Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Cell : The Unit Of Life
Exercise 1
A. Multiple Choice Question.
1. Which one of the following cell organelles is correctly matched with its function?
(a) Ribosomes  Synthesis of proteins
Synthesis of proteins
(b) Mitochondria  Secretion of enzymes
Secretion of enzymes
(c) Plasma membrane  Freely permeable
Freely permeable
(d) Centrosome  Carries genes
Carries genes
2. All life starts as
(a) an egg
(b) a single cell
(c) a gene
(d) a chromosome
3. Which one of the following is found both in the cells of a mango plant and a monkey?
(a) chloroplasts
(b) centrioles
(c) cell wall
(d) cell membrane
4. A plant cell can be identified from an animal cell by the
(a) absence of centrosome
(b) presence of cell membrane
(c) presence of vacuoles
(d) none of the above
5. Plant cell has a cell wall made of
(a) Protein
(b) Fructose
(c) Cellulose
(d) Fatty acids
6. The cell organelle that helps in respiration of the cell is
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Lysosome
(c) Ribosome
(d) Centrosome
Solution A.
1. (a) Ribosomes → Synthesis of proteins
2. (b) a single cell
3. (d) cell membrane
4. (a) absence of centrosome
5. (c) Cellulose
6. (a) Mitochondria
B. Very Short Type Answer .
(1) Name the part of the cell concerned with the following.
(a)Liberation of energy
(b) Synthesis of proteins
(c) Transmission of hereditary characters from parents to offspring
(d)Initiation of cell division
(e) Hydrolytic in function
(f) Entry of only certain substances into and out of the cell
Solution B.1.
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Chromosomes
(d) Centrosome
(e) Lysosomes
(f) Cell membrane
(2) State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(a) All animal cells contain a cell wall. T/F
(b) A cell wall is made up of protein. T/F
(c) Centrosome occurs in animal cells. T/F
(d) Plant cells contain large vacuoles. T/F
(e) Protoplasm is the part of the cell which surrounds the nucelus. T/F
(f) Genes are located in chromosomes. T/F
(g) Anthocyanins are the pigments of flowers, which are dissolved in cell-sap. T/F
Solution B.2.
(a) F (False). Animal cells do not contain a cell wall.
(b) F (False). A cell wall is made up of cellulose.
(c) T (True)
(d) T (True)
(e) F (False). In eukaryotes, cytoplasm is the part of the cell which surrounds the nucleus.
(f) T (True)
(g) T (True)
(3) How many chromosome pairs are found in human cells?
Solution B.3.
23 pairs of chromosomes are found in human cells.
(4) What is the name of the chemical substance which constitutes the genes?
Solution B.4.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
(5)
Match the items in column 'A' with those in column 'B'
Column A
|
Column B
|
(a) Vacuoles
|
(i) Intracellular digestion
|
(b) Nucleolus
|
(ii) Respiratory enzymes
|
(c) Lysosomes
|
(iii) Covered by tonoplast
|
(d) Anthocyanin
|
(iv) Dissolved in the cytoplasm
|
(e) Cristae
|
(v) Forms RNA
|
(6) Fill in the blanks:
(a) _________ consists of membranous sacs and secretes 40 types of digestive enzymes.
(b) _________ is surrounded by microtubules, located near the nucleus.
(c) Very thin flexible, living membrane which is differentially permeable, is called ___________.
(d) More than 1000 chromosomes are found in the nucleus of certain
(e) _________ are hereditary units.
(f) _________ is a plastid which stores starch.
Solution B.6.
(a) Lysosome
(b) Centriole
(c) Plasma membrane
(d) Insects
(e) Genes
(f) Leucoplast
C. Answer The Following.
(1) It is said that the protoplasm cannot be analysed chemically. Why?
Solution C.1.
Protoplasm is the living matter of the cell. Protoplasm cannot be analysed chemically because the chemical composition of protoplasm is very complex. It varies slightly from one cell to another, although the common elements included in the composition of protoplasm such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, iron and phosphorus are still the same in all the cells.
(2) What is the difference between an organ and an organelle?
Solution C.2.
Organs of an organism are the parts of the body which have a definite shape and structure and perform specific functions. Cell organelles are also parts of the cell which have a definite shape and structure and perform specific functions. Organelles have the same status in a cell as the organs have in the entire body of an animal or a plant performing specific functions.
(3) Do you think the cells of an elephant would be larger than the cells of a rat? Explain briefly.
Solution C.3.
The cells of an elephant would be of the same size as the cells of a rat. The size of cells does not vary within the organisms, however, the number of cells varies from one organism to another. A larger animal like an elephant will have more number of cells as compared to a smaller animal like a rat. However, the size of the cell will be the same.
(4) Differentiate between the following pairs of terms:
(a) Protoplasm and cytoplasm
(b) Nucleolus and nucleus
(c) Centrosome and chromosome
(d) Cell wall and cell membrane
(e) Plant cell and animal cell
(f) Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
(5) Mention three features found only in plant cells and one found only in animal cells.
Solution C.5.
Features found only in plant cells:
1. Presence of cell wall
2. Presence of large vacuoles. The liquid contained in vacuoles is called cell sap
3. Presence of plastids
Features found only in animal cells:
1. Presence of centrosome
(6) Why are the cells generally of a small size?
Solution C.6.
Cells generally remain small in size because:
1. To enable different regions of the cell to communicate with each other rapidly for the cell to function effectively
2. To have a large surface area is to volume ratio for greater diffusion of substances, in and out of the cell
D. Long Type Answer.
(1) What is the cell theory? Who propounded it and when?
Solution D.1.
Postulates of cell theory:
1. Cell is the smallest unit of structure of all living things.
2. Cell is the unit of function of all living things.
3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Cell theory was propounded by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden in the year 1839 and was modified by Rudolf Virchow in 1858.
(2) Mention any three differences between a living cell and a brick in a wall.
(3) Name the plastid and pigment likely to be found in the cells of
(a) petals of sunflower
(b) ripe tomato
(c) skin of green mango
(d) cells of potato
Solution D.3.
(4) State the major functions of the following:
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Ribosome
(c) Lysosome
(d) Mitochondria
(e) Golgi apparatus
(f) Cytoplasm
(g) Asters of centrosome
(h) Chromosomes
(i) Glycogen granule
(j) Vacuoles
Solution D.4.
(a) Plasma membrane:
1. Separates contents of the cell from its surroundings
2. Regulates the entry of certain solutes and ions
3. Maintains the shape of animal cell
(b) Ribosome:
1. Protein synthesis
(c) Lysosomes:
1. Intracellular digestion
2. Destroy foreign substances
3. When the cell is old or injured, lysosomes rapidly destroy cell organelles and hence, are called suicide bags.
(d) Mitochondria:
1. Synthesis of respiratory enzymes
2. Release of energy from pyruvic acid produced in cytoplasm in the form of ATP
(e) Golgi apparatus:
1. Synthesis and secretion of enzymes, hormones, etc.
2. Formation of acrosome of sperm
(f) Cytoplasm:
1. Different organelles contained in it perform different functions.
2. All metabolic activities occur in it.
(g) Asters of centrosome:
1. Initiates and regulates cell division
2. Forms spindle fibres
(h) Chromosomes:
1. Carry genetic characters from parents to offspring
(i) Glycogen granule:
1. Serves as food for the cell
(j) Vacuoles:
1. Gives turgidity to the cells
2. Storage of water and other substances, food, pigments and waste products
(5) List any six features found both in plant and animal cells.
Solution D.5.
Common features found in both plant and animal cells:
1. Presence of cell membrane
2. Presence of liquid matrix called cytoplasm in the cell
3. Presence of mitochondria which produces energy
4. Presence of ribosomes that synthesize proteins
5. Presence of Golgi body
6. Presence of a prominent nucleus
E. Given below are the sketches of two types of cells A and B.
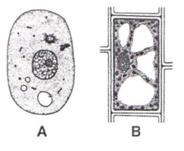
(a) Which one of these is a plant cell? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) List the cell structures which are common to both the types.
(c) Name the structures found only in plant cells and those found only in animal cells.
Solution E.1.
(a) Fig. B is a plant cell. It has a cell wall and a large vacuole which pushes the nucleus towards the periphery.
(b) Cell membrane, ribosomes, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, Golgi body and mitochondria are common to both the types.
(c) Plastids and cell wall are found only in plant cell. Centrosome is found only in animal cell.
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 - The Unit Of Life







