Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Physics Chapter 1 Matter
• MatterEvery substance living and non-living that we see is made up of matter and MATTER “is something which has mass, occupies space and can be perceived by our senses.” e.g. Hydrogen, milk, oxygen, pen, table, water, iron, air, oil, sugar etc.
• Matter is composed of tiny particles called molecules, which are in constant motion, have spaces between them and have inter-molecular attraction.
• Every molecule can exist freely in nature and has all the properties of matter.
• A molecule is composed of ATOMS, but atom cannot exist free in nature.
• INTER-MOLECULAR FORCE ‘The molecules of a matter exert a force of attraction on each other – The force of attraction is called INTER-
• MOLECULAR FORCEThis force in solid is very strong and we cannot break a solid easily. In liquids this force is less strong and in molecules of gas it is very less. –
• FORCE OF COHESION “The inter-molecular force of attraction between the molecules of same substance is called FORCE OF COHESION.” i.e. between water and water.
• FORCE OF ADHESION “The force of attraction between the molecules of two different substances is called FORCE OF ADHESION” i.e. between glue and paper.
Matter is composed of tiny particles and molecules of matter have spaces between them can be proved by experiment.
Take 50 c.c of water in a measuring cylinder. Add a small quantity of salt in it. Salt gets dissolved in water and still level remains at 50 c.c. Where has salt gone?
The salt molecules enter into spaces of water and water molecules into spaces of salt molecules. This experiment show that particles of matter are very minute and cannot be seen by naked eye and there are spaces between molecules.
• The molecules of matter are in constant motion can be seen by opening a bottle of perfume in a comer of room, it reaches the other parts of the room.
• SUBLIMATION Change of solid directly into vapours on absorbing heat.
• DEPOSITION “The change of vapours directly into solid on cooling.”
• MELTING “Change of solid in liquid at fixed temperature on heating.”
• FUSION or FREEZING “Change of liquid to solid state on cooling at a fixed temperature.”
• FUSION or MELTING “Change of a solid to liquid state at a fixed temperature on absorbing heat.”
• EVAPORATION Surface phenomenon i.e. only takes place at surface “Is change of liquid to vapours.” Evaporation has cooling effect. Takes place at all temperatures.
• VAPORIZATION “Change of liquid to vapour state on heating at constant temperature.”
It is fast process and produces hotness.
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) The temperature of a substance remains unaffected during its change of state.
Answer: True.
(b) Ice melts at 100°C.
Answer: False. The ice melts at 0° by absorption of heat.
(c) Water at 100°C has more heat than the steam at 100°C.
Answer: False.
(d) Evaporation of a liquid causes cooling.
Answer: True.
(e) Water evaporates only at 100°C.
Answer: False.
(f) Boiling takes place at all temperatures.
Answer: False.
(g) Evaporation takes place over the entire mass of the liquid.
Answer: False.
(h) The process of a gas converting directly into solid is called vaporization.
Answer: False.
The process of a liquid converting directly into gas is called vaporization.
(i) At high altitudes water boils above 100° C.
Answer: False.
(j)The melting point of ice is 0°C.
Answer: True.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Evaporation takes place at all temperature.
(b)Freezing process is just reverse of melting.
(c)Sublimation is a process that involves direct conversion of a solid into its vapouron heating.
(d) The temperature at which a solid converts into a liquid is called its melting point.
(e) The smallest unit of matter that exists freely in nature is called molecule.
(f) Molecules of a substance are always in a state of motion and so they possess kinetic energy.
(g) Intermolecular space is maximum in gases less in liquids and the least in solids.
(h) Intermolecular force of attraction is maximum in solids, less in liquids and the least in gases.
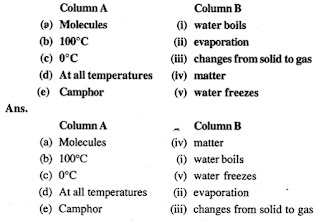
3. Match the following
4. Select the correct alternative
(a) The inter-molecular force is maximum in
1. solids
2. gases
3. liquids
4. none of the above
(b) The inter-molecular space is maximum in
1. liquids
2. solids
3. gases
4. none of the above
(c) The molecules can move freely anywhere in
1. gases
2. liquids
3. solids
4. none of the above
(d) The molecules move only within the boundary of
1. liquids
2. gases
3. solids
4. none of the above
(e) The temperature at which a liquid gets converted into its vapour state is called its
1. melting point
2. boiling point
3. dewpoint
4. freezing point.
(f) Rapid conversion of water into steam is an example of
1. evaporation
2. freezing
3. melting
4. vapourization.
(g) Evaporation takes place from the
1. surface of liquid
2. throughout the liquid
3. mid-portion of the liquid
4. bottom of liquid.
(h) Boiling takes place from the
1. the surface of the liquid
2. throughout the liquid
3. mid-portion of liquid
4. none of the above.
• MatterEvery substance living and non-living that we see is made up of matter and MATTER “is something which has mass, occupies space and can be perceived by our senses.” e.g. Hydrogen, milk, oxygen, pen, table, water, iron, air, oil, sugar etc.
• Matter is composed of tiny particles called molecules, which are in constant motion, have spaces between them and have inter-molecular attraction.
• Every molecule can exist freely in nature and has all the properties of matter.
• A molecule is composed of ATOMS, but atom cannot exist free in nature.
• INTER-MOLECULAR FORCE ‘The molecules of a matter exert a force of attraction on each other – The force of attraction is called INTER-
• MOLECULAR FORCEThis force in solid is very strong and we cannot break a solid easily. In liquids this force is less strong and in molecules of gas it is very less. –
• FORCE OF COHESION “The inter-molecular force of attraction between the molecules of same substance is called FORCE OF COHESION.” i.e. between water and water.
• FORCE OF ADHESION “The force of attraction between the molecules of two different substances is called FORCE OF ADHESION” i.e. between glue and paper.
Matter is composed of tiny particles and molecules of matter have spaces between them can be proved by experiment.
Take 50 c.c of water in a measuring cylinder. Add a small quantity of salt in it. Salt gets dissolved in water and still level remains at 50 c.c. Where has salt gone?
The salt molecules enter into spaces of water and water molecules into spaces of salt molecules. This experiment show that particles of matter are very minute and cannot be seen by naked eye and there are spaces between molecules.
• The molecules of matter are in constant motion can be seen by opening a bottle of perfume in a comer of room, it reaches the other parts of the room.
• SUBLIMATION Change of solid directly into vapours on absorbing heat.
• DEPOSITION “The change of vapours directly into solid on cooling.”
• MELTING “Change of solid in liquid at fixed temperature on heating.”
• FUSION or FREEZING “Change of liquid to solid state on cooling at a fixed temperature.”
• FUSION or MELTING “Change of a solid to liquid state at a fixed temperature on absorbing heat.”
• EVAPORATION Surface phenomenon i.e. only takes place at surface “Is change of liquid to vapours.” Evaporation has cooling effect. Takes place at all temperatures.
• VAPORIZATION “Change of liquid to vapour state on heating at constant temperature.”
It is fast process and produces hotness.
Test Yourself
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) The temperature of a substance remains unaffected during its change of state.
Answer: True.
(b) Ice melts at 100°C.
Answer: False. The ice melts at 0° by absorption of heat.
(c) Water at 100°C has more heat than the steam at 100°C.
Answer: False.
(d) Evaporation of a liquid causes cooling.
Answer: True.
(e) Water evaporates only at 100°C.
Answer: False.
(f) Boiling takes place at all temperatures.
Answer: False.
(g) Evaporation takes place over the entire mass of the liquid.
Answer: False.
(h) The process of a gas converting directly into solid is called vaporization.
Answer: False.
The process of a liquid converting directly into gas is called vaporization.
(i) At high altitudes water boils above 100° C.
Answer: False.
(j)The melting point of ice is 0°C.
Answer: True.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Evaporation takes place at all temperature.
(b)Freezing process is just reverse of melting.
(c)Sublimation is a process that involves direct conversion of a solid into its vapouron heating.
(d) The temperature at which a solid converts into a liquid is called its melting point.
(e) The smallest unit of matter that exists freely in nature is called molecule.
(f) Molecules of a substance are always in a state of motion and so they possess kinetic energy.
(g) Intermolecular space is maximum in gases less in liquids and the least in solids.
(h) Intermolecular force of attraction is maximum in solids, less in liquids and the least in gases.
3. Match the following
4. Select the correct alternative
(a) The inter-molecular force is maximum in
1. solids
2. gases
3. liquids
4. none of the above
(b) The inter-molecular space is maximum in
1. liquids
2. solids
3. gases
4. none of the above
(c) The molecules can move freely anywhere in
1. gases
2. liquids
3. solids
4. none of the above
(d) The molecules move only within the boundary of
1. liquids
2. gases
3. solids
4. none of the above
(e) The temperature at which a liquid gets converted into its vapour state is called its
1. melting point
2. boiling point
3. dewpoint
4. freezing point.
(f) Rapid conversion of water into steam is an example of
1. evaporation
2. freezing
3. melting
4. vapourization.
(g) Evaporation takes place from the
1. surface of liquid
2. throughout the liquid
3. mid-portion of the liquid
4. bottom of liquid.
(h) Boiling takes place from the
1. the surface of the liquid
2. throughout the liquid
3. mid-portion of liquid
4. none of the above.
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Physics Chapter 1 - Matter