Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Graphical Representation
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Chapter 23 Graphical Representation (Histograms, Frequency Polygon and Ogives)
Graphical Representation Exercise 23 – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.Solution:
Question 2.
Solution:
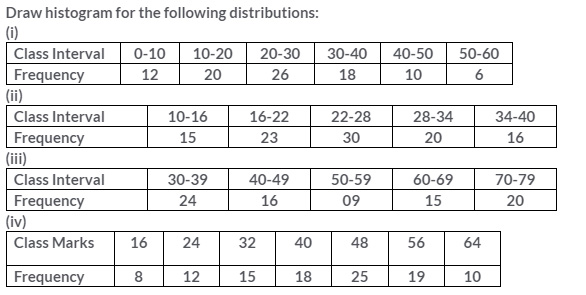
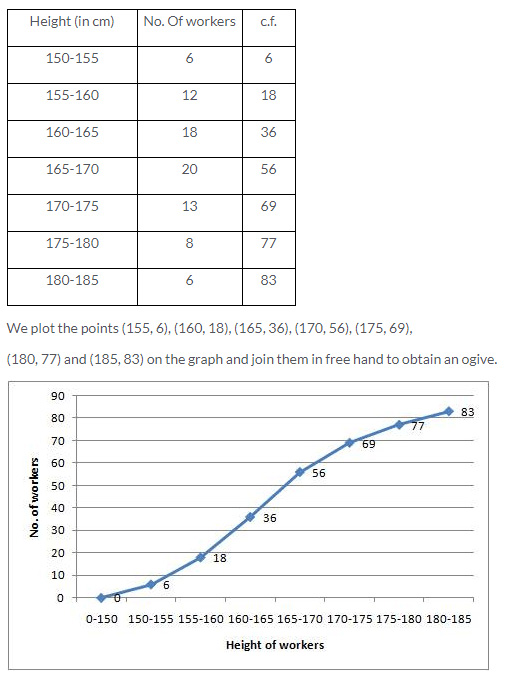
Question 3.
Solution:
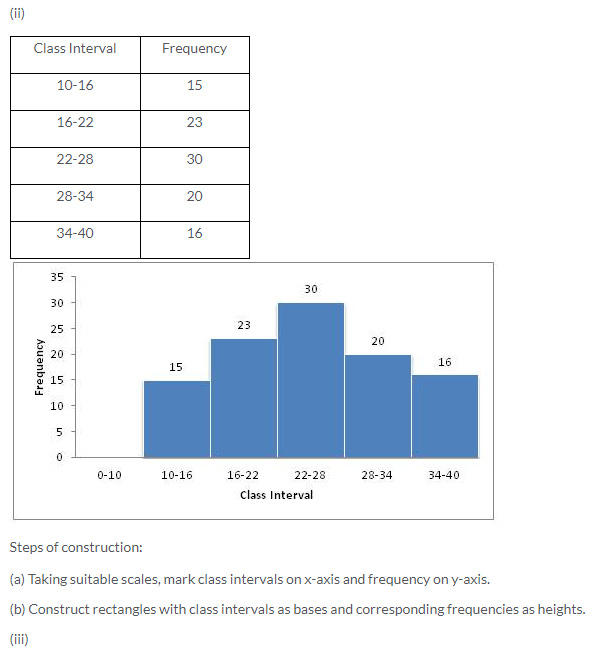
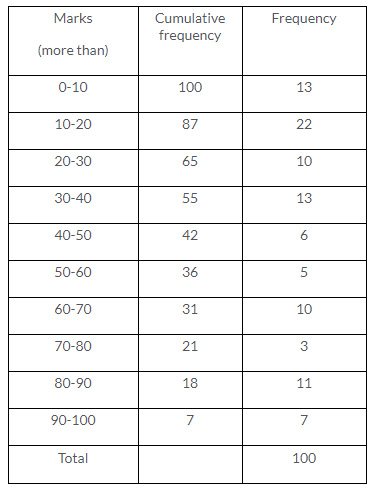
Question 4.
Construct a frequency distribution table for the number given below, using the class intervals 21-30, 31-40 … etc.
75, 67, 57, 50, 26, 33, 44, 58, 67, 75, 78, 43, 41, 31, 21, 32, 40, 62, 54, 69, 48, 47, 51, 38, 39, 43, 61, 63, 68, 53, 56, 49, 59, 37, 40, 68, 23, 28, 36, 47
Use the table obtained to draw:
(i) a histogram (ii) an ogive
Solution:
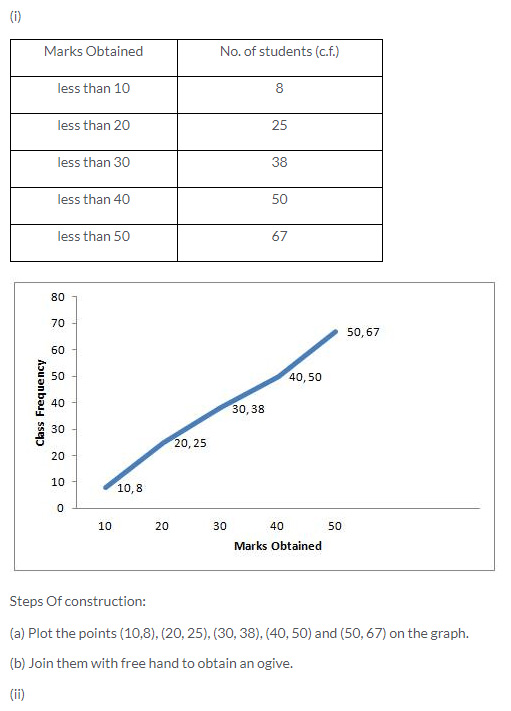
Question 5.
Solution:
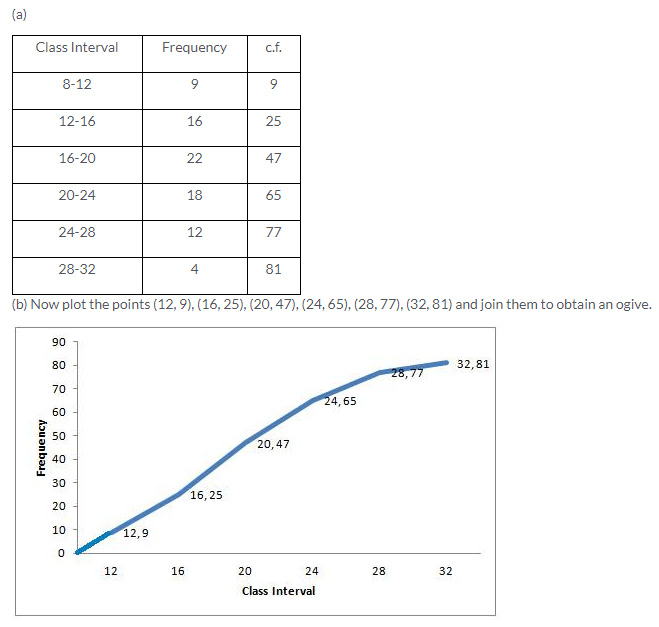
Question 6.
Solution:
Question 7.
Solution:
Question 8.
Solution:
Question 9.
Solution: