Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Fundamental Concepts
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Fundamental Concepts
IMPORTANT POINTS
1. Fundamental Concepts : Geometry is the study of position,, shape, size and other properties of different figures. The geometrical terms such as : point, line, plane, etc., contain the basic ideas for the development of geometry.
(i) Point : A point is a mark of position. It has neither length nor width nor. thickness and occupies no space.
(ii) Line : A line has only length. It has neither width nor thickness.
(iii) Ray : It is a line (i.e. a straight line) that starts from a given fixed point and moves in the same direction.
(iv) Line Segment: A line segmeftt is a part of a straight line. A line segment is a part of a line and also of a ray.
(v) Surface : A surface has length and width, but no thickness.
(vi) Plane : It is a flat surface. A plane has length and width, but no thickness.
(vii) Parallel Lines : Two straight lines are said to be parallel to each other if they lie in the same plane and do not meet when produced on either side.
(viii)Intersecting Lines : If two lines lie in the same plane and are not parallel to each other, they are called intersecting lines.
(xi) Collinearity of Points : If three of more points lie on the same straight line, then the points are called collinear points.
(x) Concurrent Lines : If three or more straight lines pass through the same point, the lines are called concurrent lines.
EXERCISE 23 (A)
State, true or false, if false, correct the statement.
(i) A dot has width but no length.
(ii) A ray has an infinite length only on one side of it.
(iii) A line segment PQ is written as

(iv)
 represents a straight line.
represents a straight line.(v) Three points are said to be collinear, if they lie in the same plane.
(vi) Three or more points all lying in the same line, are called collinear points.
Solution:
(i) False : Because a dot has no length, no breadth.
(ii) True.
(iii) False : A line segment PQ is written as PQ.
(iv) True.
( v) False: Three points are called collinear points if they are in the same straight line.
(vi) True.
Question 2.
Write how many lines can be drawn through :
(i) a given point ?
(ii) two given fixed points ?
(iii) three collinear points ?
(iv) three non-collinear points ?
Solution:
(i) Infinite (unlimited) line can be drawn through a given point.
(ii) only one line can be drawn through two given point.
(iii) only one line can be drawn through three collinear points.
(iv) None (no) line can be drawn through three non-collinear points.
Question 3.
The shaded region of the given figure shows a plane :
(a) Name :
(i) three collinear points.
(ii) three non-collinear points.
(iii) a pair of intersecting lines.
(b) State whether true or false :
(i) Line DE is contained in the given plane P.
(ii) Lines AB and DE intersect at point C.
(iii) Points D, B and C are collinear.
(iv) Points D, B and E are collinear.
Solution:
(a) (i) A, B and C are three collinear points.
(ii) A, D and C are non-collinear points.
(iii) AC and DE are intersecting lines.
(b) (i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) False
(i) A A ray can be extended infinitely on either side.
(ii) A ray has a definite length.
(iii) A line segment has a definite length.
(iv) A line has two end-points.
(v) A ray has only one end point.
Solution:
(i) A ray can be extended infinitely on one side of it only.
(ii) A ray has infinite length.
(iii) Yes, a line segment has a definite length.
(iv) A line-segment has two end-points.
(v) Yes, a ray has only one end-point.
Question 5.
State true-er false, if false give the correct statement :
(i) A line has a countable number of points in it.
(ii) Only one line can pass through a given point.
(iii) The intersection of two planes is a straight line
Solution:
(i) False, a line has length only.
(ii) False, any number of line can pass through a given point.
(iii) True.
Question 6.
State, whether the following pairs of lines or rays appear to be parallel or intersecting.
Solution:
(i) intersecting
(ii) Parallel
(iii) Parallel
(iv) Intersecting
Question 7.
Give two examples, from your surroundings, for each of the following:
(i) points
(ii) line segments
(iii) plane surfaces
(iv) curved surfaces.
Solution:
(i) Tips of your pencil (Ball Pen) and Tip of paper pin.
(ii) Lines of Exercise Note-Books and edge of school desk.
(iii) Floor of the room and top of the table.
(iv) Surface of foot-ball and front glass of the car.
Question 8.
Under what condition will two straight
lines, in the same plane, have :
(i) no point in common.
(ii) only one point in common.
(iii) an infinite number of points in common.
(iv) If possible draw diagrams in support of your answer.
Solution:
(i) When lines are parallel to each others.
(ii) When they intersect each other
Here, common point is E.
(iii) When line coincide with each other.
Question 9.
Question 10.
Mark two points P and Q on a piece of paper. How many lines can you draw:
(i) passing through both the points P and Q?
(ii) passing through the point P ?
(iii) passing through the point Q ?
Solution:
(i) From above diagram it is clear only one line can be drawn.
(ii) Infinite lines can pass through the point up
(iii) Infinite lines can pass through the point
Question 11.
The adjoining diagram shows a line AB. Draw diagram to represent:
(i) ray AB i.e.
(vi) Three or more points all lying in the same line, are called collinear points.
Solution:
(i) False : Because a dot has no length, no breadth.
(ii) True.
(iii) False : A line segment PQ is written as PQ.
(iv) True.
( v) False: Three points are called collinear points if they are in the same straight line.
(vi) True.
Question 2.
Write how many lines can be drawn through :
(i) a given point ?
(ii) two given fixed points ?
(iii) three collinear points ?
(iv) three non-collinear points ?
Solution:
(i) Infinite (unlimited) line can be drawn through a given point.
(ii) only one line can be drawn through two given point.
(iii) only one line can be drawn through three collinear points.
(iv) None (no) line can be drawn through three non-collinear points.
Question 3.
The shaded region of the given figure shows a plane :
(a) Name :
(i) three collinear points.
(ii) three non-collinear points.
(iii) a pair of intersecting lines.
(b) State whether true or false :
(i) Line DE is contained in the given plane P.
(ii) Lines AB and DE intersect at point C.
(iii) Points D, B and C are collinear.
(iv) Points D, B and E are collinear.
Solution:
(a) (i) A, B and C are three collinear points.
(ii) A, D and C are non-collinear points.
(iii) AC and DE are intersecting lines.
(b) (i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) False
Question 4.
Correct the statement, if it is wrong:(i) A A ray can be extended infinitely on either side.
(ii) A ray has a definite length.
(iii) A line segment has a definite length.
(iv) A line has two end-points.
(v) A ray has only one end point.
Solution:
(i) A ray can be extended infinitely on one side of it only.
(ii) A ray has infinite length.
(iii) Yes, a line segment has a definite length.
(iv) A line-segment has two end-points.
(v) Yes, a ray has only one end-point.
Question 5.
State true-er false, if false give the correct statement :
(i) A line has a countable number of points in it.
(ii) Only one line can pass through a given point.
(iii) The intersection of two planes is a straight line
Solution:
(i) False, a line has length only.
(ii) False, any number of line can pass through a given point.
(iii) True.
Question 6.
State, whether the following pairs of lines or rays appear to be parallel or intersecting.
Solution:
(i) intersecting
(ii) Parallel
(iii) Parallel
(iv) Intersecting
Question 7.
Give two examples, from your surroundings, for each of the following:
(i) points
(ii) line segments
(iii) plane surfaces
(iv) curved surfaces.
Solution:
(i) Tips of your pencil (Ball Pen) and Tip of paper pin.
(ii) Lines of Exercise Note-Books and edge of school desk.
(iii) Floor of the room and top of the table.
(iv) Surface of foot-ball and front glass of the car.
Question 8.
Under what condition will two straight
lines, in the same plane, have :
(i) no point in common.
(ii) only one point in common.
(iii) an infinite number of points in common.
(iv) If possible draw diagrams in support of your answer.
Solution:
(i) When lines are parallel to each others.
(ii) When they intersect each other
Here, common point is E.
(iii) When line coincide with each other.
Question 9.
Mark two points A and B on a page of your exercise book. Mark a third point P, such that :
(i) P lies between A and B ; and the three points A, P and B are collinear.
(ii) P does not lie between A and B yet the three points are collinear.
(iii) the three points do not lie in a line.
Solution:Question 10.
Mark two points P and Q on a piece of paper. How many lines can you draw:
(i) passing through both the points P and Q?
(ii) passing through the point P ?
(iii) passing through the point Q ?
Solution:
(i) From above diagram it is clear only one line can be drawn.
(ii) Infinite lines can pass through the point up
(iii) Infinite lines can pass through the point
Question 11.
The adjoining diagram shows a line AB. Draw diagram to represent:
(i) ray AB i.e.

(ii)
(iii) line segment AB.
Solution:
Question 12.
The adjoining diagram shows a ray AB. Draw diagrams to show :
(i) ray BA i.e.
(ii) lineAB
(iii) line segment BA.

(iii) line segment AB.
Solution:
Question 12.
The adjoining diagram shows a ray AB. Draw diagrams to show :
(i) ray BA i.e.

(ii) lineAB
(iii) line segment BA.

Solution:
Question 13.
The adjoining diagram shows a line segment AB. Draw diagrams to represent :
(i) ray AB i.e.

(ii) line AB i.e.
(iii) ray BA.
Solution:
Question 14.
Use a ruler and And whether following points are collinear or not:
(i) D, A and C
(ii) A, B and C
(iii) A, B and E
(iv) B, C and E
Solution:
Question 15.
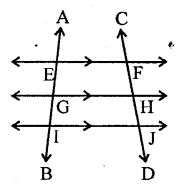
From the adjoining figure, write:
(i) all pairs f parallel lines
(ii) all the lines which intersect EF.
(iii) lines whose point of intersection is G.
Solution:
(i) The pairs of parallel lines are EF || GH, EF || IJ and GH || IJ
(ii) The lines which intersect EF are AB and CD
(iii) AB and GH are the lines whose point of intersection is G.
EXERCISE 23 (B)
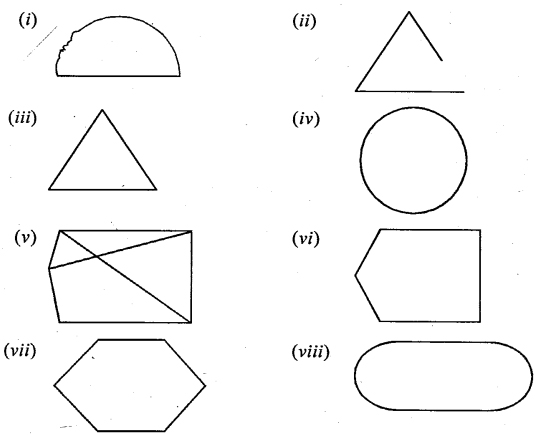
State, which of the following is a plane closed figure :
Solution:
(i) , (iii) ,(iv),(vi)and (viii) are plane close figures.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) ….. is a three sided plane closed figure.
(ii) A square is a plane closed figure which is not bounded by …..
(iii) A rectangle is a …. sided plane ……
(iv) A rectangle has opposite sides ….. and adjacent sides ….. to each other.
(v) The sides of a square are ……. to each other and each angle is
(vi) For a line segment, a line making angle of ……… with it, is called perpendicular to it.
(vii) For a line segment, a line ……. it and making angle of ……. with it, is called ……. bisector of the line segment.
(viii) How many perpendiculars can be drawn to a line segment of length 6 cm ?
(ix) How many perpendicular bisectors can be drawn to a line segment of length 6 cm ?
(x) A perpendicular to a line segment will be its perpendicular bisector if it passes through the ……. of the given line segment.
Solution:
(i) Triangle
(ii) any curved line.
(iii) four, closed figure.
(iv) parallel, perpendicular.
(v) Equal, 90°
(vi) 90°
(vii) bisecting, 90°, perpendicular.
(viii) Infinite.
(ix) Only one.
(x) mid-point
Question 3.
State, which of the lines/line- segments are perpendicular to the line PQ :
Solution:
CD and MN are perpendicular to the line PQ. forming angle to 90°
Question 4.
Which of the following figures show two mutually perpendicular lines :
Solution:
figures (i) and (iii) show two mutually perpendiculars lines forming angles of 90°.
Question 5.
For each figure given below name the line segment that is perpendicular bisector of the other :
Solution:(i) AB of CD
(ii) AB to MN
(iii) PQ to RS and RS to PQ
(iv) None
(v) None.
Question 6.
Name three objects from your surroundings that contain perpendicular edges.
Solution:
(i) My Text-Book of Mathematics r
(ii) My Note-Book
(iii) My Scale or My school’s Black Board
Question 7.
Using the given figure, answer the following :
(i) Name the pairs of parallel lines.
(ii) Name the pairs of mutually perpendicular lines.
(iii) Is the line p parallel to the line l ?
(iv) Is the line q perpendicular to the line m ?
Solution:
(i) l || m and p || q
(ii) p and l, p and m, q and l, q and m.
(iii) No, p is perpendicular to line l.
(iv) Yes.
Question 8.
Place a scale (ruler) on a sheet of paper and hold it firmly with one hand. Now draw two line segments AB and CD along the longer edges of the scale. State whether segment AB is parallel to or perpendicular to segment CD.
Solution:
Check your text book :
(i) How many pairs of its edges are parallel to each other ?
(ii) How many pairs of its edges are perpendicular to each other ?
Solution:
(i) 8
(ii) Three at each corner = 24
Question 10.
Give two examples from your surroundings for each of the following :
(i) intersecting lines
(ii) parallel lines
(iii) perpendicular lines.
Solution:
(i) Edges of my Text-Book and Note Book through any comer.
(ii) opp. edges of my Text-Book and Note Book.
(iii) Adjacent edges of my Text-Book and Black Board in my class-room.
Question 11.
State true or false; if false, give the correct statement :
(i) The maximum number of lines through three collinear points is three.
(ii) The maximum number of lines through three non-collinear points is three.
(iii) Two parallel lines always lie in the same plane.
(iv) Concurrent lines always meet at the same point.
(v) A surface can be plane or curved.
(vi) There are an infinite number of points in a line segment of length 10 cm.
(vii) There are an infinite number of points in a line.
(viii) A plane has an infinite number of lines.
(ix) A plane has an infinite number of points.
Solution:
(i) False: Because only one line passes through three collinear points.
(ii) False : No line passes through all the three non-collinear points.
(iii) True.
(iv) True.
(v) True.
(vi) True.
(vii) True.
(viii) True.
(ix) True.
REVISION EXERCISE
Mark a point O on a piece of paper. Using a sharp pencil and a ruler, draw a line through the point O. Then draw one more line through the point O. How many lines can you draw through O?
Write a statement regarding your observations.
Solution:
We take a point O on a piece of paper. Using a sharp pencil, we draw a line OA through O
another line OB is drawn as shown in the figure.
We can draw an infinite number of lines from O as we know that an infinite number of lines can be drawn through a point in aplane,
Question 2.
Mark two points A and B on a plain sheet “ of paper. Using a sharp pencil and a ruler, draw a line through points A and B. Try to draw one more line through A and B. What do you observe ?
Write a statement regarding your observations.
Solution:
Two points A and B are marked On the plain sheet of paper. Using pencil, draw a line through there two points.
We cannot draw any other line joining them as only one line can be drawn passing through two fixed (given) points in a plane.
Question 3.
Draw two straight lines on a sheet of paper so that the lines drawn :
(i) intersect each other.
(ii) do not intersect.
(iii) appear to intersect when extended.
Solution:
Two straight lines are drawn on the sheet of a paper
(i) Intersecting each other:
(ii) Not intersecting each other:
(iii) Intersect each other when produced them:
Question 4.
Draw a figure to show that :
(i) points A, B and C arc collinear.
(ii) lines AB, CD and EF are concurrent.
Solution:
(i) We know that three or more points are collinear if they lie on the same straight line. Therefore the required figure (line) is given below on which three points A, B and C lie
(ii) If three or more lines pass through a common point, these are called concurrent lines. Below is given the figure, in which three lines AB, CD and EF are passing (or intersecting each other) at O.
Question 5.In your note-book, draw two rays with the same initial point O and going in opposite directions. Write the special name for the final figure obtained.
Solution:
Two rays OA and OB are drawn through O in opposite direction as given below.
Question 6.
In each figure, given below, write the number of line segments used :
Solution:
(i) In the given figure, there as Ten (10) line segments which are AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GH, HI, IJ and JA.
(ii) In the given figure, there are 12 line segments which are AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GH, HI, IJ, JK, KL and LA.
(iii) In the given figure, there are 13 line segments which are AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GH, HI, IJ, JK, KL, LM and MA.
(iv) In the given figure, there are 7 line segments which are AB, BC, CD, DE, DA, DB, CE.
Question 7.
In a circle, point P is its centre and PA = PB = radius of the circle. Where do points A and B lie ?
Solution:
A circle is given with centre P and PA = PB = radius of the circle.
∵ The radii of a circle are equal there they lie on the circumference of the circle In other words, path of a point which is equidistant from a fixed point is the circumference of a circle. The fixed point is called the centre and equidistance is the radius.
Question 8.
Draw a four-sided closed figure, in which:
(i) all the sides are equal and each angle is 90°.
(ii) opposite sides are equal and each angle is 90°.
Write the special name of each figure drawn.
Solution:
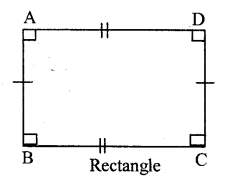
(i) In this four sided closed figure all the sides are equal and each angle is 90°. This figure is called a square. In ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA and ∠A = ∠B =∠C = ∠D = 90°
(ii) In this four sided closed figure opposite sides are equal and each angle is 90°. This figure is called a rectangle In rectangle ABCD, AB = CD and BC = AD
∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90°.