Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 13 Skin- “The Jack of All Trades”
Exercise 1
A. Mutiple Choice Questions:
1. If for some reason the sebaceous glands fail to function,
(a) the body will not be able to regulate the body temperature
(b) the skin will turn darker with more melanin
(c) the hairs will fail to grow
(d) the skin will turn dry and rough
2. Which one pair of two conditions includes both as abnormal conditions of skin pigmentation?
(a) Leucoderma, Ringworm
(b) Albinism, Leucoderma
(c) Baldness, Albinism
(d) Rickets, Baldness
3. Which one out of the organs listed below, most actively functions in regulating our body temperature?
(a) Heart
(b) Lungs
(c) Skin
(d) Stomach
4. Sweat glands are situated in:
(a) Epidermis
(b) Dermis
(c) Both
(d) None of the above
5. The epidermis is highly thickened in:
(a) Eyelid
(b) Thigh
(c) Lip
(d) Palm
Solution A.
1. (d) the skin will turn dry and rough
2. (b) Albinism, Leucoderma
3. (c) Skin
4. (b) Dermis
5. (d) Palm
B. Very Short Type Answer
1. Name the principal body heat regulating centre in our brain.
Solution B.1.
Hypothalamus, a portion of the forebrain is the principal body heat regulating centre in our brain.
2. Name any one modified sweat gland and any one modified sebaceous gland.
Solution B.2.
Modified sweat gland: Mammary gland
Modified sebaceous gland: Ceruminous gland
3. Name the skin glands which when inflamed cause acne.
Solution B.3.
Sebaceous glands
C. Short Type Answer
1. State any two functions of the mammalian skin other than those concerned with heat regulation.
Solution C.1.
Functions of the mammalian skin other than those concerned with heat regulation:
1. Storage of food: Skin acts as a storehouse of energy by storing reserve food in the form of fat in the hypodermis.
2. Synthesis of Vitamin D: Skin has the ability to synthesize small quantity of Vitamin D in the presence of sunlight.
2. What is "goose-flesh"? How is it brought about?
Solution C.2.
A peculiar roughness of the skin produced by cold or fear, in which the hair follicles become erect and form bumps on the skin is called goose flesh.
Goose flesh occurs when the muscles at the base of hair known as erectors or arrectors, contract. The erector muscles are obliquely placed between the hair follicle and the outer part of dermis. They are smooth muscles that are necessary to move the hair. The contraction of erector muscle pulls the hair vertical and depresses the epidermis, resulting in goose flesh.
Solution C.3.
Man is a warm-blooded mammal. Our body must maintain an average temperature of 98.6 degree Fahrenheit to function properly. When we feel too hot or too cold, our nervous system sends certain automatic and autonomic reflexes that help to keep us warm. In cold weather, the blood vessels get narrowed (vasoconstricted). Shivering occurs when our muscles expand and contract rapidly to produce extra body heat. The amount of heat produced is increased by increased metabolic rate and muscular activity, which occurs in the form of shivering. That is why, our body shivers and teeth chatter to protect from cold by generating more heat.
4. What is the difference between leucoderma and albinism?
Solution C.4.
5. Name any two glands found in the human skin. State their functions.
Solution C.5.
Two glands found in the human skin are:
1. Ceruminous gland: It is a modified sebaceous gland found in the auditory canal. It secretes wax-like substance called ear wax.
2. Mammary gland: It is a modified sweat gland. It is related to reproductive hormones and pregnancy.
6. An otherwise normal healthy young man started perspiring while it was intensely cold outside. What could have been one reason for it?
Solution C.6.
Fever and sickness or any kind of vigorous activity can lead to perspiration even in cold outside.
D. Long Type Answer
1. Enumerate in a tabular form the different structures found in the epidermis and dermis of the human skin respectively.
Solution D.1.
2. Explain the terms "vasodilation" and "vasoconstriction". How do these processes contribute in temperature regulation of the body?
Solution D.2.
Vasodilation: Dilation of blood vessels in the skin leading to an increase in the blood supply.
Vasoconstriction: Narrowing of blood vessels leading to reduction in the blood supply to the skin.
Temperature regulation in cold weather:
1. At low temperature, the blood vessels get narrowed or vasoconstricted. This reduces the blood supply to the skin.
2. There is less loss of heat by convection, conduction and radiation. There is less loss of heat through vapourization as reduced blood supply lowers the secretion of sweat by sweat glands.
Temperature regulation in hot weather:
1. At high temperature, the blood supply to the skin is increased by vasodilation or dilation of blood vessels in the skin.
2. This results in greater loss of heat by convection, conduction and radiation.There is more loss of heat through vapourization as more sweat is secreted due to rich supply of blood to the skin.
(a) Entry of germs ____________
(b) Excessive loss of heat in severe cold ____________
(c) Entry of harmful ultra-violet rays ____________
Solution D.3.
(a) Entry of germs: Skin prevents the entry of harmful substances or infectious agents inside the body.
(b) Excessive loss of heat in severe cold: Skin prevents energy loss from the body. It conserves body heat in cold weather and facilitates loss of heat in hot weather.
(c) Entry of harmful ultra-violet rays: Skin protects the body against harmful ultraviolet light.
1. Draw a labelled diagram of the generalized vertical section of the mammalian skin.
Solution E.1.
2. Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of the vertical section of the human skin.
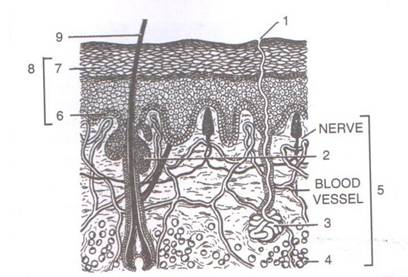
(a) Label the parts numbered from 1 to 9.
(b) State one main function of each of the following parts :
Part 2___________
Part 3___________
Part 4___________
Part 9___________
Name any one of the above parts which has at least three functions.
(C) Part 4 may add to one's good appearance or the "figure". State one example of this function which may be common to both men and women.
Solution E.2.
(a)
1. Sweat pore
2. Sebaceous gland
3. Sweat gland
4. Fat
5. Dermis
6. Stratum malpighian
7. Stratum corneum
8. Epidermis
9. Hair
(b)
• Function of part 2 (Sebaceous gland): It produces oil called sebum, which plays a role in keeping our skin moist.
• Function of part 4 (Fat): The skin reserves food in the form of a layer of fat.
• Function of part 3 (Sweat gland): It secretes a transparent liquid (sweat) containing water and salts from the body in order to regulate body temperature.
• Function of part 9 (Hair): Hair provide a sensation of touch and are also helpful in forensic investigations.
Sebaceous gland:
1. Skin protection
2. Secretes an oily substance known as sebum that lubricates hair and skin of mammals
3. Presence of sebum enables to experience a wet skin even when we have not taken bath for days
3. Presence of sebum enables to experience a wet skin even when we have not taken bath for days
(c) The one function which may be common to both men and women is that the fat serves as a food reserve and heat insulating layer as well as a shock absorber.
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 13 Skin - “The Jack of All Trades”



