Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]
Exercise 12(A)1.In triangle ABC, M is mid-point of AB and a straight line through M and parallel to BC cuts AC in N. Find the lengths of AN and MN if Bc = 7 cm and Ac = 5 cm.
Solution 1:
2.Prove that the figure obtained by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of a rectangle is a rhombus.
Solution 2:
3.D, E and F are the mid-points of the sides AB, BC and CA of an isosceles
Solution 3:
4.The following figure shows atrapezium ABCD in which AB // DC. P is the mid-point of AD and PR // AB. Prove that:
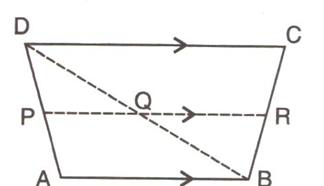
Solution 4:
5.The figure, given below, shows a trapezium ABCD. M and N are the mid-point of the non-parallel sides AD and BC respectively. Find:
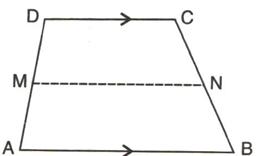
(i) MN, if AB = 11 cm and DC = 8 cm.
(ii) AB, if Dc = 20 cm and MN = 27 cm.
(iii) DC, if MN = 15 cm and AB = 23 cm.
Solution 5:
6.The diagonals of a quadrilateral intersect at right angles. Prove that the figure obtained by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of the quadrilateral is rectangle.
Solution 6:
7.L and M are the mid-point of sides AB and DC respectively of parallelogram ABCD. Prove that segments DL and BM trisect diagonal AC.
Solution 7:
8.ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC. E, F, G and H are the mid-points of AB, BD, CD and Ac respectively. Prove that EFGH is a rhombus.
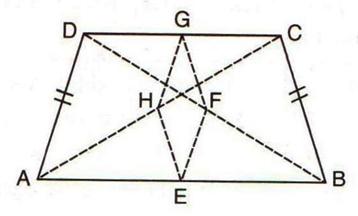
Solution 8:
9.A parallelogram ABCD has P the mid-point of Dc and Q a point of Ac such that CQ =
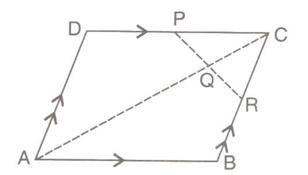
Prove that
(i)R is the midpoint of BC
(ii)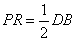
Solution 9:
10.D, E and F are the mid-points of the sides AB, BC and CA respectively of
Solution 10:
11.In triangle ABC, P is the mid-point of side BC. A line through P and parallel to CA meets AB at point Q; and a line through Q and parallel to BC meets median AP at point R. Prove that
(i)AP=2AR
(ii)BC=4QR
Solution 11:
12.In trapezium ABCD, AB is parallel to DC; P and Q are the mid-points of AD and BC respectively. BP produced meets CD produced at point E. Prove that:
(i) Point P bisects BE,
(ii) PQ is parallel to AB.
Solution 12:
13.In a triangle ABC, AD is a median and E is mid-point of median AD. A line through B and E meets AC at point F.
Prove that: AC = 3AF
Solution 13:
14.D and F are mid-points of sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC. A line through F and parallel to AB meets BC at point E.
(i) Prove that BDFE is parallelogram
(ii) Find AB, if EF = 4.8 cm.
Solution 14:
15.In triangle ABC, AD is the median and DE, drawn parallel to side BA, meets AC at point E. Show that BE is also a median.
Solution 15:
16.In ∆ABC, E is mid-point of the median AD and BE produced meets side AC at point Q. Show that BE : EQ = 3:1.
Solution 16:
17.In the given figure, M is mid-point of AB and DE, whereas N is mid-point of BC and DF. Show that: EF = AC.
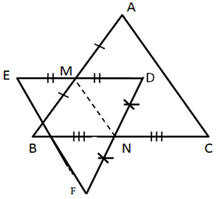
Solution 17:
Exercise 12(B)
1.Use the following figure to find:
(i) BC, if AB = 7.2 cm.
(ii) GE, if FE = 4 cm.
(iii) AE, if BD = 4.1 cm
(iv) DF, if CG = 11 cm.
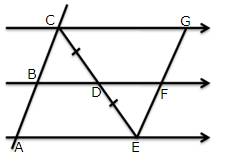
Solution 1:
2.In the figure, give below, 2AD = AB, P is mid-point of AB, Q is mid-point of DR and PR // BS. Prove that:
(i) AQ // BS
(ii) DS = 3 Rs.
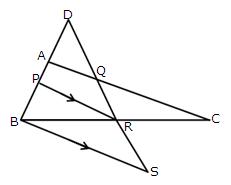
Solution 2:
3.The side AC of a triangle ABC is produced to point E so that CE =
(i) 3DF = EF(ii) 4CR = AB.
Solution 3:
4.In triangle ABC, the medians BP and CQ are produced upto points M and N respectively such that BP = PM and CQ = QN. Prove that:
(i) M, A and N are collinear.
(ii) A is the mid-point of MN.
Solution 4:
5.In triangle ABC, angle B is obtuse. D and E are mid-points of sides AB and BC respectively and F is a point on side AC such that EF is parallel to AB. Show that BEFD is a parallelogram.
Solution 5:
6.In parallelogram ABCD, E and F are mid-points of the sides AB and CD respectively. The line segments AF and BF meet the line segments ED and EC at points G and H respectively. Prove that:
(i) Triangles HEB and FHC are congruent;
(ii) GEHF is a parallelogram.
Solution 6:
7.In triangle ABC, D and E are points on side AB such that AD = DE = EB. Through D and E, lines are drawn parallel to BC which meet side AC at points F and G respectively. Through F and G, lines are drawn parallel to AB which meet side BC at points M and N respectively. Prove that: BM = MN = NC.
Solution 7:
8.In triangle ABC; M is mid-point of AB, N is mid-point of AC and D is any point in base BC. Use intercept Theorem to show that MN bisects AD.
Solution 8:
9.If the quadrilateral formed by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle, show that the diagonals AC and BD intersect at right angle.
Solution 9:
10.In triangle ABC; D and E are mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively. Through E, a straight line is drawn parallel to AB to meet BC at F. Prove that BDEF is a parallelogram. If AB = 16 cm, AC = 12 cm and BC = 18 cm, find the perimeter of the parallelogram BDEF.
Solution 10:
11.In the given figure, AD and CE are medians and DF//CE. Prove that:
_SHR_files/20141020120110_image003.jpg)
Solution 11:
12.In parallelogram ABCD, E is the mid-point of AB and AP is parallel to EC which meets DC at point O and BC produced at P.
Prove that:
(i) BP = 2AD
(ii) O is the mid-point of AP.
_SHR_files/20141020120110_image008.jpg)
Solution 12:
Given ABCD is parallelogram, so AD = BC, AB = CD.
Consider triangle APB, given EC is parallel to AP and E is midpoint of side AB. So by midpoint theorem, C has to be the midpoint of BP.
So BP = 2BC, but BC = AD as ABCD is a parallelogram.
Hence BP = 2AD
Consider triangle APB, AB || OC as ABCD is a parallelogram. So by midpoint theorem, O has to be the midpoint of AP.
Hence Proved
13.In trapezium ABCD, sides AB and DC are parallel to each other. E is mid-point of AD and F is mid-point of BC. Prove that: AB + DC = 2EF.
Solution 13:
Consider trapezium ABCD.
Given E and F are midpoints on sides AD and BC, respectively.
Consider LHS,
AB + CD = AB + CJ + JI + ID = AB + 2HF + AB + 2EG
So AB + CD = 2(AB + HF + EG) = 2(EG + GH + HF) = 2EF
AB + CD = 2EF
Hence Proved
14.In Δ ABC, AD is the median and DE is parallel to BA, where E is a point in AC. Prove that BE is also a median.
Solution 14:
Given Δ ABC
AD is the median. So D is the midpoint of side BC.
Given DE || AB. By the midpoint theorem, E has to be midpoint of AC.
So line joining the vertex and midpoint of the opposite side is always known as median. So BE is also median of Δ ABC.
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh9nNvNXfyoKUgDb2utxxqQA-y_4cQyrx54jWiOdK-LJSWVsznFe5fprpty5RvRVhhE3hfYeY0jJx_nQx-XZx3FX4-Xfq5RdkTCYOxPR9CAqcePA1YrwdUabAcyBmL1EX9vybO7DWQRk4DQ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjdzp5pU-4MIcGCR9BfRDYUsdu_5AsvKjDvXOWqVMGPw9jt0Y6Qnm3CKDh7QV8oRCWcVLeP1r3YXG5Ndw3Avm8DlFDRIIBGup8aJeDbvWcbuWZQ5CESuNAetcommk3twjr_BlyzbwZdKmSc/s640/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem1.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi_Y895pEyEXOHzxCbvgFBZNigv5Nb_CBHabPtSSa9BXb0x9WlGpJ2a-Q24nFdPnOkLmABON7HT9GfHogf7BuGnX_xI2zHMj_I6Ix928Wnt6k4zoLMhNE3nHwLV3jimWNVp72HACkwWWD1d/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem2.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjMFNf461ng-cJBfMnK1A5i_3d5tBxR7SBQst4Z6kTRJKhux4pMr0WkGYK93hHZpKeZg7zSVZankxqhbmXxPGY0poKMSq5ny5z230IWjAeTp9mCQPmkOGhZ0gkcm_nq8brubmqcTIy8vP8i/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem3.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg22hgUg8Mo2SbYNVQ8RaozUoIlxFvU_V1IOM3frhsDxGiaEtm0rUXKAKKG-cwqqgAjTI5acwcHj58ShoUbFpI_c51nUbxrqCC31o1H2QJ0FafeckOL4sAa1zEnYNbVwQz01_iy9Q60JCkP/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem4.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjXOQgTM2TtSj9ryKoi9G5pzWly5OfhUJMpLbxiPkvPFlq5TaEJYSxuYsWE24ptBHpPKoIvgdla4T5DPF0V3xRwJWLLIEA2yUfsdWLeHFWFqSjqjQE4NpRWYzY4coUFXyMGlQpiDwgxo6xB/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem5.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh_mRjAjAre88EN7557rgsiJdMinPxNMjMum_rCEsJxFDQvVQlBHFS9x4xnMmxW_W5_3amkHjsf8Z_v9KD-DX7NhPAwbpkNs6_aP16Xj-hsSaVJO5P6AmPI7Ub4WZ7CIBMc2D57GzkgznoE/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem6.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg9V_UrUe0xlSLRC-ezzs4kzMg9v_bZXT6gUlYYPFOr9ZtrxOLsyacVYuMMXtPUy28fpwX886Q7Fvr6kmgVWBkFb0RSQktv6Iq1X54t3oKNrOs81qfFJ22Y528X9BEcRNsagLFNxZHuPwwv/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem7.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjO4UT1z-DFu9quV59x-2fod3OZWqpSXu1hN3RJrv1iR2Z7dac7PIAvp15jm2-V-BQfm0tKHPVq-dGls98RBXzyvy3BfSRc114x9WRQ_Tzqd30fAt7Sexuwg91lK_dY3mP3iPZnHWC_Jc2U/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem8.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhNziS44nwNmSkCXF72Xj9lcAheDh-vcDh0QLawHRzn8NsDK2RxTSe-QSnntfKalXESPLukqBTCRi7ApmT4P12Vc70LeY2fJUBCH0mwCE_6cNpIxDe7ut7Tu0hd2uVSeXA4SlxkpX9nFt8W/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem9.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi-D06pWl0cTFTVxpcxN5_-hnnkEcVzTe6jej_mdEJlA7qi12Yi7dkuX5TMGHRo1o0RxxwUVOIwgWleAnOBsf_Xp5c-JvefjRCb8eS7VEvmXJdzUBizmwrlmoURNIi5EFDZbex36t-cW7EQ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem10.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgeRZw4-6FR1HDPxf91zoqlOfZ4UzhlnGTIfTIwq-dJ2PmAGL_b0ZjsDJswWMK53e3TV2mRzi0BaklDaUOG8alVIUuLwpXt4fn_Ibb60TY5EvSQtwybMcAzekac21UlwB3V5lW8-0XYVc0F/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem11.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgEkqsOIGyzHS8vxVXGUEFiauB5OxlHzwnWBZF9w18L-DGIIYMoFLk_-byZeOoX_jWtm0I1Xyt1vXT8NZMisiPm1LVYK5E_fHdlNMI6tFcRQTzQcNfbpLUdWRZ55wfXZQSbjYB2bkWxE-tn/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem12.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhJUIrFtvX_NBYVk-sNOUBxHYiI3Oo-F-YAZwOHcXtyVD8HZHVFb5Cx127WUN-U5eF4gviA1GYu7sx9jtxYeTw5izXZ6A1t4CetuxQgAoUb1rEXVI7pyK2T53TO64jY2TcCPLg1_TRet-h3/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem13.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi0rw2giotnATX8u8-aA09vSQfGZB5wcdq-XlMRbCQ5zeY8Jna4XOFTJjzNtiBm1Wp7LP-aoXkvdKx4hdQTGHpnolc7A9In6d4_K5nMycSn3klTFV6doTXrZHm0ZOv54dq5QTRVUvYBfsCw/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem14.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjK8wZ0KZ2OYA1jsb_t-0N2C472YkdeF3-pWSZT351pZcr-0tbG15x_bQgIE2PiwLwRUtAyX3D83l_1XFpDnJqNT_893AbEUjTxBPYOsK5trVfsMo8QO6rkudeQOkRafEx1aUMGMAaYrnb6/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem15.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgaheOJYxBKO5wkTphSMS_OFG5MxWtRMAzntHd4QKdkMp5E9T-2ZfDihIns397039I_D6ztbPVkpkB8kBxPVdOfoITIpw0PYejAgSvj5tnXbw5l3eE8tvocNdm8VkD7v4eMhleSAr_GfKpQ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem16.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgNp5r-5b5OeNvWRHrLCXYPe3LclHxnKY0q4Hpl3vtUff_TlCGZDaJE29xLsnaEIlYdutuJZae06_alDElwgn-RLjzYtZ2iyejjvMyngqJy7XOqprvBSTRpXqFViu4WpHOC7JAiZk54oxrZ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem17.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiU6z1Ta3HGPg0G5Hb6NmfMyAVhdaUX5ye_VDT7WKoRujMKEcPHqBT0EMxbVvv2mokSsvxPED0vmG6ZJyofh24nWnL6lPaDFOkJ2U7s2mZxBO2ow2HANq_C5dyC7ngsg7pyedAVi4pVIaNe/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem18.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3lSXvZQAzC93UZ8idY2jiaj37iuOUQ3U43FNi6lsjySdH7MJd2ntPlOB2GFzA3dB_WulC5opdzyGaz1b27jILJrwk54Nt_vEmL6es_DNzQe9-v_G9WqKSp9_6pw9KKM5Jxw0VqXjamYP_/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem19.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiXx1B0fpqxj-oPkzGim6jR3RjmmpmfQKKoYFEf0E0V21PpTM8QaT7Ss95Ha5cn5whPywRtPbHkTYDdPa6BaezoMhUtoCuHq0voz9m-U9Sv3OCUYulMPuaA99jPOFWBdivMIAD_retN4EmD/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem20.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgOPwA6Rg_EkomTEB5Q9IXMIt_it-at42BpmXxgH8j44CGM0BBKNEKiL5MQBffeoloDQt5X6irbXchRIBJQxgG9piN57cYTTJgOwlZt8xayiiEpTYZaJxPA7wLwinmnMgNyNJlfplOxbhp2/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem21.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhFf1MlxUoD6SL53cgsIXQ2IS1udWxpn0oYzSRNbqMmnCQJP5M79iWGpJ4GZ8IwgTRkHatBWyS0TXWEr-zFEQaXgt2hZAiKICw2RGyoPJgbZ6hSJyJh0r3F6huOHjqZLJzvt3EiXP3EiWIL/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem22.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj6zwD49z3qZV6YouujJkD3QZ95VYxOd9gkRzSgooJctYnL-hgkWToxtP3AXDGlwmpLAuXMpSGKeHQqNsoiv8_0gFuIxIQCfJzNmd6V_Pj3n7dCCIPN1L-dt7adpsaaIWHBDi1HhmCm3iTe/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem23.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjr_TQMgqU2ViDw_x7qTeFes3nCGk0L5QyRtraZXJGWNyxJWUDG6wVUjkP3BkC6NbABqhGcuerZG9rMAVZokhbbslHExkijAyzAcG5RAmOjVl11QaY7tY5YZXW7kiiphR6mduCd0x6I0hpY/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem24.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj6Vk9pv3dvGWwGBEUIZZtmN0E-2R8QPOQwZ0pmXgofyGe2Tr9WQLQLm0-o5XJRE5guT30PzZO2iTtGliSw02iwc1OeeSP3ZaWT_FM2fF51WKz0KXMMHq7F_029KIJ11vhEV-_OulBQ_CPt/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem25.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEivP6inwemkvNkzhnNzrLDZHKvRK9ilAizoPRWmRrWTiG5fKXC4G7w6E0adzrHLTusBBhisKLg-izNWxB7ZyUIc-ryxwmI1A_AYbXodlAfHS5A3LB866z9lu_MSZoh1YqVmjuHrA-kcXiVo/s640/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem26.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi2aVL7JOXv5vP4MGLz00Twwl3qMnD-SeepdHJfP-eFNrLp9jug713V25gREWo_hAprbChEr_1bDX0NKcGzzkcTqsYkzh2HOSrR-cYjkI9KYBxMQPo75IM0QMONSEEIKcL2u9k6HoYwFbD3/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem27.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhEGCpyfB5qQIZeahBDdxO5YkDtdSkKcyzLT0seacOhdlXKtscdsztxyZGuqKRnasSKxe0lQKUi27KlXVIxfUoMi5sR3QH-7KyMGhe2zNMjWWOHMxrosCXsv6MFYuQ1SngegDcRVrU3exIa/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem28.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 12 - Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEisP5eN0DbXR_nwe6clGHjcBcMVufb8kb16hyXY5HPVQbuZTJHKNyKE5NOLDwrGqaTsqcf4MTlzC2vDT6ykObX-JXwwTy1sm9IcGYnOD61WLsLR-l12sgPxuqk0EOGmlmuSBnNzi1npeat3/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-mid-point-and-its-converse-including-intercept-theorem29.jpg)
