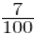Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Value Added Tax
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Value Added Tax
Exercise 1(A)Question 1.
Rajat purchases a wrist-watch costing ₹ 540. The rate of sales tax is 8%. Find the total amount paid by Rajat for the watch.
Solution:
Sale price of watch = ₹ 540
Rate of sales tax = 8%
Total amount paid by Rajat = ₹ 540 + 8% of ₹ 540
= ₹ 540 + ₹ 43.20
= ₹ 583.20
Ramesh paid ₹ 345.60 as sales tax on a purchase of ₹ 3,840. Find the rate of sales tax.
Solution:
Sale price = ₹ 3,840
Sales tax paid = ₹ 345.60
Question 3.
The price of a washing machine, inclusive of sales tax is ₹ 13,530/-. If the sales tax is 10%, find its basic cost price.
Solution:
Selling price of washing machine = ₹ 13,530
Rate of sales tax = 7%
Question 4.
Sarita purchases biscuits costing ₹ 158 on which the rate of sales tax is 6%. She also purchases some cosmetic goods costing ₹ 354 on which the rate of sales tax is 9%. Find the total amount to be paid by Sarita.
Solution:
Sale price of biscuits = ₹ 158
Rate of sales tax on biscuits= 6%
Amount paid for biscuits= ₹ 158 + 6% of ₹ 158
= ₹ 158 + ₹ 9.48
= ₹ 167.48
Sale price of cosmetic goods = ₹ 354
Rate of sales tax= 9%
Amount paid for cosmetic goods = ₹ 354 + 9% of ₹ 354
= ₹ 354 + ₹ 31.86
= ₹ 385.86
Total amount paid by Sarita = ₹ 167.48 + ₹ 385.86
= ₹ 553.34
The marked price of two articles A and B together is ₹ 6,000. The sales tax on article A is 8% and that on article B is 10%. If on selling both the articles, the total sales tax collected is ₹ 552, find the marked price of collected of the articles A and B.
Solution:
Let the marked price of article A be ₹ x and article B be ₹ y.
The marked price of A and B together is ₹ 6,000.
⇒ x + y = 6,000 ……..(i)
The sales tax on article A is 8% and that on article B is 10%.
Also the total sales tax collected on selling both the articles is ₹ 552.
⇒ 8% of x + 10% of y = 552
⇒ 8x + 10y = 55,200 ……..(ii)
Multiply equation (i) by 8 and subtract it from equation (ii) we get,
2y = 7,200
⇒ y =3,600
Substituting y = 3,600 in equation (i) we get,
x + 3,600 = 6,000
⇒ x = 2,400
The marked price of article A is ₹ 2,400 and article B is ₹ 3,600.
The price of a T.V. set inclusive of sales tax of 9% is ₹ 13,407. Find its marked price. If sales tax is increased to 13%, how much more does the customer has to pay for the T.V.?
Solution:
(i) Total price paid for T.V. = ₹ 13,407
Rate of sales tax = 9%
Let sale price = ₹ y
According to question
New rate of sales tax = 13%
New total price for T.V. = ₹ 12,300+ 13% of ₹ 12,300
= ₹ 12,300 + ₹ 1,599
= ₹ 13,899
More money paid = ₹ 13,899 – ₹ 13,407 = ₹ 492
The price of an article is ₹ 8,250 which includes sales tax at 10%. Find how much more or less does a customer pay for the article, if the sales tax on the article:
(i) increases to 15%
(ii) decreases to 6%
(iii) increases by 2%
(iv) decreases by 3%
Solution:
Let sale price of article = ₹ y
Total price inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 8,250
Rate of sales tax = 10%
According to question
(i) New rate of sales tax = 15%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 15% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + ₹ 1,125 = ₹ 8,625
More money paid = ₹ 8,625 – ₹ 8,250 = ₹ 375
(ii) New rate of sales tax = 6%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 6% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 +₹ 450 = ₹ 7,950
Less money paid = ₹ 8,250 – ₹ 7,950 = ₹ 300
(iii) New rate of sales tax = (10+2)% = 12%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 12% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500+ ₹ 900 = ₹ 8,400
More money paid = ₹ 8,400 – ₹ 8,250 = ₹ 150
(iv) New rate of sales tax =(10-3)%= 7%
New total price = ₹ 7,500+ 7% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + ₹ 525 = ₹ 8,025
Less money paid = ₹ 8,250 – ₹ 8,025 = ₹ 225
A bicycle is available for ₹ 1,664 including sales tax. If the list price of the bicycle is ₹ 1,600, find :
(i) the rate of sales tax.
(ii) the price, a customer will pay for the bicycle if the sales tax is increased by 6%.
Solution:
Price of bicycle inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 1,664
List price of bicycle = ₹ 1,600
(i) Sales tax= ₹ 1,664 – ₹ 1,600 = ₹ 64
New total price = ₹ 1,600+ 10% of ₹ 1,600
= ₹ 1,600 + ₹ 160
= ₹ 1,760
When the rate of sale-tax is decreased from 9% to 6% for a coloured T.V.; Mrs. Geeta will save ₹ 780 in buying this T.V. Find the list price of the T.V.
Solution:
Question 10.
A trader buys an unfinished article for ₹ 1,800 and spends ₹ 600 on its finishing, packing, transportation, etc. He marks the article at such a price that will give him 20% profit. How much will a customer pay for the article including 12% sales tax.
Solution:
Purchase price = ₹ 1,800
Expenditure = ₹ 600
Total price = ₹ 1,800+ ₹ 600 = ₹ 2,400
M.P. of article = ₹ 2,400 + 20% of ₹ 2400
= ₹ 2,400 + ₹ 480 = ₹ 2,880
Cost price for customer = ₹ 2,880+ 12% of ₹ 2,880
= ₹ 2,880 + ₹ 345.60
= ₹ 3,225.60
A shopkeeper buys an article for ₹ 800 and spends ₹ 100 on its transportation, etc. He marks the article at a certain price and then sells it for ₹ 1,287 including 10% sales tax. Find his profit as percent.
Solution:
C.P. of an article = ₹ 800
Expenditure = ₹ 100
Total C.P. = ₹ 800 + ₹ 100 = ₹ 900
Let sale price = ₹ y
Sale price inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 1,287
Rate of sales tax = 10%
Then y + 10% of y = ₹ 1,287
Question 12.
A shopkeeper announces a discount of 15% on his goods. If the marked price of an article, in his shop, is ₹ 6,000; how much a customer has to pay for it, if the rate of sales tax is 10%?
Solution:
Marked price of article = ₹ 6,000
Sale price after discount = ₹ 6,000 – 15% of ₹ 6,000
= ₹ 6,000 – ₹ 900
₹ 5,100
Rate of sales tax = 10%
Cost price for customer = ₹ 5,100 + 10% of ₹ 5,100
= ₹ 5,100+ ₹ 510
= ₹ 5,610
The catalogue price of a colour T.V. is ₹ 24,000. The shopkeeper gives a discount of 8% on the list price. He gives a further off season discount of 5% on the balance. But sales tax at 10% is charged on the remaining amount. Find :
(a) the sales tax a customer has to pay.
(b) the final price he has to pay for the T.V
Solution:
Exercise 1(B)
Question 1.
A shopkeeper purchases an article for ₹ 6,200 and sells it to a customer for ₹ 8,500. If the sales tax (under VAT) is 8%; find the VAT paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Purchase price for shopkeeper = ₹ 6,200
Sale price for shopkeeper = ₹ 8,500
Tax paid by the shopkeeper = 8% of 6,200 = ₹ 496
Tax charged by the shopkeeper= 8% of 8,500
Then VAT paid by the shopkeeper= ₹ 680 – ₹ 496 = ₹ 184
A purchases an article for ₹ 3,600 and sells it to B for ₹ 4,800. B, in turn, sells the article to C for ₹ 5,500. If the sales tax(under VAT) is 10%, find the VAT levied on A and B.
Solution:
Purchase price for A = ₹ 3,600
Tax paid by A = 10% of ₹ 3,600
Purchase price for B = ₹ 4,800
Tax paid by B to A = 10% of ₹ 4,800
Purchase price for C = ₹ 5,500
Tax paid by C to B = 10% of ₹ 5,500
VAT paid by A = ₹ 480 – ₹ 360 = ₹ 120
VAT paid by B = ₹ 550 – ₹ 480 = ₹ 70
A manufacturer buys raw material for ₹ 60,000 and pays 4% tax. He sells the ready stock for ₹ 92,000 and charges 12.5% tax. Find the VAT paid by the manufacturer.
Solution:
Purchase price for manufacture = ₹ 60,000
Tax paid by manufacturer = 4% of ₹ 60,000
Sale price for manufacturer = ₹ 92,000
Tax charged by manufacturer = 12.5% of ₹ 92,000
VAT paid by manufacturer = ₹ 11,500 – ₹ 2,400
= ₹ 9,100
The cost of an article is ₹ 6,000 to a distributor. He sells it to a trader for ₹ 7,500 and the trader sells it to a customer for ₹ 8,000. If the VAT rate is 12.5%; find the VAT paid by the :
(i)distributor
(ii)trader.
Solution:
Cost price for distributor = ₹ 6,000
Tax paid by distributor = 12.5% of ₹ 6,000
Sale price for distributor= ₹ 7,500
Tax charged by distributor= 12.5% of ₹ 7,500
VAT paid by distributor = ₹ 937.50 – ₹ 750
= ₹ 187.50
Sale price for trader = ₹ 8,000
Tax charged by trader = 12.5% of ₹ 8,000
VAT paid by trader= ₹ 1,000 – ₹ 937.50 = ₹ 62.50
The printed price of an article is ₹ 2,500. A wholesaler sells it to a retailer at 20% discount and charges sales tax at the rate of 10%. Now the retailer, in turn, sells the article to a customer at its list price and charges the sales tax at the same rate. Find :
(i) the amount that retailer pays to the wholesaler.
(ii) the VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:
Question 6.
A retailer buys an article for ₹ 800 and pays the sales tax at the rate of 8%. The retailer sells the same article to a customer for ₹ 1,000 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Find:
(i) the price paid by a customer to buy this article.
(ii) the amount of VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:
Cost price for retailer = ₹ 800
Sales tax paid by retailer = 8% of ₹ 800
Sale price for retailer = ₹ 1,000
Tax charged by retailer = 8% of ₹ 1,000
Price paid by customer = ₹ 1,000 + ₹ 80 = ₹ 1,080
VAT paid by retailer = ₹ 80 – ₹ 64 = ₹ 16
A shopkeeper buys 15 identical articles for ₹ 840 and pays sales tax at the rate of 8%. He sells 6 of these articles at ₹ 65 each and charges sales tax at the same rate. Calculate the VAT paid by the shopkeeper against the sale of these six articles.
Solution:
Question 8.
The marked price of an article is ₹ 900 and the rate of sales tax on it is 6%. If on selling the article at its marked price, a retailer has to pay VAT = ₹ 4.80; find the money paid by him (including sales tax) for purchasing this article.
Solution:
Question 9.
A manufacturer marks an article at ₹ 5,000. He sells this article to a wholesaler at a discount of 25% on the marked price and the wholesaler sells it to a retailer at a discount of 15% on its marked price. If the retailer sells the article without any discount and at each stage the sales tax is 8%, calculate the amount of VAT paid by :
(i) the wholesaler (ii) the retailer
Solution:
Question 10.
A shopkeeper buys an article at a discount of 30% and pays sales tax at the rate of 8%. The shopkeeper, in turn, sells the article to a customer at the printed price and charges sales tax at the same rate. If the printed price of the article is ₹ 2,500; find :
(i) the price paid by the shopkeeper.
(ii) the price paid by the customer.
(iii) the VAT (value added tax) paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Question 11.
A shopkeeper sells an article at its list price (₹ 3,000) and charges sales tax at the rate of 12%. If the VAT paid by the shopkeeper is ₹ 72, at what price did the shopkeeper buy the article inclusive of sales tax?
Solution:
Question 12.
A manufacturer marks an article for ₹ 10,000. He sells it to a wholesaler at 40% discount. The wholesaler sells this article to a retailer at a discount of 20% on the marked price. If retailer sells the article to a customer at 10% discount and the rate of sales tax is 12% at each stage; find the amount of VAT paid by the (i) wholesaler (ii) retailer.
Solution:
VAT paid by wholesaler = ₹ 960 – ₹ 720= ₹ 240
VAT paid by retailer = ₹ 1080 – ₹ 960= ₹ 120
Question 1.
Madan purchases a compact computer system for ₹ 47,700 which includes 10% rebate on the marked price and then a 6% sales tax on the remaining price. Find the marked price of the computer.
Solution:
Question 2.
An article is marked at ₹ 500. The wholesaler sells it to a retailer at 20% discount and charges sales tax on the remaining price at 12.5%. The retailer, in turn, sells the article to a customer at its marked price and charges sales tax at the same rate. Calculate:
(i) The price paid by the customer.
(ii) The VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:Question 3.
An article is marked at ₹ 4,500 and the rate of sales tax on it is 6%. A trader buys this article at some discount and sells it to a customer at the marked price. If the trader pays ₹ 81 as VAT; find:
How much per cent discount does the trader get?
The total money paid by the trader, including tax, to buy the article.
Solution:
Question 4.
A retailer sells an article for ₹ 5,350 including 7% sales tax on the listed price. If he bought it at a discount and has made a profit of 25% on the whole, find the rate of discount the retailer received.
Solution:
Question 5.
A shopkeeper buys a camera at a discount of 20% from the wholesaler, the printed price of the camera being ₹ 1,600 and the rate of sales tax being 6%. The shopkeeper sells it to a buyer at the printed price and charges tax at the same rate. Find:
The price at which the camera can be bought from the shopkeeper.
The VAT (Value Added Tax) paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Printed price of camera = ₹ 1,600
Discount% = 20%
Purchase price for the shopkeeper
= ₹ 1,280 + ₹ 76.80 = ₹ 1,356.80
Selling price for the shopkeeper = ₹ 1,600
Purchase price for a customer = ₹ 1,600 + ₹ 96 = ₹ 1,696
The price at which the camera can be bought from the shopkeeper is ₹ 1,696.
VAT paid by the shopkeeper= Tax charged – Tax paid
= ₹ 96 – ₹ 76.80 = ₹ 19.20
The VAT (Value Added Tax) paid by the shopkeeper is ₹ 19.20.
Tarun bought an article for ₹ 8,000 and spent ₹ 1,000 on its transportation. He marked the article at ₹ 11,700 and sold it to a customer. If the customer had to pay 10% sales tax, find:
(i) The customer’s price (ii) Tarun’s profit percent.
Solution:
Purchase price for = ₹ 8,000
Expense on transportation = ₹ 1,000
Cost price for Tarun = ₹ 8,000 + ₹ 1,000 = ₹ 9,000
Marked price by Tarun = ₹ 11,700
Question 7.
A shopkeeper sells an article at the listed price of ₹ 1,500 and the rate of VAT is 12% at each stage of sale. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of ₹ 36 to the Government, what was the price, inclusive of Tax, at which the shopkeeper purchased the article from the wholesaler?
Solution:
Question 8.
A shopkeeper bought a washing machine at a discount of 20% from a wholesaler, the printed price of the washing machine being ₹ 18,000. The shopkeeper sells it to a consumer at a discount of 10% on the printed price. If the rate of VAT (or sales tax) is 8%, find :
(i) The VAT paid by the shopkeeper.
(ii) The total amount that the consumer pays for the washing machine.
Solution:
Question 9.
Mohit, a dealer in electronic goods, buys a high class TV set for ₹ 61,200. He sells this TV set to Geeta, Geeta to Rohan and Rohan sells it to Manoj. If the profit at each stage is ₹ 2,000 and the rate of VAT at each stage is 12.5%, find:
(i) total amount of tax (under VAT) paid to the Government.
(ii) Money paid by Manoj to buy the TV set.
Solution:
Question 10.
A shopkeeper buys an article at a discount of 30% of the list price which is ₹ 48,000. In turn, the shopkeeper sells the article at 10% discount. If the rate of VAT is 10%, find the VAT to be paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Question 11.
A company sells an article to a dealer for 40,500 including VAT (sales-tax). The dealer sells it to some other dealer for 42,500 plus tax. The second dealer sells it to a customer at a profit of 3,000. If the rate of sales-tax under VAT is 8%, find :
(i) The cost of the article (excluding tax) to the first dealer.
(ii) The total tax (under VAT) received by the Government.
(iii) The amount that a customer pays for the article.
Solution:
Question 12.
A wholesaler buys a TV from the manufacturer for ₹ 25,000. He marks the price of the TV 20% above his cost price and sells it to a retailer at 10% discount on the marked price. If the rate of VAT is 8%, find the :
(i) Marked price.
(ii) Reailer’s cost price inclusive of tax.
(iii) VAT paid by the wholesaler.
Solution: