 8 are whole numbers, but 5 + 8 is not a whole number
Closure property does not exist for division.
(ii) For example
2 + 1 =2, 18 + 1 = 18, 129 + 1 = 129
The above statement is true.
(iii) For example
2 ÷ 2 = 1, 128 ÷ 128 = 1, 256 ÷ 256 = 1
The above statement is true.
(iv) For example
0 ÷ 138 = 0, 0 ÷ 2028 = 0, 0 ÷ 15140 = 0
The above statement is true.
(v) For example
3 ÷ 0 = Not defined or 19 ÷ 0 is not defined
The above statement is true.
Question 2.
If x is a whole number such that x ÷ x = x, state the value of x.
Solution:
Since, we know that any number divided by 1, always gives the number itself.
x can be any number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ………… and so on.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) 987 + 1 = …………
(ii) 0 + 987 = ……….
(iii) 336 – (888 + 888) = ……….
(iv) (23 + 23) – (437 + 437) = ………
Solution:
(i) 987 ÷ 1 = 987
(ii) 0 ÷ 987 = 0
(iii) 336 – (888 + 888) = 335
(iv) (23 + 23) – (437 + 437) = 0
Question 4.
Which of the following statements are true ?
(i) 12 ÷ (6 x 2) = (12 ÷ 6) x (12 ÷ 2)
(ii) a ÷ (b – c) =

(iii) (a – b) ÷ c =

(vi) (15 – 13) ÷ 8 = (15 ÷ 8) – (13 ÷ 8)
(v) 8 ÷ (15 – 13) =

Solution:
(iii) and (iv) are true.
EXERCISE 5 (E)
Question 1.
Find the difference between the largest number of four digits and the smallest number of six digits.
Solution:
Largest number of four digits = 9999 and, smallest number of six digits = 100000
Difference = 100000 – 9999 = 90001
Question 2.
Find the difference between the smallest number of eight digits and the largest number of five digits.
Solution:
Smallest number of eight digits = 10000000
and, largest number of five digits = 99999
Difference = 10000000 – 99999 = 9900001
Question 3.
The product of two numbers is 528. If the product of their unit’s digits is 8 and the product of their ten’s digits is 4 ; find the numbers.
Solution:
Product of unit’s digit = 8 = 2 x 4
Unit’s digits are 2 and 4
Thus, the numbers are either 24 and 22
24 x 22 = 528
The required numbers are 528
Question 4.
Does there exist a number a such that a ÷ a = a ?
Solution:
Yes, A number a is 1
a ÷ a = a
1 ÷ 1 = 1
Question 5.
Divide 5936 by 43 to find the quotient and remainder. Also, check your division by using the formula,
dividend = divisor x quotient + remainder.
Solution:
On dividing 5936 by Divisor 43 gives quotient 138 and remainder 2.
Now, to verify,
Divided = divisor x quotient + remainder
5936 =43 x 138 + 2
= 43 x (100 + 38) + 2
= 4300 + 1634 + 2
= 5936
Hence verified.
EXERCISE 5(F)
Question 1.
(i) 1 x 9 + 1 = 10
12 x 9 + 2 = 110
123 x 9 + 3 = 1110
(ii) 9 x 9 + 7 = 88
98 x 9 + 6 = 888
987 x 9 + 5 = 8888
(iii) 1 x 8 + 1 = 9
12 x 8 + 2 = 98
123 x 8 + 3 = 987
(iv) 111 ÷ 3 = 37
222 ÷ 6 = 37
333 ÷ 9 = 37
Solution:
(i) 1 x 9 + 1 = 10
12 x 9 + 2 = 110
123 x 9 + 3 = 111O
1234 x 9 + 4 = 11110
12345 x 9 + 5 = 111110
123456 x 9 + 6 = 1111110
(ii) 9 x 9 + 7 = 88
98 x 9 + 6 = 888
987 x 9 + 5 = 8888
9876 x 9 + 4 = 88888
98765 x 9 + 3 = 888888
987654 x 9 + 2 = 8888888
(iii) 1 x 8 + 1 = 9
12 x 8 + 2 = 98
123 x 8 + 3 = 987
1234 x 8 + 4 = 9876
12345 x 8 + = 98765
123456 x 8 + 6 = 987654
(iv) 111 ÷ 3 = 37
222 ÷ 6 = 37
333 ÷ 9 = 37
444 ÷ 12 =37
555 ÷ 15 = 37
666 ÷ 18 =37
Question 2.
Complete each of the following magic squares :
Solution:
Question 3.
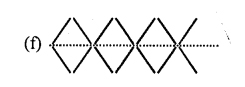
See the following pattern carefully :
(i) If n denotes the number of figure and S denotes the number of matches ; find S in terms of n.
(ii) Find how many matches are required to make the :
(1) 15th figure
(2) 40th figure
(iii) Write a discretion of the pattern in words.
Solution:
(ii) (1) 15th figure has = 3 x 15 + 4 = 49 matches
(2) 40th figure has = 3 x 40 + 4 = 124 matches
(iii) It can easily be observed that each time the figure (n) is increased by 4, the number of matches (S) increased by 3.
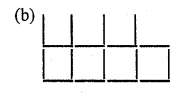
Question 4.
(i) In the following pattern, draw the next two figures.
(ii) Construct a table to describe the figures in the above pattern.
(iii) If n denotes the number of figure and L denotes the number of matches, find L in terms of n.
(iv) Find how may matches are required to make the :
(1) 12th figure
(2) 20th figure
Solution:
(iii) L = 2n
(iii) (1) 12th figure
12th figure has = 2 x 12 = 24
(2) 20th figure = 2 x 20 = 40
Question 5.
In each of the following patterns, construct next figure.
(i) In each case, if n denotes the number of figure and F denotes the number of matchsticks used, find F in terms of n.
(ii) Also find, in each case, how many matches are required to make the : 16th figure and 30th figure.
Solution: