Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Electrolysis
Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Electrolysis
Exercise Intext 1
1.Fill in the blanks:
(a) Powdered sodium chloride (common salt) does not conduct an electric current, but it does so when ____ or when _____.
(b) Molten lead bromide conducts electricity. It is called an____. It is composed of lead ____ and bromide _____. The lead ions are ____charged and are called_____. The bromide ____ are _____ charged and are called ______.
(c) Substances which conduct electricity in the solid state are generally ______.
(d) The electron releasing tendency of zinc is _____than that of copper.
(e) A solution of HCl gas in water conducts electricity because _____, but a solution of HCl gas in toluene does not conduct an electric current because_____.
(a) Powdered sodium chloride (common salt) does not conduct an electric current, but it does so when ____ or when _____.
(b) Molten lead bromide conducts electricity. It is called an____. It is composed of lead ____ and bromide _____. The lead ions are ____charged and are called_____. The bromide ____ are _____ charged and are called ______.
(c) Substances which conduct electricity in the solid state are generally ______.
(d) The electron releasing tendency of zinc is _____than that of copper.
(e) A solution of HCl gas in water conducts electricity because _____, but a solution of HCl gas in toluene does not conduct an electric current because_____.
(a) Powdered sodium chloride (common salt) does not conduct an electric current, but it does so when dissolved in water or when melted.
(b) Molten lead bromide conducts electricity .It is called an electrolyte. It is composed of lead ions and bromide ions. The lead ions are positivelycharged and are called cations. The bromide ions are negatively charged and are called anions.
(c) Substances which conduct electricity in the solid state are generally metals.
(d) The electron releasing tendency of zinc is more than that of copper.
(e) A solution of HCl gas in water conducts electricity because it ionizes, but a solution of HCl gas in toluene does not conduct an electric current because it does not ionize in toluene.
2.Define the following terms:
(a) Electrolysis
(b) Non-electrolyte
(c) Cation and an anion
(d) Weak electrolyte
(a) Electrolysis: It is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound in aqueous solutions or in molten state accompanied by a chemical change using direct electric current.
(b) Non-electrolyte: It is a compound which neither in solution nor in the molten state allows an electric current to pass through it.
(c) Cation and anion: Atoms which carry positive charge are called cations.
Atoms which carry negative charge are called anions.
(d) Weak electrolyte: Electrolytes which allow small amount of electricity to flow through them and are partially dissociated in fused or aqueous solution are called weak electrolyte.
3.What is the difference between:
(a) Modern explanation and Arrhenius explanation for the theory of electrolysis
(b) Electrolytic dissociation and ionization
(c) A cation and an anion
(d) Electrolytic dissociation and thermal dissociation
(a) Difference between Modern explanation and Arrhenius explanation for the theory of electrolysis:
Arrhenius considered that water ionizes electrolytes but Modern theory explained that electrolytes are ionic even in solid state and their ions are held by strong electrostatic forces which make them immobile. Water renders these ions mobility by breaking the electrostatic forces.
(b) Difference between electrolytic dissociation and ionization :
(c) A cation and anion:
(d) Electrolytic dissociation and thermal dissociation:
Electrolytic dissociation is the dissociation of an electrovalent compound into ions in the fused state or in aqueous solution state.
Thermal dissociation: Reversible breakdown of a chemical compound into simpler substances by heating it. The splitting of ammonium chloride into ammonia and hydrogen chloride is an example. On cooling, they recombine to form the salt.
4.Name:
(a) A salt which is a weak electrolyte
(b) A base which is a weak electrolyte
(c) An inert electrode and an active electrode
(d) A positively charged non-metallic ion
(e) The electrode at which reduction occurs
(f) A non-metallic element which is a conductor of electricity
Solution 4.
(a) Sodium carbonate
(b) NH4OH
(c) An inert electrode: graphite and Active electrode: silver
(d) H+
(e) Electrode is cathode
(f) Graphite
5.Electrolysis is a redox process. Explain.
Solution 5.
Electrolysis is a redox process. The reaction at the cathode involves reduction of cations as they gain of electrons while the reaction at anode involves oxidation of anions as they loss of electrons to become neutral.
Example: Dissociation of sodium chloride during electrolysis.
Cathode : Na+ + e– → Na (reduction)
Cl– – e– → Cl (oxidation)
Cl + Cl → Cl2
Overall reaction: 2NaCl → 2Na + Cl2
Exercise Intext 2
1.Name two substances in each case:
(a) Contain only molecules
(b) Contain only ions
(c) Contain ions as well as molecules
Solution 1.
(a) Glucose, Kerosene
(b) NaCl and NaOH
(c) CH3COOH and NH4OH
2.
Solution 2.
(a) Cane sugar is a compound which does not have ions even in solution and contains only molecules. Hence, it does not conduct electricity. On the other hand, sodium chloride solution contains free mobile ions and allows electric current to pass through it. This makes it a good conductor of electricity.
(b) Hydrochloric acid is a strong electrolyte and dissociates completely in aqueous solution. The solution contains free mobile ions which allow electric current to pass through it. Hence, hydrochloric acid is a good conductor of electricity.
(c) Hydrogen is placed lower in the electrochemical series and sodium is placed at a higher position. This is because H+ ions are discharged more easily at the cathode than Na+ during electrolysis and gains electrons more easily.
Therefore, H+ ion is reduced at the cathode and not Na+ ion.
3.(a) Among Zn and Cu, which would occur more readily in nature as metal and which as ion?
(b) Why cannot we store AgNO3 solution in copper vessel?
(c) Out of Cu and Ag, which is more active?
Solution 3.
(a) Zn occurs readily as ion whereas Cu occurs more readily as metal in nature.
(b) Copper is above silver in the electrochemical series and is thus more reactive than silver. So, copper displaces silver from silver nitrate. Hence, we cannot store AgNO3 solution in copper vessel.
Cu +AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) Copper is more active than Ag.
4.(a) How would you change a metal like Cu into ions?
(b) How would you change Cu2+ ions to Cu?
Solution 4.
(a) By treating its salt with a more reactive metal.
(b) By supplying two electrons to Cu+2
Cu+2 + 2e– → Cu
5.A solution of caustic soda (NaOH) in water or when fused, conducts an electric current. What is the similarity in these two cases?
Solution 5.
In the aqueous state, the slightly negatively charged oxygen atoms of the polar water molecule exerts a pull on the positively charged sodium ions. A similar pull is exerted by the slightly charged hydrogen atoms of the water on the negatively charged chloride ions. Thus the ions become free in solution. These free ions conduct electricity.
In the molten state, the high temperatures required to melt the solid weakens the bond between the particles and the ions are set free.
6.During electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sulphuric acid between platinum electrodes, two types of anions migrate towards the anode but only one of them is discharged.
(a) Name the two anions.
(b) Name the main product of the discharge of anion at the anode and write the anode reaction.
(c) Name the product at the cathode and write the reaction.
(d) Do you notice any change in colour. State why?
(e) Why this electrolysis is considered as an example of catalysis.
Solution 6.
(a) Two anions are
(b) OH– is discharged at anode and the main product of the discharge of OH– is O2
Reaction is :
OH– → OH + e–
4OH → 2H2O + O2
(c) The product formed at cathode is hydrogen. The reaction is :
H+ + e– → H
H + H → H2
(d) No change in colour is observed.
(e) Dilute sulphuric acid catalyse the dissociation of water molecules into ions, hence electrolysis of acidified water is considered as an example of catalysis.
7.
Solution 7.
(a) Labelled diagram of electrolytic cell is:
(b) The ions present in the cell are Cu2+, H+, SO42- , OH–.
(c) SO42- and OH– ions both migrate towards anode.
(d) Both Cu2+ and H+ ions migrate towards cathode.
(e) SO42- and H+ will not discharge at electrodes.
(f) Reaction at cathode:
Cu+2 +2e– → Cu
(g) Reaction at anode:
OH– – e– → OH
2OH + 2OH → 2H2O + O2
(h) Sulphate ions are the spectator ions because they do not change in the reaction.
8.
Solution 8.
(a) Reaction at anode during the electrolysis ofvery dilute sulphuric acid:
OH– → OH + e–
4OH → 2H2O + O2
(b) Reaction at anode during the electrolysis of aqueous copper sulphate solution
4OH– → 4OH + 4e–
4OH → 2H2O + O2
(c) Reaction at anode during the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
(d) Reaction at anode during the electrolysis of fused lead bromide
Br– – e– → Br
Br + Br → Br2
(e) Reaction at anode during the electrolysis of magnesium chloride (molten)
2Cl– → Cl2 +2e–
(f) Concentrated HCl,
HCl in the pure liquid state is unionised and hence does not conduct electricity.
(g) Very dilute HCl,
Cl– – e– → Cl
Cl + Cl → Cl2
9.Choosing only words from the following list, write down the appropriate words to fill in the blanks (i) to (v) below: Anions , anode, cathode, cations , electrode, electrolyte, nickel , voltameter.
The electroplating of an article with nickel requires an (i) ____ which must be solution containing (ii) ____ ions. The article to be plated is placed as the (iii) ____ of the cell in which the plating is carried out. The (iv) ____ of the cell is made from pure nickel. The ions that are attracted to the negative electrode and discharged are called (v) _____.
Solution 9.
(a) Electrolyte
(b) Nickel
(c) Cathode
(d) Anode
(e) Cations
Exercise 1
1.Give reasons for the following:
(a) Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be a reaction in which oxidation and reduction go side by side i.e, a redox reaction.
(b) The blue colour of aqueous copper sulphate fades when it is electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.
(c) Lead bromide undergoes electrolytic dissociation in the molten state but is a non-electrolyte in the solid state.
(d) Aluminium is extracted from its oxide by electrolytic reduction and not by conventional reducing agents.
(e) The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen formed at the cathode and anode is 2:1 by volume.
(f) In the electrolysis of acidified water, dilute sulphuric acid is preferred to dilute nitric acid for acidification.
(g) Ammonia is unionized in the gaseous state but in the aqueous solution, it is a weak electrolyte.
(h) A graphite anode is preferred to other inert electrode during electrolysis of fused lead bromide.
(i) For electroplating with silver, silver nitrate is not used as electrolyte.
(j) Carbon tetrachloride is a liquid but does not conduct electricity.
Solution 1.
(a) During electrolysis of lead bromide, there is loss of electrons at anode by bromine and gain of electrons at cathode by lead. Thus oxidation and reduction go side by side. Therefore, it is a redox reaction.
PbBr2 → Pb+2 + 2Br–
(b) The blue colour of copper ions fades due to decrease in Cu+2 ions and finally the solution becomes colourless as soon as Cu+2 ions are finished.
(c) Lead bromide dissociate into ions in the molten state whereas it does not dissociate in solid state. The ions become free when lead bromide is in molten state but in the solid state the ions are not free since they are packed tightly together due to electrostatic force between them. Therefore, lead bromide undergoes electrolytic dissociation in the molten state.
(d) Aluminium has great affinity towards oxygen, so it is not reduced by reducing agent. Therefore it is extracted from its oxide by electrolytic reduction.
(e) As per electrolytic reactions, 4H+1 are needed at cathode and 4OH– at the anode and two molecules of water are produced at the anode. Hence for every two molecules of water, two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen are liberated at the cathode and anode respectively.
(f) This is because HNO3 is volatile.
(g) Ammonia is a covalent compound. Therefore, it is unionized in the gaseous state but in the aqueous solution it gives NH4OH which is a weak electrolyte and dissociates into ions.
(h) Graphite is unaffected by the bromine vapours.
(i) Silver nitrate is not used as electrolyte for electroplating with silver because the deposition of silver will be very fast and hence not very smooth and uniform.
(j) Carbon tetrachloride is a liquid and does not conduct electricity because it is a covalent compound and there are no free ions present and contain only molecules.
2.Classify the following substances under three headings:
a. strong electrolytes
b. weak electrolytes
c. non-electrolytes
Acetic acid, ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide, carbon tetrachloride, dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium acetate, dilute sulphuric acid.
(a) Strong electrolyte : Dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulphuric acid, ammonium chloride, sodium acetate
(b) Weak electrolyte: Acetic acid, ammonium hydroxide
(c) Non-electrolyte: Carbon tetrachloride
3.
Solution 3.
(a) Molecules
(b) Will not
4.
Solution 4.
Water is a non-conductor of electricity and consists entirely of molecules. It can be electrolytically decomposed by addition of traces of dilutesulphuric acid which dissociate as H+ and SO42- ions and help in dissociating water into H+ and OH–, water being a polar solvent.
5.Copy and complete the following table which refers to two practical applications of electrolysis
Anode
|
Electrolyte
|
Cathode
| ||
Silver plating of spoon
|
Solution of potassium argentocyanide
| |||
Purification of copper
| ||||
Solution 5.
6.
Solution 6.
Electricity, Chemical
7.(a) Draw a labeled diagram to show how iron is electroplated with copper.
(b) Which solution is preferred as electrolyte, CuSO4 or FeSO4?
(c) Describe what happens to the iron object and the copper rod.
Solution 7.
(a)
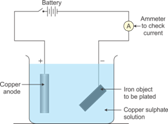
(b) CuSO4 is preferred as an electrolyte.
(c) The copper anode continuously dissolves as ions in solution and is replaced periodically. The electrolyte dissociates into Cu+2 ions which migrate towards the iron object taken as the cathode and are deposited as neutral copper atoms on the cathode.
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of nickel sulphateDissociation: CuSO4 → Cu2+ + SO42-
H2O → H+ + OH–
Electrodes:
Cathode: Article to be electroplated
Anode: Block of pure copper
Electrode reactions:
Reaction at cathode: Cu2+ + 2e–→ Cu (deposited)
Reaction at anode: Cu – 2e–→ Cu2+
1(2004).Element X is a metal with a valency 2. Element Y is a non-metal with a valency 3.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions?
(b) If Y is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
(c) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the _____ and Y at the _________of the electrolytic cell.(Provide the missing words)
Solution 1 (2004).
(a) X → X2+ + 2e– , Y + 3e– → Y3-
(b) Y2 + 3X → X3Y2
(c) Cathode, Anode
1(2005).
Solution 1 (2005).
(a) Because Copper is an electronic conductor as it is a metal.
(b) In solid sodium chloride, Na+ and Cl – ions are not free due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction among them. The ions, therefore are unable to move to any large extent when electric field is affected. Hence no current.
1(2006).
Solution 1 (2006).
(a) (i) The name of electrode A is Platinum anode and that of electrode B is platinum or copper cathode.
(ii) Anode act as oxidizing electrode.
(b) AgNO3 solution will turn blue.
1(2007).
Solution 1 (2007).
(i) Molten ionic compound: Strong electrolytes
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride: Non-electrolyte
(iii) An aluminium wire: Metallic conductor
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by dissociation of solute molecules: Weak electrolyte
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules: Non- electrolyte
1(2008).(a) Here is an electrode reaction :
Cu Selina Solutions Icse Class 10 Chemistry Chapter - ElectrolysisCu+2 +2e-
At which electrode (anode or cathode) would such a reaction take place? Is this an example of oxidation or reduction?
(b) A solution contains magnesium ions (Mg+2), iron (II) ions (Fe+2) and copper ions (Cu+2).On passing an electric current through this solution, which ions will be first to be discharged at the cathode? Write the equation for the cathode reaction.
(c) Why is carbon tetrachloride, which is a liquid a non-electrolyte?
Solution 1 (2008).
(a) The reaction takes place at anode. This is an example of oxidation.
(b) Cu+2 will discharge easily at cathode.
Reaction at cathode:
Cu+2 +2e– → Cu
(c) Carbon tetrachloride is a non-electrolyte because it is a covalent compound. It does not ionize and hence do not conduct electricity.
2(2004).
Solution 2 (2004).
(a) Non-electrolyte contains molecules.
(b) Molecules of HX and H+ and X– ions.
(c) Loss
(d) The electrolyte used for the purpose must contain the ions of metal which is to be electroplated on the article.
(e) The reaction at the cathode involves reduction of cations as they gain electrons to become neutral atoms while that at anode involves oxidation of anions as they lose electrons to become neutral.
Example: Dissociation of sodium chloride during electrolysis.NaCl → Na+ + Cl–
At cathode: Na+ + e– Na (Reduction)
At anode: Cl– – e– → Cl(oxidation)
Cl + Cl → Cl2
Overall reaction: 2NaCl → 2Na + Cl2
2(2005).
Solution 2 (2005).
Hydrogen gas is released at cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
2(2008).During electrolysis of molten lead bromide, graphite anode is preferred to other electrodes. Give reason.
Solution 2 (2008).
During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide. Lead is deposited at cathode.





