Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions Chapter 30 Revision Exercise Symmetry (Including Constructions on Symmetry)
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Revision Exercise Symmetry (Including Constructions on Symmetry)
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Revision Exercise Symmetry (Including Constructions on Symmetry)
IMPORTANT POINTS
1. Concept of Symmetry (Linear Symmetry) : Consider a plane mirror mm’. If your face F is at a distance ‘d’ before the mirror ; the image F, of your face is also formed behind the mirror at distance “d” from it.
Now, if the Figure 1, given alongside, is folded about the mirror mm’, the object F and its image F’ coincide. Since on folding the figure about mm’ its two parts exactly coincide, we say that the figure is symmetrical about the mirror line mm’. For the reason, the mirror line mm’ is called line of symmetry of the whole figure including face F, its image F’ and the mirror mm’.
Keep in Mind :
in order to check, whether a given figure is symmetrical about a line in it or not; fold the figure about that line. If part of the figure, which lies on one side of the line exactly coincides with the part of the figure on the other side of the line, then the figure is symmetrical about that line.
For Example :
(i) A line segment is symmetrical about its perpendicular bisector
(ii) An angle (with equal arms) is symmetrical about its bisector
(iii) An isosceles triangle has only one line of symmetry. The line of symmetry is the bisectors of the angle contained by equal sides.
(iv) An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry. The bisectors of the angles are the lines of symmetry.
(v) A kite shaped figure has only one line of symmetry.
(vi) A figure of the shape of an arrow-head has only one line of symmetry.
(vii) The letter ‘A’ has only one line of symmetry.
(viii) The letter ‘H’ has two lines of symmetry.
(ix) A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Every line, which passes through the centre of the circle, is a line of symmetry.

Solution:
(If both the semi-circles of B are equal)
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) False
(v) False
(vi) True
(vii) True
(viii) False.
Question 2.
Construct a triangle ABC, in which AB = AC = 5 cm and BC 6 cm. Draw all its lines of Symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line BC = 6 cm.

(ii) With B as centre and radius 5 cm draw
(iii) With C as centre and radius 5 cm draw on arc which cut the previous arc at a.
(iv) Join AB and AC.
(v) ∆ABC is the required triangle line of symmetry is shown in the figure.
Question 3.
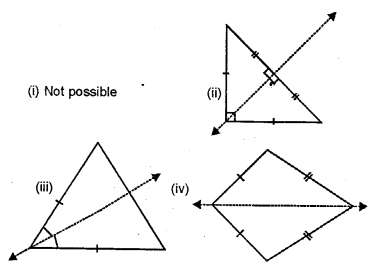
Examine each of the following figures carefully, draw line(s) of symmetry in which ever figure possible :

(If both the semi-circles of B are equal)
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) False
(v) False
(vi) True
(vii) True
(viii) False.
Question 2.
Construct a triangle ABC, in which AB = AC = 5 cm and BC 6 cm. Draw all its lines of Symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line BC = 6 cm.

(ii) With B as centre and radius 5 cm draw
(iii) With C as centre and radius 5 cm draw on arc which cut the previous arc at a.
(iv) Join AB and AC.
(v) ∆ABC is the required triangle line of symmetry is shown in the figure.
Question 3.
Examine each of the following figures carefully, draw line(s) of symmetry in which ever figure possible :

Question 4.
(i) Draw line XY = 4.5 cm

(ii) With X as a centre and radius 4.5 cm draw an arc at Z.
(iii) With Y as a centre and radius 4.5 cm draw an arc which cuts the previous arc at Z.
(iv) Join XZ and YZ.
∆XYZ is the required triangle and lines of symmetries are shown in the figure.
Question 5.
(i) Draw a line AB = 4 cm.

(ii) At B draw an angle of 60° with the help of compass.
(iii) With B as centre and radius upon cut BC = 4 cm.
(iv) Join AC.
∆ABC is the required triangle and line of symmetry is shown in centre.
Question 6.
Draw the line(s) of symmetry for each figure drawn below :

Construct a triangle XYZ, in which XY = YZ = ZX = 4.5 cm. Draw all its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :(i) Draw line XY = 4.5 cm

(ii) With X as a centre and radius 4.5 cm draw an arc at Z.
(iii) With Y as a centre and radius 4.5 cm draw an arc which cuts the previous arc at Z.
(iv) Join XZ and YZ.
∆XYZ is the required triangle and lines of symmetries are shown in the figure.
Question 5.
Construct a triangle ABC, in which AB = BC = 4 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Draw all its lines of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :(i) Draw a line AB = 4 cm.

(ii) At B draw an angle of 60° with the help of compass.
(iii) With B as centre and radius upon cut BC = 4 cm.
(iv) Join AC.
∆ABC is the required triangle and line of symmetry is shown in centre.
Question 6.
Draw the line(s) of symmetry for each figure drawn below :

Question 7.
Solution:

(i) Draw PQ perpendicular to AB from PO produced cut OQ = OP.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
(ii) Draw PO perpendicular to AB from P and produce PO to Q such that OQ = PO.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
(iii) Draw PQ perpendicular to AB from PO produced cut OQ = OP.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
Question 8.

Take points A and B 5.5 cm apart draw perpendicular bisect of the line segment AB. The perpendicular bisector PQ is the required line of symmetry with respect to A and B.
PQ is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Question 9.

Question 10.
Draw all the possible lines of symmetry for each figure given below :

In each of the following case, construct a point that is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.

(i) Draw PQ perpendicular to AB from PO produced cut OQ = OP.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
(ii) Draw PO perpendicular to AB from P and produce PO to Q such that OQ = PO.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
(iii) Draw PQ perpendicular to AB from PO produced cut OQ = OP.
Point Q is symmetric to the given point P with respect to the given line AB.
Question 8.
Mark two points A and B 5.5 cm apart. Draw a line PQ so that A and B are symmetric with respect to the line PQ. Give a special name to line PQ.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
Take points A and B 5.5 cm apart draw perpendicular bisect of the line segment AB. The perpendicular bisector PQ is the required line of symmetry with respect to A and B.
PQ is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Question 9.
For each letter of the English alphabet, draw the maximum possible number of lines of symmetry.
Solution:

Question 10.
Draw all the possible lines of symmetry for each figure given below :

Solution:
The line or lines of symmetry of tile given figure are drawn as given below :
(i) A parallelogram has no line of symmetry.
(ii) A rectangle has two lines of symmetry.
(iii) A square has form lines of symmetry.

(iv) A semicircle has one line of symmetry.
(v) A quadrant has one line of symmetry.
Question 11.
For each shaded portion given below, draw all the possible lines of symmetry :
Solution:
The shaded portion of each figure given has the line or lines of symmetry as given below

(i) A minor segment has one line of symmetry.
(ii) A major segment has one line of symmetry.
(iii) quadrant has one line of symmetry.
(iv) The given figure has one line of symmetry.
The line or lines of symmetry of tile given figure are drawn as given below :
(i) A parallelogram has no line of symmetry.
(ii) A rectangle has two lines of symmetry.
(iii) A square has form lines of symmetry.

(iv) A semicircle has one line of symmetry.
(v) A quadrant has one line of symmetry.
Question 11.
For each shaded portion given below, draw all the possible lines of symmetry :
Solution:
The shaded portion of each figure given has the line or lines of symmetry as given below

(i) A minor segment has one line of symmetry.
(ii) A major segment has one line of symmetry.
(iii) quadrant has one line of symmetry.
(iv) The given figure has one line of symmetry.