Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Study of Compounds – Hydrogen Chloride
Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Study of Compounds – Hydrogen Chloride
Exercise 1
1.
Solution 1.
2.
Solution 2.
(a) Hydrogen chloride is dried by passing through conc. Sulphuric acid.
(b) Phosphorous pentoxide and CaO cannot be used to dry HCl because they react with HCl.
2P2O5+ 3HCl → POCl3 + 3HPO3
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
3.Explain why:
(a) Anhydrous HCl is a poor conductor while aq. HCl is an excellent conductor.
(b) When the stopper of a bottle full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened there are fumes in the air.
(c) A solution of hydrogen chloride in water turns blue litmus red and conducts electricity , while a solution of the same gas in toluene:
(i) Has no effect on litmus ,and
(ii) Does not conduct electricity
(d) Thick white fumes are formed when glass rod dipped in NH4OH is brought near the mouth of bottle full of HCl gas.
(e) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not affect a dry strip of blue litmus paper but it turns red in the presence of drop of water.
(f) Hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water.
Solution 3.
(a) Anhydrous HCl is poor conductor due to the absence of ions in it whereas aqueous HCl is excellent conductor since it contains ions.
(b) When the stopper is opened HCl gas comes in contact with water vapors of air and gives white fumes due to the formation of hydrochloric acid.
(c) A solution of HCl in water gives hydronium ions and conducts electricity, but HCl is also soluble in dry toluene, but in that case it neither (i) turns blue litmus red (ii) nor does conducts electricity.
This indicates the absence of H+ ions in toluene showing thereby that hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound.
This indicates the absence of H+ ions in toluene showing thereby that hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound.
(d) When ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of HCl, dense white fumes are formed due to the formation of ammonium chloride.
HCl + NH4OH → NH4Cl + H2O
(e) Dry hydrogen chloride is not acidic whereas moist Hydrogen chloride is acidic. In presence of a drop of water HCl gas dissolves in water and forms hydrochloric acid which turns blue litmus paper red.
(f) Hydrogen chloride is not collected over water as it is highly soluble in water.
4.
Difference between Hydrogen chloride gas and Hydrochloric acid is:
5.The given set up of the figure is for preparation of an acid.
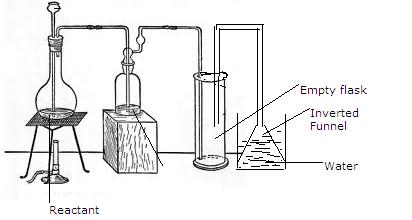
(a) Name the acid prepared by this method.
(b) Name the reactants used.
(c) Why empty flask is used.
(d) What is drying agent used? Why is this drying agent chosen?
(e) What is the role of inverted funnel in the arrangement?
(a) Hydrochloric acid is prepared by this method.
(b) The reactants are sodium chloride and Sulphuric acid.
(c) The empty flask acts as Anti-Suction device. In case the back suction occurs the water will collect in it and will not reach the generating flask.
(d) The drying agent is Conc. Sulphuric acid. Sulphuric acid is chosen as drying agent because it does not react with HCl.
(e) The Inverted funnel :Prevents or minimizes back suction of water.
Provides a large surface area for absorption of HCl gas.
6.Write an equation for the reactions of hydrochloric acid on
a. silver nitrate solution
b. magnesium foil
c. caustic soda solution
d. zinc carbonate
e. Lead(II) Nitrate
f. copper oxide
Solution 6.
7.
Solution 7.
(a) Chlorine.
The compound formed which is strongly acidic in water, is HCl.
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(b) A dilute aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid gets gradually concentrated on distillation, till the concentration of the acid reaches 22.2% HCl by weight which boils at 1100C.When this concentration is reached, no further increase in concentration of the acid becomes possible by boiling. This is because vapours evolved before 1100C are vapours of water but at temperature above 1100C vapours consist mostly of molecules of HCl.
8.
We can prove that hydrochloric acid contains both hydrogen and chlorine by the following experiment.
Take a voltameter used for electrolysis of water, fitted with platinum cathode and graphite anode.
Into the voltameter pour 4 molar HCl and pass direct current.
It is seen that a colourless gas is evolved at cathode and a greenish gas is evolved at anode.
When a burning splinter is brought near a colourless gas, it bursts into flame thereby proving that it is hydrogen gas.
When moist starch iodide paper is held in the greenish yellow gas, it turns blue black, thereby proving that the gas is chlorine.
2HCl → H2 + Cl2
This experiment proves that hydrochloric acid contains both hydrogen and chlorine.
9.
Solution 9.
(a) Manganese dioxide
(b) Hydrogen chloride and ammonia
(c) Hydrogen and oxygen
(d) AgCl(Silver chloride)
(e) Aqua regia
(f) Fountain experiment
(g) Hydrogen chloride gas
10.
Solution 10.
(a) An aqueous solution of chlorine is acidic as it dissolves in water to form hydrochloric and hypochlorous acids.
(b) Silver nitrate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form thick curdy white ppt. of silver chloride whereas silver nitrate does not react with nitric acid.
AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3(White ppt.)
11.
Solution 11.
A is Silver nitrate
B is Hydrochloric acid
C is Silver chloride
12.Complete and balance the following reactions, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used.
(a) NH4OH + HCl 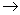
(b) NaHSO3 + HCl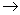
(c) Pb(NO3)2 +HCl 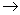
(d) Pb3O4 + HCl 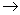
(c)
(d)
Solution 12.
13.
Solution 13.
a. Sodium carbonate on treating withdil.HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of carbon dioxide gas.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
Sodium sulphite on treating with dil.HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of sulphur dioxide gas.
Na2SO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 ↑
b. Sodiumthiosulphate reacts with dil. HCl to produce sulphur dioxide gas and precipitates yellow sulphur.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 + S↓
Sulphur is not precipitated when sulphites are treated with dil.HCl.
14.
Three tests are:
1. HCl gas gives thick white fumes of ammonium chloride when glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near the vapours of the acid.
NH3 + HCl NH4Cl
2. With silver nitrate HCl gives white precipitate of silver chloride. The precipitate is insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
AgNO3 + HCl AgCl + HNO3
3. A greenish yellow gas is liberated when concentrated hydrochloric acid is heated with oxidizing agent like manganese dioxide.
MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 +2H2O + Cl2
15.
15.
MnO2, PbO2 and red lead react with conc. HCl acid to liberate Cl2. This shows that hydrochloric acid is oxidized to chlorine by oxidizing agents.
16.
Solution 16.
HCl dissolves both in water and toluene, when HCl dissolves in water it ionizes and forms hydronium and chloride ions. Whereas this ionization is not observed in toluene hence a solution of HCl in water can be used as an electrolyte.
17.
Solution 17.
18.
Solution 18.
A mixture having three parts of conc. Hydrochloric acid and one part of conc. Nitric acid is called aqua-regia.
Nitric acid acts as oxidizing agent.
19.
Solution 19.
20.
Solution 20.
1(2004).A solution of hydrogen chloride in water is prepared. The following substances are added to separate portions of the solution:
S.No.
|
Substances added
|
Gas evolved
|
Odour
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium ribbon
Manganese(IV) oxide with heating
Sodium sulphide
|
_________
|
________
|
Complete the table by writing the gas evolved in each case and its odour.
Solution 1 (2004).
Solution 1 (2005).
(a) (i) CuO +2HCl CuCl2 + H2O
(ii) MnO2+ 4HCl MnCl2 +2H2O +Cl2
(b) (i) The experiment is called Fountain Experiment.
(ii) This experiment shows that hydrogen chloride is highly soluble in water.
(iii) Red
Solution 1 (2007).
Solution 1 (2008).
When hydrogen chloride is collected by downward delivery or upward displacement, it shows that it is heavier than air.
Solution 2 (2008).
Hydrogen chloride is not collected over water as it is soluble in water.
Solution 3 (2008).









