Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 - The Flower
Exercise 1
A. Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Bougainvillea flower is an example of
(a) incomplete flower
(b) having a large nectary
(c) water pollination
(d) large colourful bracts
2. A flower is said to be complete when:
(a) It has the corolla and calyx
(b) It has the corolla and gynoecium
(c) It has the androecium and gynoecium
(d) It has all the four whorls
3. The part of the flower that gives rise to the fruit is
(a) Sepals
(b) Petals
(c) Ovary
(d) Stamens
4. The part of the flower that gives rise to the seed is
(a) Ovary
(b) Placenta
(c) Ovule
(d) Pollen grain
5. The essential whorls of a flower are the
(a) Calyx and corolla
(b) Stamen and ovary
(c) Calyx and epicalyx
(d) Androecium and gynoecium
Solution A.
1. (d) large colourful bracts
2. (d) It has all the four whorls.
3. (c) Ovary
4. (c) Ovule
5. (d) Androecium and gynoecium
B. Match the parts in Column A with the flowers or parts of flower in Column B.
Column A
|
Column B
|
(a) Polyadelphous
|
(i) Polypetalous
|
(b) Pollen grains
|
(ii) Calyx, corolla
|
(c) Free petals
|
(iii) Nectar
|
(d) Non-essential
|
(iv) Bombax
|
(e) Sweet fragrant fluid
|
(v) Pollen sac
|
C. Answer the Following.
1. Explain the following terms:
(a) Incomplete flower
(b) Staminate flower
(c) Pistillate flower
(d) Bisexual flower
(a) Incomplete flower – If one or more sets of floral structures are missing, the flower is called incomplete flower. E.g. American elm.
(b) Staminate flower – A unisexual flower which contains only the stamens, i.e., male parts of a flower is called male or staminate flower. E.g. Eastern cottonwood.
(c) Pistillate flower – A flower which contains only the carpels, i.e., female parts of a flower is called female or pistillate flower. E.g. Date palm.
(d) Bisexual flower – A flower which contains both stamens and carpels is called bisexual or hermaphrodite flower. E.g. Hibiscus.
2. Distinguish between the following pairs:
(a) Flower and inflorescence
(b) Petals and petaloid sepals
3. Where the following structures/parts located and what are their functions?
(a) Placenta
(b) Thalamus
(c) Anther
(d) Stigma
Solution C.3.
(a) Placenta:
Location: Cushion or swollen region in the ovary
Function: Gives origin to ovules
(b) Thalamus:
Location: Tip of the flower stalk
Function: Bears all the parts of the flower
(c) Anther:
Location: Part of the stamen
Function: Produces male gametes or pollen grains
(d) Stigma:
Location: Terminal knob-like part
Function: Serves as the landing place for pollen grains during pollination
4. Why are the following describes as stated:
(a) The androecium of pea flower is diadelphous
(b) Ray florets of sunflower as neuters
(c) Saliva sepals as petaoid
(d) China Rose stamens are epipetaloid
Solution C.4.
(a) The androecium of pea flower is diadelphous because the filaments of anther are united in two bundles. In case of pea, out of ten, nine stamens form a staminal tube while one is free.
(b) Ray florets of sunflower are neuters because both male and female reproductive organs are lacking or absent.
(c) Salvia sepals are petaloid because the three sepals are united and are red in colour like petals. Hence, they are undifferentiated from the petals.
(d) China rose stamens are epipetaloid because they arise from the base of the petals.
D. Long Answer Type
1. Name the different types of androecium found in flowers
Solution D.1.
Types of androecium in flowers:
1. Polyandrous: When the stamens of a flower are free, the condition is called polyandrous.
2. Monadelphous: When the filaments of anthers in a flower are fused into one group, the
condition is called monadelphous.
3. Diadelphous: When the filaments of anthers in a flower are fused into two groups, the condition is called diadelphous.
4. Polyadelphous: When the filaments of anthers in a flower are fused into more than two
grouthe condition is called polyadelphous.
2. Name the type of androecium found in
(a) China rose
(b) Bombax
(c) Pea
Solution D.2.
(a) China rose: Monadelphous
(b) Bombax: Polyadelphous
(c) Pea: Diadelphous
E. Skill type
1. The figure given alongside represents generalized arrangement of the different parts of a bisexual flower. Name the parts numbered 1-10.
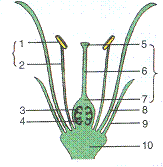
Solution E.1.
1: Anther; 2: Filament: 3: Ovule: 4: Placenta; 5: Stigma;
6: Style; 7: Ovary; 8: Petal; 9: Sepal; 10: Receptacle/Thalamus
2. Given below are two figures (A and B) of a certain part of a flower. Study the figures carefully and answer the following questions:
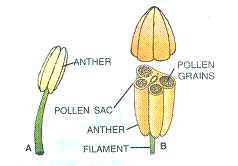
(a) Which major organ of a flower does the figure A represent? What is the collective term for this organ ?
(b) Are the contents of the pollen sacs in B male or female?
(c) Can you state how the contents of the pollen sacs would come out?
Solution E.2.
(a) Figure A represents stamen. Stamens collectively form Androecium.
(b) Contents of the pollen sacs in B are male gametes.
(c) The contents of the pollen sacs would come out through agents like air, wind, insects leading to pollination in flowers.
3. What are bracts? State their function
Solution E.3.
When a flower arises in the axil of a leaf-like structure, this structure is known as bract. Because bracts are large and brightly coloured structures, they are often mistaken for petals. This helps to attract insects for pollination
4. Explain the terms Monadelphous, Diadelphous and Polyadelphous. In each case name a flower possessing such an androecium.
Solution E.4.
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 - The Flower


