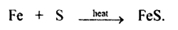EXERCISE - I
(a) Define a chemical reaction.
Answer:
Any chemical change in matter which involves transformation into one or more substances with entirely different properties is called a chemical reaction.
(b) What happens during a chemical reaction ?
Answer:
A chemical reaction involves breaking of chemical bonds between the atoms or groups of atoms of reacting substances and rearrangement of atoms making new bonds to form new substances.
(c) What do you understand by a chemical bond ?
Answer:
(b) A chemical reaction involves breaking of chemical bonds between the atoms or groups of atoms of reacting substances and rearrangement of atoms making new bonds to form new substances.
(c) A chemical bond is the attractive force that holds the atoms of a molecule together, in a compound.
Question 2.
Give one example each of which illustrates the following characteristics of a chemical reaction:
(a) evolution of a gas
(b) change of colour
(c) change in state
Answer:
(a) When Zinc reacts with dil. sulphuric acid. Hydrogen gas is evolved, with an effervescence
(b) When blue coloured copper sulphate reacts with hydrogen sulphide gas, a black coloured substance copper sulphide is formed.
(c) The reaction between hydrogen sulphide and chlorine (both gases) produces sulphur (solid) and hydrogen chloride (gas).
Question 3.
How do the following help in bringing about a chemical change?
(a) pressure (b) light
(c) catalyst (d) heat.
Answer:
(a) Some chemical reactions take place when reactants are subjected to high pressure.
e.g: Nitrogen and hydrogen when subjected to high pressure produce ammonia gas.

(b) Some chemical reactions can take place in the presence of light. Ex. Photosynthesis.

(c) A catalyst can either increases or decreases the rate of chemical reaction and some chemical reactions need a catalyst to change the rate of the reaction, in case it is too slow or too fast.
1. Positive catalyst: When a catalyst increase the rate of reaction finely divided iron is used as a positive catalyst in the manufacturing of ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen.

2. Negative Catalyst: When a catalyst decreases the rate of reaction.
Ex. Phosphoric acid act as a negative catalyst to decrease the rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
(d) Some chemical reactions take place only in the presence of heat.
e.g. When lead nitrate is heated, it breaks into lead monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
Question 4.
(a) Define catalyst.
(b) What are (i) positive catalysts and (ii) negative catalysts? Support your answer with one example for each of them.
(c) Name three biochemical catalysts found in the human body.
Answer:
(a) Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change during the reaction.
(b) (i) Positive catalyst: When a catalyst increases the rate of chemical reaction, it is called positive catalyst.
e.g. when potassium chlorate heated to 700°C decomposes to evolve oxygen gas, when MnO2 is added the decomposition takes place at 300°C

(ii) Negative catalyst: When a catalyst decreases the rate of chemical reaction it is called negative catalyst.
Example. Phosphoric acid acts as a negative catalyst to decrease the rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Alcohol too acts as a negative catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
(c) Biochemical catalysts found in human body:
1. Pepsin
2. Tryspin
3. lipase.
Question 5.
What do you observe when
(a) dilute sulphuric acid is added to granulated zinc?
(b) a few pieces of iron are dropped in a blue solution of copper sulphate?
(c) silver nitrate is added to a solution of sodium chloride?
(d) ferroussulphate solution is added to an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
(e) solid lead nitrate is heated?
(f) when dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution ?
Answer:
(a) When Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, hydrogen gas is evolved with an effervesence.
Zn + dil. H2SO4 → Zn SO4 + H2.
(b) When a few pieces of iron are dropped into a blue coloured copper sulphate solution, the blue colour of the solution fades and eventually turns into green.
(c) When a solution of silver nitrate is added to a solution of sodium chloride, white insoluble ppt. of silver chloride is formed.
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (ppt) + NaNO3 (aq)
(d) When ferrous sulphate solution is added to sodium hydroxide solution, a dirty green ppt. of ferrous hydroxide is formed.
FeSO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) → Fe(OH)2 ↓ + Na2SO4(aq)
(e) When solid lead nitrate is heated, it decomposes to produce light yellow solid lead monoxide, reddish brown nitrogen dioxide gas and colourless oxygen gas.

(f) When few drops of dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.

Question 6.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:

Answer:


Exercise – II
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) A reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance is called a combination reaction.
(b) A catalyst is a substance which changes the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing a chemical change.
(c) The formation of gas bubbles in a liquid during a reaction is called effervesence
(d) The reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization reaction.
(e) Soluble bases are called alkalis.
(f) The chemical change involving iron and hydrochloric acid illustrates a displacement reaction.
(g) In the type of reaction called double decomposition reaction, ions two compounds exchange their positive and negative radicals ions respectively.
(h) A catalyst either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical change but itself remains unchanged at the end of the reaction.
(i) The chemical reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is a combinatonreaction
(j) When a piece of copper is added to silver nitrate solution, it turns blue in colour.
Question 2.
Classify the following reactions as combination, decomposition, displacement, precipitation and neutralization. Also balance the equations.
Question 3.
Define:
(a) precipitation (b) neutralization (c) catalyst
Answer:
(a) Precipitation: A chemical reaction in which two compounds in their aqueous state react to form an insoluble salt as one of the product.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Example.
(b) Neutralization: A chemical reaction in which a base or an alkali reacts, with an acid to produce a salt and water only.
(c) Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change.
here iron act as a catalyst and increases the rate of chemical reaction.
Question 4.
Explain the following types of chemical reactions giving two examples for each of them.
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double decomposition reaction
Answer:
(a) Combination reaction: A reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance is called combination reaction.
A + B → AB
e.g (i) When iron and sulphur are heated together, they combine to form iron sulphide.
(ii) When carbon bums in oxygen to form a gaseous compound called carbon dioxide.
(b) Decomposition reaction: A reaction in which a compound breaks up due to the application of heat into two or more simple substances is called decomposition reaction.
e.g. (i) Mercuric oxide when heated, decomposes to form two elements mercury and oxygen
(ii) CaCO3 when heated decomposes to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(c) Displacement reaction: A reaction in which a more active element displaces a less active element from a compound is called displacement reaction.
AB + C → CB + A
e.g. (i) Zinc, displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
Zn + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu
(ii) Iron piece when added to copper sulphate solution, copper is displaced.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu.
(d) Double decomposition reaction: A chemical reaction in which two compounds in their aqueous state exchange their ions to form new compounds is called a double decomposition reaction.
AB + CD → CB + AD
e.g. (i) AgNO3 + HCl AgCl + HNO3(aq)
(ii) NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O.
Question 5.
Write the missing reactants and products and balance the equations.
Question 6.
How will you obtain?
(a) Magnesium oxide from magnesium.
(b) Silver chloride from silver nitrate.
(c) Nitrogen dioxide from lead nitrate.
(d) Zinc chloride from zinc.
(e) Ammonia from nitrogen.
Also give balanced equations for the reactions
Answer:
(a) Magnesium when burnt in air (oxygen) Magnesium oxide is formed
(b) When silver nitrate solution reacts with sodium chloride, silver chloride is formed.
(c) Lead nitrate when heated nitrogen oxide is obtained
(d) Zinc when reacts with hydrochloric acid zinc chloride and hydrogen (g) is formed.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
(e) Nitrogen when reacts with hydrogen at 450°C and under 200 atm, ammonia is formed.
Question 7.
What do you observe when
(a) Iron nail is kept in copper sulphate solution for sometime.
(b) Phenolphthalein is added to sodium hydroxide solution.
(c) Blue litmus paper is dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid.
(d) Lead nitrate is heated.
(e) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen.
(f) Ammonia is brought in contact of hydrogen chloride.gas.
Answer:
(a) A brown layer of copper gets deposited on iron nail. This is due to chemical reaction.
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(b) Solution turns pink.
(c) Blue litmus turns red in an acid solution.
(d) The pale yellow solid is lead monoxide, the reddish brown gas is nitrogen dioxide and the colourless gas is oxygen.
(e) Magnesium ribbon bums with a dazzling white light and produces a white powder which is magnesium oxide.
The reaction can be represented as
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO (white powder)
(f) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride, both compounds, combine to form a compound, ammonium chloride.
Question 8.
Give reason:
(a) A person suffering from acidity is advised to take an antacid.
(b) Acidic soil is treated with quick lime.
(c) Wasp sting is treated with vinegar.
Answer:
(a) An antacid neutralizes stomach acidity.
(b) If the soil is acidic it can be treated with base like quick lime, to make it neutral.
(c) Wasp stings are alkaline and they can be neutralized by vinegar which is a weak acid.
Question 9.
What is meant by the metal reactivity series ? State its importance, (any two points).
Answer:
A list in which the metals are arranged in the decreasing order of their chemical reactivity is called the metal reactivity series.
Special features of the activity series:
1. The ease with which a metal in solution loses electron(s) and forms a positive ion decreases down the series, i.e. from potassium to gold.
2. Hydrogen is included in the activity series because, like metals do, it too loses an electron and becomes positively charged (H+) in most chemical reactions.
3. The series facilitates the comparative study of metals in terms of the degree of their reactivity.
4. The compounds of the metals (oxides, carbonates, nitrates and hydroxides) too can be easily compared.
Question 10.
What are oxides ? Give two examples of each of the following oxides.
(a) Basic oxide (b) Acidic oxide
(c) Amphoteric oxide (d) Neutral oxide
Answer:
An oxide is a compound which essentially contains oxygen in its molecule, chemically combined with a metal or a non-metal.
Question 11.
Define exothermic and endothermic reactions. Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Exothermic reactions: The chemical reaction in which heat is given out is called exothermic reactions. It causes rise in temperature. .
e.g. (i) When carbon bums in oxygen to form carbon dioxide, a lot of heat is produced.
C + O2 → CO2 + heat.
When water is added to quicklime a lot of heat is produced which boils the water.
CaO + H2O → Ca (OH)2 + Heat.
Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed is called endothermic reaction. It causes fall in temperature.
e.g. (i) When nitrogen and oxygen together are heated to a temperature of about 3000°C, nitric oxide gas is formed.
N2 + O2 + heat → 2NO (g)
(ii) Decomposition of calcium carbonate into carbon dioxide and calcium oxide when heated to a 1000°C.
CaCO3 + Heat → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Question 12.
State the effect of:
(a) an endothermic reaction
(b) an exothermic reaction on the surroundings.
Answer:
(a) Carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is trapped by infrared radiations, gives rise to temperature which is exothermic reaction.
(b) The melting of glaciers by global warming.
Question 13.
What do you observe when
(a) an acid is added to a basic solution.
(b) ammonium chloride is dissolved in water.
Answer:
(a) A chemical reaction in which a base or an alkali reacts with an acid to produce a salt and water.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
(b) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water is an endothemic reaction in which heat energy is absorbed.
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Chemical Reactions