Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 17 - Aids To Health
Exercise 1
A. Multiple Choice Type.
1. Penicillin is
(a) an antiseptic
(b) a disinfectant
(c) an antibiotic
(d) an anti-toxin
2. 'T' in DTP vaccination stands for
(a) Tuberculosis
(b) Typhoid
(c) Tetanus
(d) Tonsillitis
(a) April 7
(b) February 21
(c) October 10
(d) January 15
Solution A.
- (c) An antibiotic
- (c) Tetanus
- (a) April 7
B. Very Short Answer Type.
1. Name the following:
(a) The drug based on arsenic compound, produced in 1910, which killed germs of syphilis.
(b) The antibiotic that was discovered first.
(c) The category of immunity required in the treatment of snake-bite.
(d) Any four antiseptics, any two disinfectants and any two antibiotics.
(e) The vaccine that helps to produce immunity against polio.
Solution B.1.
(a) Arsphenamine or Salvarsan
(b) Penicillin
(c) Passive acquired immunity
(d) Antiseptics – Lysol, iodine, boric acid and carbolic acid
Disinfectants – Cresol and phenol
Antibiotics – Ampicillin and penicillin
(e) Oral polio vaccine (OPV)
2. Write the full forms of:
(i) AIDS
(ii) BCG
(iii) DPT vaccine
(iv) WHO
Solution B.2.
(i) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
(ii) Bacillus Calmette Guerin
(iii) Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus
(iv) World Health Organization
3.Give the technical term for the kind of proteins produced in the blood to fight and destroy harmful microbes.
Antibodies are immunoglobulins which are produced in the blood to fight and destroy harmful microbes.
1. Mention if the following statements are true (T) or false (F).
(a) Lysol is an antibiotic.
(b) Sweat and tears contain germs-killing substances.
(c) Our body can make only a limited variety of different antibodies.
(d) Salk vaccine is used against tuberculosis.
(e) Treatment by the use of chemicals is known as allopathy.
(f) Alexander Fleming coined the term 'antibiotic' for substances like penicillin.
Solution C.1.
(a) False. Lysol is an antiseptic.
(b) True
(c) False. Our body can make an unlimited variety of different antibodies.
(d) False. Salk’s vaccine is used against poliomyelitis.
(e) False. Treatment by the use of chemicals is known as chemotherapy.
(f) False. Selman Waksman coined the term ‘antibiotic’ for substances like penicillin.
2. Differentiate between:
(a) Antiseptic and antibiotic,
(b) Antiseptic and disinfectant,
(c) Disinfectant and deodorant,
(d) Vaccination and sterilisation,
(e) Active immunity and passive immunity,
(f) Innate immunity and acquired immunity
Solution C.2.
(a) Antiseptic is a mild chemical substance which is applied to the body to kill germs, whereas an antibiotic is a chemical substance produced by a microorganism which can kill or inhibit the growth of some other disease-producing microorganisms.
(b) Antiseptic is a mild chemical substance which is applied to the body to kill germs, whereas a disinfectant is a strong chemical applied to spots or places on the body where germs thrive and multiply.
(c) Disinfectant is a strong chemical applied to spots or places on the body where germs thrive and multiply, whereas deodorants are neither antiseptics nor disinfectants; they are aerosols used to mask a bad smell.
(d) Vaccination is the introduction of any kind of dead or weakened germs into the body of a living being to develop immunity (resistance) against a disease, whereas sterilisation is a process of eliminating or killing all the microbes present on a surface, contained in a fluid, in medication or in a compound such as biological culture media.
(e) Active immunity is the immunity developed by an individual due to a previous infection or antigen which enters the body naturally, whereas passive immunity is the immunity provided to an individual from an outside source in the form of ‘readymade’ antibodies.
(f) Innate immunity is the immunity by the virtue of genetic constitutional makeup, i.e. it is inherited from parents. It is present in the body without any external stimulation or a previous infection, whereas acquired immunity is the resistance to a disease which an individual acquires during a lifetime. It may be the result of either a previous infection or from readymade antibodies supplied from outside.
3. Name any three vaccines and the diseases for which they provide immunity.
Solution C.3.
(i) TAB vaccine for typhoid
(ii) BCG vaccine for measles
(iii) DTP vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough
4.Given below are the groups of certain substances of particular categories. Mention the category of each group and identify the wrong example giving reason.
(a) Lysol, benzoic acid, DDT, mercurochrome.
(b) Formalin, iodine, lysol, phenol.
(c) BCG, DTP, ATP.
(d) Tears, skin, nasal secretion, HCl (in stomach).
Solution C.4.
(a) Lysol, benzoic acid, DDT, mercurochrome
Antiseptics. DDT is a wrong example for this category as it is a disinfectant which is not good for human skin.
(b) Formalin, iodine, lysol, phenol
Disinfectants. Iodine is a wrong example as it is an antiseptic.
(c) BCG, DTP, ATP
Vaccines. ATP is a wrong example as it is an energy carrier in the cells of all known organisms.(d) Tears, skin, nasal secretion, HCl (in stomach)
(d)Germ-killing secretions. Skin is a wrong example as it is a protective mechanical barrier and prevents the entry of germs in our body.
5. Given below is a table of certain vaccines, the diseases against which they are used and the nature of vaccine. Fill up the gaps 1-10.
Vaccine
|
Disease(s)
|
The Nature of Vaccine
|
TAB
|
1. _______________
|
2. ___________________
|
Salk's vaccine
|
3. _______________
|
4. ___________________
|
BCG
|
5. _______________
|
Living weakened germs
|
Vaccines for measles
|
Measles
|
6. ___________________
|
Cowpox virus
|
7. _______________
|
8. ___________________
|
Toxoids
|
9. _______________
|
Extracts of toxins
|
10. ______________
|
Secreted by bacteria
|
Solution C.5.
6. Given below is a scheme of classifying immunity against human diseases. Fill up the types of immunity in the blanks 1-9.
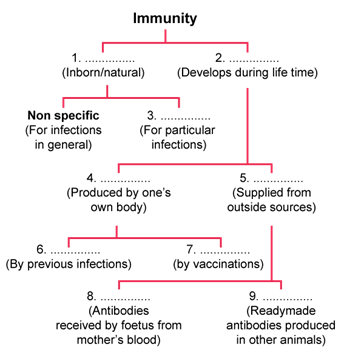
Solution C.6.
- Innate immunity
- Acquired immunity
- Specific immunity
- Active acquired immunity
- Passive acquired immunity
- Natural acquired active immunity
- Artificial acquired active immunity
- Natural acquired passive immunity
- Artificial acquired passive immunity
7.List any four ways in which the antibiotics are being used.
Solution C.7.
- Antibiotics have a wide use in medicine to fight infections.
- Certain antibiotics are used as food preservatives, especially for fresh meat and fish.
- Some antibiotics are used in treating animal feed to prevent internal infection.
- Some antibiotics are used for controlling plant pathogens.
8.List the merits of local defence systems.
Solution C.8.
Merits of local defence systems:
1. Local defence systems start working instantaneously.
2. These systems are not dependent on previous exposure to infections.
3. They are effective against a wide range of potentially infectious agents.
9.Suppose a person develops the disease diphtheria. Comment upon the principle of the treatment he should receive.
Solution C.9.
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infectious disease. It leads to cold, coughing, sneezing and, in severe cases if undiagnosed, it might result in heart failure or paralysis.
Treatment includes a combination of medications and supportive care. The most important step is prompt intravenous administration of diphtheria toxoid which is made harmless. The harmless toxoid once administered in a patient’s body triggers the production of antibodies against the pathogens causing diphtheria.
D. Long Answer Types
1. The principle of vaccination is to produce immunity against a disease. Explain.
• Vaccination is the practice of artificially introducing germs or the germ substance into the body for developing resistance to particular diseases.
• Scientifically, this practice is called prophylaxis and the material introduced into the body is called the vaccine.
• The vaccine or germ substance is introduced into the body usually by injection and sometimes orally (e.g. polio drops).
• Inside the body, the vaccine stimulates lymphocytes to produce antibodies against the germs for that particular disease.
• Antibodies are an integral part of our immunity. Their function is to destroy the unwanted particles which enter the body.
• Vaccines give our immunity a signal to produce specific antibodies. Hence, the principle of vaccination is to produce immunity against a disease.
2.'Abnormally, large numbers of WBCs in the blood are usually an indication of some infection in our body''. Comment on the statement.
Solution D.2.
Whenever a germ or infection invades the body, a signal is sent to the immune system to produce specific antibodies. To cope with the number of germs being multiplied inside the body, white blood cells start multiplying rapidly. This enables them to produce more number of antibodies and stop the infection in time. So, abnormally large numbers of WBCs in the blood are usually an indication of some infection in our body.
3.Explain briefly, the role of the following health aids:
(a) Antiseptics
(b) Disinfectants
(c) Vaccines
Solution D.3.
(a) Antiseptics:
Antiseptics are mild chemical substances applied to the body which prevent the growth of some bacteria and destroy others.
Examples: Lysol and iodine
(b) Disinfectants:
Disinfectants are chemicals which kill microorganisms they come in contact with. Disinfectants are usually too strong to be used on the body.
Examples: Cresol and phenol
(c) Vaccines:
Vaccines are materials administered in the body to provide passive immunity. The materials are generally germs or substances secreted by germs.
Examples: OPV (oral polio vaccine) and DTP (diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis)
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 17 - Aids To Health
