Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions The Reproductive System
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions The Reproductive System
Exercise 10.1
A.1. Which one of the following is the correct route that a sperm follows when it leaves the testis of a mammal?
(a) Vas deferens epididymis
epididymis  urethra
urethra
(b) Urethra epididymis
epididymis  vas deferens
vas deferens
(c) Epididymis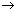 urethra
urethra 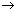 vas deferens
vas deferens
(d) Epididymis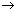 vas deferens
vas deferens 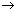 urethra
urethra
(a) Vas deferens
(b) Urethra
(c) Epididymis
(d) Epididymis
(d) Epididymis → vas deferens → urethra
A.2.When pregnancy does not occur, the life of corpus luteum is about:-
(a) 4 days
(b) 10 days
(c) 14 days
(d) 28 days
Solution A.2.
(d) 28 days
A.3.In female, after how much time after fertilization, does the fertilized egg get implanted in the uterine wall?
(a) Few months
(b) One month
(c) Three weeks
(d) About seven days
Solution A.3.
(d) About seven days
B.1.Name the following:
(a) The body part in which the testes are present in a human male.
(b) The part where the sperms are produced in the testes.
(c) The fully developed part of the ovary containing a mature egg.
(d) The accessory gland in human males whose secretion activates the sperms.
(e) The tubular knot fitting like a cap on the upper side of the testis.
Solution B.1.
(a) Scrotum
(b) Seminiferous Tubules
(c) GraafianFollicle
(d) Seminal vesicle
(e) Epididymis
B.2.Choose the odd one in each of the following:
(a) Oestrogen; progesterone; testosterone; prolactin.
(b) Ovary; fallopian tube; ureter; uterus.
(c) Seminiferous tubule; ovum; epididymis; sperm duct; urethra.
(d) Sperm; implantation; fertilization; ovum; after birth.
Solution B.2.
(a) Testosterone
(b) Ureter
(c) Ovum
(d) After birth
B.3.Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence.
(a) Sperm duct, penis, testes, sperms, semen.
(b) Puberty, menopause, menstrual, menarche, reproductive age.
(c) Graafian follicle, Ostium, Uterus, Fallopian tube.
Solution B.3.
(a) Testes → Sperms → Sperm duct → Semen → Penis
(b) Menarche Puberty → Reproductive age → Menstruals → Menopause
(c) Graafian follicle → Ostium → Fallopian tube → Uterus
B.4.
Solution B.4.
Seminiferous tubule → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Penis
C.1.What is semen?
Solution C.1.
Semen is the mixture of sperms and secretions from seminal vesicles, prostate gland and Cowper’s (bulbo-urethral gland).
C.2.Describe the functions of the following:
(a) Inguinal canal
(b) Prostate gland
(c) Testis
(d) Ovary
(e) Oviduct
Solution C.2.
(a) Inguinal canal: It is the canal which allows the descent of testes along with their ducts, blood vessels and nerves into the abdomen.
(b) Prostate gland: It is a bilobed structure which surrounds the urethra and pours an alkaline secretion into the semen.
(c) Testis: Testis is a male reproductive organ. There a pair of testes present in a scrotal sac descended outside the body cavity. Testes produce sperms which are the male gametes.
(d) Ovary: Ovary is a female reproductive organ.It produces ova i.e. female gametes.
(e) Oviduct: A pair of oviduct is present on either side of the uterus. Oviduct carries the released ovum from the ovary to the uterus.
C.3.What are the secondary sexual characters in the human male and female respectively?
C.3.What are the secondary sexual characters in the human male and female respectively?
Secondary sexual characters in males:
- Beard and moustache
- Stronger muscular built
- Deeper voice
Secondary sexual characters in females:
- Breasts in females
- Large hips
- High pitched voice
C.4.What are the accessory reproductive organs?
Solution C.4.
The accessory reproductive organs include all those structures which help in the transfer and meeting of two kinds of sex cells leading to fertilization and growth and development of egg up to the birth of the baby.
For example: uterus in females, penis in males.
C.5.Differentiate between the primary and accessory reproductive organs.
Solution C.5.
C.6.What is Hymen?
Solution C.6.
Hymen is a thin membrane which partially covers the opening of the vagina in young females.
C.7.Define the following terms:
(a) Hernia
(b) Ovulation
(c) Puberty
Solution C.7.
(a) Hernia: It is an abnormal condition which is caused when the intestine due to the pressure in abdomen bulges into the scrotum through the inguinal canal.
(b) Ovulation: It is the release of the mature ovum by the rupture of the Graafian follicle.
(c) Puberty: It is the period during which immature reproductive system in boys and girls matures and becomes capable of reproduction.
C.8.List any two changes each in human male and female, which occur during puberty.
Changes in human male:
- Development of Beard and moustache
- Voice becomes deeper
Changes in human female:
- Development of Breasts in females
- Development of high pitched voice
(a) Menarche and menopause
(b) Cowper's gland and prostate gland
(c) Hymen and clitoris
(d) Uterus and vagina
(e) Efferent duct and sperm duct
Solution C.9.
(a) Menarche is the onset of menstruation in young females at about 13 years of age whereas menopause is the permanent stoppage of menstruation at about 45 years of age.
(b) Cowper’s gland opens into urethra in human males and its secretion serves as a lubricant whereas the prostate gland surrounds the urethra in males and its alkaline secretion neutralizes acid in female’s vagina.
(c) Hymen is a thin membrane that partially covers the opening of vagina in young females whereas clitoris is a small erectile structure located in the uppermost angle of vulva in front of the urethral opening.
(d) Uterus is a hollow, pear shaped muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity. It is the site of implantation for the embryo after fertilisation whereas the vagina is the muscular tube extending from the cervix to the outside. At the time of sexual intercourse, the vagina receives the male penis and provides entry for the sperms.
(e) Efferent ducts join to form the epididymis whereas the epididymis is continued by the side of the testes to give rise to the sperm duct or vas deferens.
D.1.What is the significance of the testes being located in the scrotal sacs outside the abdomen? Can there be any abnormal situation regarding their location? If so, what is that and what is the harm caused due to it?
Solution D.1.
- Testes are responsible for the production of male gametes i.e. sperms. The normal body temperature does not allow the maturation of the sperms. Being suspended outside the body cavity, the temperature in the scrotal sac is 2 to 3oC which is the suitable temperature for the maturation of the sperms.
- When it is too hot, the skin of the scrotum loosens so that the testes hang down away from the body. When it is too cold, the skin contracts in a folded manner and draws the testes closer to the body for warmth.
- In an abnormal condition, in the embryonic stage, the testes do not descend into the scrotum. It can lead to sterility or incapability to produce sperms.
Solution D.2.
Testosterone is the male reproductive hormone produced by the interstitial cells or the Leydig cells. These cells are located in the testes. They serve as a packing tissue between the coils of the seminiferous tubules. Therefore, it can be said that the testes produce the male hormone testosterone.
D.3.Suppose a normal woman has never borne a child. How many mature eggs would she have produced in her lifetime? Your calculation should be based on two clues:-
(a) Eggs are produced at the rate of 1 egg every 28 days (one menstrual cycle)
(b) A woman's total reproductive period is 13-45 years.
Solution D.3.
otal reproductive period = 45 – 13 = 32 years
Total eggs produced = 32 x 12 = 384 eggs approximately
E.1.Given below is a diagram of two systems together in the human body.
(a) Name the systems.
(b) Name the parts numbered 1-10.
(c) Describe the functions of the parts 3, 4, 5 and 6.
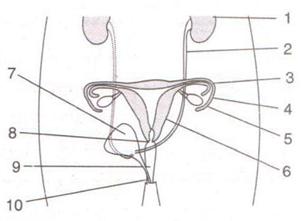
Solution E.1.
(a) Excretory system and Female Reproductive system
(b)
- Kidney
- Ureter
- Fallopian Tube
- Infundibulum
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Urinary Bladder
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Vulva
(c)
- Function of Fallopian Tube (part 3): The fallopian tubes carry the ovum released from the ovary to the uterus.
- Function of Infundibulum (part 4): Infundibulum is the funnel shaped distal end of the ovary which picks up the released ovum and pushes it further on its passage into the fallopian tube.
- Function of Ovary (part 5): Ovary produces female gametes i.e. ova.
- Function of Uterus (part 6): Uterus allows the growth and development of the embryo.
E.2.The following diagram represents the vertical sectional view of the human female reproductive system.
(a) Label the parts indicated by the guidelines 1 to 8.
(b) How does the uterus prepare for the reception of zygote?
(c) What happens to the uterus, if fertilization fails to take place?

(a)
1. Fallopian Tube
2. Infundibulum
3. Ureter
4. Vagina
5. Ovary
6. Uterus
7. Urinary Bladder
8. Urethra
(b) Oestrogen secreted by the corpus luteum secrets oestrogen. Oestrogen stimulates the thickening of the endometrial wall of the uterus. The uterine wall becomes thickened and is supplied with a lot of blood to receive the fertilized egg.
(c) If fertilization fails to take place, the endometrial lining of the uterus starts shedding on the 28th day of the menstrual cycle. Finally it is discharged out along with the unfertilised ovum as the menstrual flow.
E.3.Given below is the schematic diagram of the sectional view of the human male reproductive system.
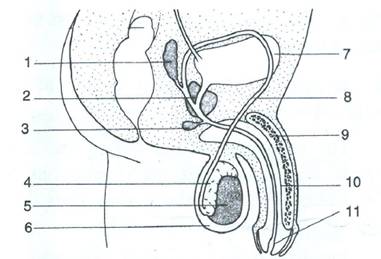
a. Name the parts numbered 1-11.
b. State the functions of the parts numbered 1, 2, 3, 5, 8 and 11.
Solution E.3.
a.
1. Seminal vesicles
2. Prostate gland
3. Bulbo-urethral gland
4. Epididymis
5. Testis
6. Scrotum
7. Urinary bladder
8. Vas deferens
9. Erectile tissue
10. Penis
11. Urethra
b. Functions of
1. Seminal vesicles
They produce the fluid which serves as the transporting medium for sperms.
2. Prostate gland
It produces an alkaline secretion which mixes with the semen and helps neutralise the vaginal acids.
3. Bulbo-urethral gland
It produces a secretion which serves as a lubricant for the semen to pass through the urethra.
4. Testis
It produces the male gamete sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone.
5. Vas deferens
They carry the sperms from the epididymis to the urethra.
6. Urethra
It serves as an outlet for delivering the sperms into the vagina.
Exercise 10.2
A.1.In humans, the fertilization takes place in
(a) Uterus
(b) Oviduct funnel
(c) Fallopian tube
(d) vagina
Solution A.1.
(c) fallopian tube
A.2.The middle piece of sperm provides:
(a) energy
(b) food
(c) gene
(d) chromosomes
Solution A.2.
(a) energy
A.3.The normal gestation period in humans is:
(a) 270 days
(b) 290 days
(c) 280 days
(d) 295 days
Solution A.3.
(c) 280 days
B.1.Name the following:
(a) The fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
(b) The body part in which the embryo develops.
(c) The membrane which protects the foetus and encloses a fluid.
(d) The canal through which the testes descend into the scrotum just before birth in human male child.
Solution B.1.
(a) Amniotic fluid
(b) Uterus
(c) Amniotic membrane
(d) Inguinal canal
B.2.Choose the odd one in each of the following:
(a) Sperm; implantation; fertilization; ovum; afterbirth
(b) Relaxin; cervix dilates; amniotic sac ruptures; child birth; follicle
Solution B.2.
(a) Sperm
(b) Follicle
B.3.Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence.
(a) Implantation, ovulation, child birth, gestation, fertilization.
(b) Coitus, ovum, sperm, sperm duct, urethra, vagina.
Solution B.3.
(a) Ovulation → fertilization → implantation → gestation → child birth
(b) Sperm → sperm duct → urethra → coitus → vagina → ovum
B.4.Give appropriate terms for each of the following:
(a) The onset of reproductive phase in a female.
(b) Rupture of follicle and release of ovum from the ovary.
(c) Monthly discharge of blood and disintegrated tissues in human female.
(d) Process of fusion of ovum and sperm.
(e) Fixing of developing zygote (blastocyst) on the uterine wall.
Solution B.4.
(a) Menarche
(b) Ovulation
(c) Menstruation
(d) Fertilization
(e) Implantation
B.5.Match the items in column I with those in column II and write down the matching pairs (some may not match)
Column I
|
Column II
|
(a) Acrosome
|
(i) An embryo which looks like human baby
|
(b) Gestation
|
(ii) Luteinizing hormone
|
(c) Menopause
|
(iii) Ovum producing cells
|
(d) Foetus
|
(iv) Semen
|
(e) Oogenesis
|
(v) Spermatozoa
|
(f) Ovulation
|
(vi) Complete stoppage of menstrual cycle
|
(vii) Time taken by a fertilized egg till the delivery of baby
|
Solution B.5.
C.1.(a) State whether the following statements are TRUE (T) or FALSE (F):
(i) Fertilization occurs in vagina. (T/F)
(ii) Uterus is also known as birth canal. (T/F)
(iii) Nutrition and oxygen diffuse from the mother's blood into the foetus's blood through amnion. (T/F)
(iv) Gestation period in humans is about 380 days. (T/F)
(b) Rewrite any two of the wrong statements by correcting only one word either at the beginning or at the end of the sentence.
Solution C.1.
(a)
- False
- False
- False
- False
(b)
- Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube.
- Vagina is also known as the birth canal.
- Nutrition and oxygen diffuse from the mother’s blood into the foetus’s blood through placenta.
- Gestation period in humans is about 280 days.
C.2.Complete the following table by writing the name of the structure or the function of the given structure:
Structure
|
Function
|
1. corpus luteum
|
1.-----
|
2. -----
|
2. produces male gametes in mass
|
3. placental disc
|
3. -----
|
4. -----
|
4. increases the force in uterine contractions
|
5. umbilical cord
|
5. -----
|
6. fallopian tube
|
6.-----
|
Solution C.2.
C.3.Given below are the names of certain stages/substances related to reproduction and found in human body.
(a) Foetus
Where is it contained?
How does it differ from embryo?
(b) Hyaluronidase
Is it an enzyme or simply a protein?
What is its function?
(c) Morula
What is this stage?
Name the stage which comes next to it.
(d) Amniotic fluid
Where is it found?
What are its functions?
(e) Placenta
What are the two sources that form placenta?
Name any two main substances which pass from foetus to mother through placenta.
Name any two hormones it produces.
(f) Implantation
The development stage that undergoes this process.
The approximate time after fertilization, when it occurs.
Solution C.3.
(a) Foetus:
- It is contained in the uterus.
- In foetus, limbs have appeared and resembles the humans unlike the embryo which is a growing or dividing zygote.
(b) Hyaluronidase:
- Enzyme
- It is an enzyme secreted by the sperm that allows the sperm to penetrate the egg.
(c) Morula:
It is the stage in the development of human embryo which consists of a spherical mass of cells. Blastocys.
(d) Amniotic fluid:
- Between amnion and embryo
- It protects the embryo from physical damage, keeps the pressure all around embryo and prevents sticking of foetus to amnion.
(e) Placenta:
- Placenta is formed by two sets of minute finger like processes called the villi. One set of villi is from the uterine wall and the other set is from the allantois.
- Oxygen and amino acids.
- Progesterone and oestrogen.
(f) Implantation:
- Blastocyst
- It occurs in about 5-7 days after ovulation.
D.1.Differentiate between:
(a) Semen and sperm
(b) Implantation and pregnancy
(c) Follicle and corpus luteum
(d) Amnion and allantois
(e) Prostate gland and Cowper's gland (the nature of secretion)
(f) Identical twins and fraternal twins
Solution D.1.
(a) Sperm is the male gamete produced by the testes. Semen on the other hand is the mixture of sperms and alkaline secretions from the seminal vesicle, prostate gland and Cowper’s gland.
(b) Implantation is the fixing of embryo in the wall of uterus. The state that implantation produces is known as pregnancy.
(c) Follicle is the cellular sac containing a maturing egg. Corpus luteum on the other hand is the remnant of the follicle the release of ovum during ovulation.
(d) Amnion is a sac which develops around the embryo whereas allantois is an extension from the embryo which forms villi of placenta.
(e) Sterility is the incapability to produce sperms whereas impotency is the inability to copulate.
(f) Prostate gland pours alkaline secretions into the semen to neutralize the acid in female’s vagina whereas the secretion of Cowper’s gland serves as a lubricant.
(g) Identical twins are produced from one ovum i.e. one developing zygote splits and grows into two foetuses whereas fraternal twins are produced when two ova get fertilized at a time.
D.2.Name and describe very briefly, the stages in the development of human embryo.
Solution D.2.
- After fertilization zygote is formed inside the fallopian tube.
- The zygote then divides repeatedly to form a spherical mass of cells known as ‘Morula’.
- The morula then develops into a hollow sphere of cells with a surrounding cellular layer and an inner cell mass projecting from it centrally. This stage is known as the ‘blastocyst’. It implants itself into the uterine wall.
- From the blastocyst arises an embryo which is around 3 weeks old. It is a tiny organism that hardly resembles human being.
- By the end of 5 weeks, the embryo is with a develoed heart and blood vessels.
- By the end of 8 weeks, limbs are developed. This stage is known as ‘foetus’.
- At the end of nearly 40 weeks i.e. end of gestation period, the infant is born.
(a) Amnion
(b) Placenta
Solution D.3.
(a) Amnion:
- Amnion contains the amniotic fluid which surrounds the embryo.
- This fluid protects the embryo from physical damage.
- It maintains even pressure all around the embryo.
- It also prevents sticking of foetus to amnion.
(b) Placenta:
- The placenta allows the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients such as glucose, vitamins and amino acids from mother to foetus.
- Similarly, it also allows the diffusion of carbon dioxide, urea and waste products from foetus to mother.
- Placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue. It secretes oestrogen and progesterone.
E.1.The diagram below represents two reproductive cells A and B. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
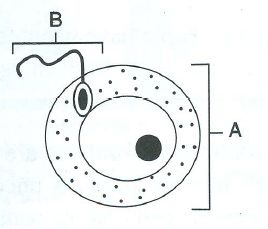
a. Identify the reproductive cells A and B
b. Name the specific part of the reproductive system where the above cells are produced.
c. Where in the female reproductive system do these cells unite?
d. Name the main hormone secreted by the (1) ovary (2) testes.
e. Name an accessory gland found in the male reproductive system and state its secretion.
Solution E.1.
a. A – ovum
B – sperm
b. Sperms are produced in the testis.
The ovum is produced in the ovary.
c. The reproductive cells unite in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system.
d. Ovary – Oestrogen and progesterone
Testis – Testosterone
e. Accessory glands:
• Seminal vesicle – Seminal fluid
• Prostate gland – Alkaline secretion
• Bulbo-urethral gland – Lubricant
E.2.The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus in the womb. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the parts '1' to '5' indicated by guidelines.
(b) What term is given to the period of development of the foetus in the womb?
(c) How many days does the foetus take to be fully developed?
(d) Mention two functions of the parts labelled '2' other than its endocrine functions.
(e) Name (any one) hormone produced by the part labelled '2'.

Solution E.2.
(a)
1. umbilical cord,
2. placenta,
3. amnion,
4. mouth of uterus,
5. muscular wall of uterus
(b) Gestation
(c) 280 days
(d) Placenta provides the foetus with oxygen and nutrients. In addition, the placenta also removes carbon dioxide and waste products of the foetus.
(e) Progesterone
E.3.Given below is a portion of the diagram to show the diagrammatic highly magnified view of a single human sperm. Complete the diagram to show its internal structure.

Solution E.3.
E.4.The figure given below represents the female reproductive system of a mammal.
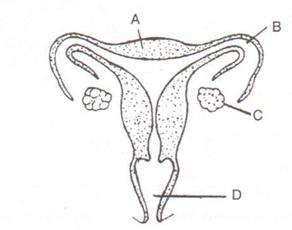
(a) Name the parts labeled A-D.
(b) What will happen if the part B on both sides gets blocked?
(a) A – Muscular wall of uterus,
B – Oviduct,
C – Ovary,
D – Cervix
(b) If part B will get blocked, ovum released from the ovary will not get fertilized by the sperm and hence pregnancy will be prevented.
E.5.
Solution E.5.
- Prostate gland
- Bulbo-urethral gland
- Urethra
- Vas deferens
- Testis




