Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology - Chapter 12 Movement And Locomotion
Exercise 1
A. Multiple Choice Type
1. Your external ear (pinna) is supported by
(a) Bone
(b) Cartilage
(c) Tendon
(d) Capsule
2. The type of joint found at shoulder is also found at
(a) Elbow
(b) Knee
(c) Ankle
(d) Hip
3. Which one of the following categories of vertebrae are correctly matched?
(a) Cervical-7
(b) Thoracic-10
(c) Lumbar-4
(d) Sacral-4
4. Human skeleton altogether contains 213 bones. Which of these are the 6 bones?
(a) Neck vertebrae
(b) Ear ossicles
(c) Carpals
(d) Metacarpals
Solution A.
1. (b) Cartilage
2. (d) Hip
3. (a) Cervical-7
4. (b) Ear ossicles
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Name the parts of the skeleton where the following are located:
transverse process, glenoid cavity, shoulder-blade, acetabulum
Solution B.1.
2.Name any two parts of your body where the supporting skeleton is made of cartilage instead of bone.
Solution B.2.
1. External Ear
2. Tip of the nose
C. Short Answer Type
1. What is the difference between a true rib and a floating rib?
Solution C.1.
2. Do the muscles pull the structures, or push them? Explain briefly.
Solution C.2.
Muscles pull the structure. A muscle has two ends; a fixed end where the muscle originates and a movable end that pulls some other part. The movable end is drawn out to form a tough structure known as a tendon that is attached to the bone. When a muscle is stimulated by a nerve, it contracts and becomes shorter and thicker and this pulls the bone at its movable end. Muscles can only contract and relax, they cannot lengthen.
3.Just as the humerus corresponds to femur, what bones correspond to tarsals, metacarpals, ulna and radius respectively?
Solution C.3.
4. What are antagonistic muscles? Give one example.
Solution C.4.
Once a structure has been moved by a muscle, it cannot return to its original position without another muscle acting on it. Muscles that cause opposing movements are known as antagonistic muscles.
Example of antagonistic muscles:
When you flex your arm at the elbow, the muscle that lies above the upper arm, i.e. the biceps is seen and felt bulging. This muscle bulges due to contraction and becomes smaller in length, stiffer and thicker. Contraction of biceps draws the forearm towards the upper arm. However, relaxation of biceps cannot push the forearm back to its original position. When the arm is extended or straightened, the muscle at the back of the upper arm, i.e. the triceps contracts. The two muscles work antagonistically or in opposite directions to bend or flex and straighten the arm at the elbow.
Solution C.5.
Some joints like shoulder joint, knee joint need to be held firmly in position to be well-lubricated. Such joints contain a lubricating fluid called synovial fluid, which serves as a cushion between the bones and removes friction during movements. As we age, the joint movement becomes stiffer and less flexible because the amount of lubricating fluid inside the joints decreases and the cartilage becomes thinner. Ligaments also tend to shorten and lose some flexibility, making the joints feel stiff.
1. What are the uses of the skeleton in our body?
Solution D.1.
Uses of skeleton:
1. Support and shape: The skeletal system provides a framework to the body. It provides support to all soft parts and gives a definite shape to the body and all body parts.
2. Protection: The skeleton protects the internal delicate and important organs of the body. For example in human beings, the skull protects thebrain, ribs protect the heart and lungs, vertebra column protects the spinal cord, etc.
3. Movement: The skeletal system helps in movement. It co-ordinates the movement of attached bones and muscles to bring about locomotion.
4. Leverage: Some bones and joints of the skeletal system form levers and help in magnifying, either the movement or the force. For example, slight contraction of biceps moves the hand to a distance of about a foot.
5. Formation of blood cells: The skeleton is the site of haematopoiesis. Various types of blood cells like red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are formed in the bone marrow of some long bones.
6.Storehouse for minerals: The bones are a storehouse of calcium and phosphorus for the rest of the body.
2. What are the different types of joints? Give one example of each type.
Solution D.2.
3. What is the difference between ligament and tendon? What are their functions?
Solution D.3.
4. What are bones made of? Are the bones living or non living? Give reasons.
Solution D.4.
(i) Bone is a strong, hollow and non-flexible connective tissue.
(ii) It is hard, greyish-white tissue, composed of 2/3rd of inorganic substances or minerals like calcium, phosphorus, carbonates, etc. and 1/3rd of organic substances.
(iii) The outer surface of the bone is called periosteum. Periosteum is a thin, dense membrane that consists of outer fibrous and inner cellular layer, nerves and blood vessels that nourish the bone.
(iv) The next layer is made up of compact bone. This part is highly calcified, very hard and rigid connective tissue. This tissue gives bones a smooth, white and solid appearance.
(v) The middle layer of bone consists of bone cells called osteocytes, which are arranged in the form of concentric rings. They are embedded in a hard matrix made up of collagen fibre and mineral deposits.
(vi) The innermost hollow cavity of long bones contains bone marrow, which produces blood cells. Red bone marrow is present at the ends of the bone and produces majority of red blood cells, platelets and most of the white blood cells. Yellow bone marrow contains higher amount of fat cells than red marrow and helps in the production some white blood cells.
(vii) Bones are living tissue as long as they are present in the living body. However, when they are taken out of the body, their cells die and the bones are then said to be dead.
5.Given below is a diagram of human skeleton. Name the bones numbered 1-11.
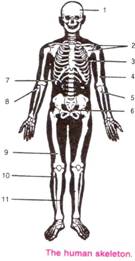
Solution D.5.
1: Cranium/Skull; 2: Clavicle, Scapula; 3: Sternum; 4: Humerus:
5: Ulna; 6: Coccyx; 7: Ribs; 8: Radius; 9: Femur; 10: Fibula; 11: Tibia
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 12 - Movement And Locomotion






