Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 21 Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]
Exercise 21(A)1.
Solution 1:
Therefore, the length, breadth and height of rectangular solid are
2.The volume of a cube is 729 cm3. Find its total surface area.
Solution 2:
3.The dimensions of a Cinema Hall are 100 m, 60 m and 15 m. How many persons can sit in the hall, if each requires 150 m3 of air?
Solution 3:
4.75 persons can sleep in a room 25 m by 9.6 m. If each persons requires 16 m3 of air; find the height of the room.
Solution 4:
5.The edges of three cubes of metal are 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm. They are melted and formed into a single cube. Find the edge of the new cube.
Solution 5:
6.Three cubes, whose edges are x cm, 8 cm and 10 cm respectively, are melted and recasted into a single cube of edge 12 cm. Find 'x'.
Solution 6:
7.Three equal cubes are placed adjacently in a row. Find the ratio of the total surfaced area of the resulting cuboid to that of the sum of the total surface areas of the three cubes.
Solution 7:
8.The cost of papering the four walls of a room at 75 paisa per square meter Rs. 240. The height of the room is 5 metres. Find the length and the breadth of the room, if they are in the ratio 5 : 3.
Solution 8:
9.The area of a playground is 3650 m2. Find the cost of covering it with gravel 1.2 cm deep, if the gravel costs Rs. 6.40 per cubic metre.
Solution 9:
The area of the playground is 3650 m2 and the gravels are 1.2 cm deep. Therefore the total volume to be covered will be:
3650 x 0.012 =43.8 m3.
Since the cost of per cubic meter is Rs. 6.40, therefore the total cost will be:
43.8 x Rs.6.40 = Rs.280.32
10.A square plate of side 'x' cm is 8 mm thick. If its volume is 2880 cm3; find the value of x.
Solution 10:
11.The external dimensions of a closed wooden box are 27 cm, 19 cm and 11 cm. If the thickness of the wood in the box is 1.5 cm; find:
(i) Volume of the wood in the box;
(ii) The cost of the box, if wood costs Rs. 1.20 per cm3;
(iii) Number of 4 cm cubes that could be placed into the box.
Solution 11:
12.A tank 20 m long, 12 m wide and 8 m deep is to be made of iron sheet. If it is open at the top. Determine the cost of iron-sheet, at the rate of Rs. 12.50 per metre, if the sheet is 2.5 m wide.
Solution 12:
13.A closed rectangular box is made of wood of 1.5 cm thickness. The exterior length and breadth are respectively 78 cm and 19 cm, and the capacity of the box is 15 cubic decimeters. Calculate the exterior height of the box.
Solution 13:
Let exterior height is h cm. Then interior dimensions are 78-3=75, 19-3=16 and h-3 (subtract two thicknesses of wood). Interior volume = 75 x 16 x (h-3) which must = 15 cu dm
14.The square on the diagonal of a cube has an area of 1875 sq. cm. Calculate:
(i) The side of the cube.
(ii) The total surface area of the cube.
Solution 14:
15.A hollow square-shaped tube open at both ends is made of iron. The internal square is of 5 cm side and the length of the tube is 8 cm. There are 192 cm3 of iron in this tube. Find its thickness.
Solution 15:
16.Four identical cubes are joined end to end to form a cuboid. If the total surface area of the resulting cuoid as 648 m2; find the length of edge of each cube.
Also, find the ratio between the surface area of resulting cuboid and the surface area of a cube.
Solution 16:
Exercise 21(B)
1.The following figure shows a solid of uniform cross-section. Find the volume of the solid. All measurements are in centimetres.
Assume that all angles in the figures are right angles.
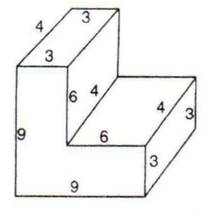
Solution 1:
The given figure can be divided into two cuboids of dimensions 6 cm, 4 cm, 3 cm, and 9 cm respectively. Hence, volume of solid
2.A swimming pool is 40 m long and 15 m wide. Its shallow and deep ends are 1.5 m and 3 m deep respectively. If the bottom of the pool slopes uniformly, find the amount of water in litres required to fill the pool.
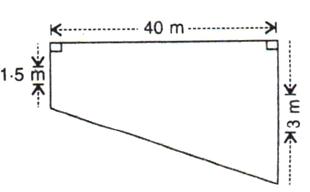
Solution 2:
3.The cross-section of a tunnel perpendicular to its length is a trapezium ABCD as shown in the following figure; also given that:
AM = BN; AB = 7 m; CD = 5 m. The height of the tunnel is 2.4 m. The tunnel is 40 m long. Calculate:
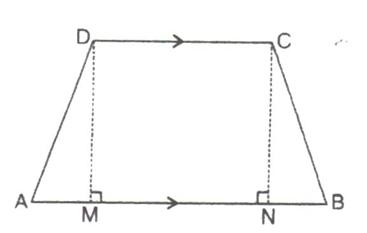
(i) The cost of painting the internal surface of the tunnel (excluding the floor) at the rate of Rs. 5 per m2 (sq. metre).
(ii) The cost of paving the floor at the rate of Rs. 18 per m2.
Solution 3:
The cross section of a tunnel is of the trapezium shaped ABCD in which AB = 7m, CD = 5m and AM = BN. The height is 2.4 m and its length is 40m.
4.Water is discharged from a pipe of cross-section area 3.2 cm2 at the speed of 5m/s. Calculate the volume of water discharged:
(i) In cm3 per sec.
(ii) In litres per minute.
Solution 4:
5.A hose-pipe of cross-section area 2 cm2 delivers 1500 litres of water in 5 minutes. What is the speed of water in m/s through the pipe?
Solution 5:
6.The cross-section of a piece of metal 4 m in length is shown below. Calculate:
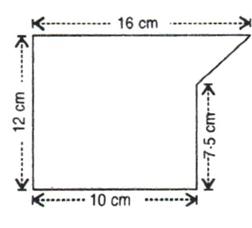
(i) The area of the cross-section;
(ii) The volume of the piece of metal in cubic centimetres.
If 1 cubic centimetre of the metal weighs 6.6 g, calculate the weight of the piece of metal to the nearest kg.
Solution 6:
7.A rectangular water-tank measuring 80 cm 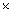 60 cm
60 cm 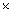 60 cm is filled form a pipe of cross-sectional area 1.5 cm2, the water emerging at 3.2 m/s. How long does it take to fill the tank?
60 cm is filled form a pipe of cross-sectional area 1.5 cm2, the water emerging at 3.2 m/s. How long does it take to fill the tank?
Solution 7:
8.A rectangular card-board sheet has length 32 cm and breadth 26 cm.Squares each of side 3 cm, are cut from the corners of the sheet and the sides are folded to make a rectangular container. Find the capacity of the container formed.
Solution 8:
9.A swimming pool is 18 m long and 8 m wide. Its deep and shallow ends are 2 m and 1.2 m respectively. Find the capacity of the pool, assuming that the bottom of the pool slopes uniformly.
Solution 9:
10.The following figure shows a closed victory-stand whose dimensions are given in cm.
_SHR_files/20141014183308_image002.jpg)
Find the volume and the surface are of the victory stand.
Solution 10:
Exercise 21(C)
1.Each face of a cube has perimeter equal to 32 cm. Find its surface area and its volume.
Solution 1:
2.A school auditorium is 40 m long, 30 m broad and 12 m high. If each student requires 1.2 m2 of the floor area; find the maximum number of students that can be accommodated in this auditorium. Also, find the volume of air available in the auditorium, for each student.
Solution 2:
3.The internal dimensions of a rectangular box are 12 cm 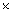 x cm
x cm 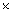 9 cm. If the length of the longest rod that can be placed in this box is 17 cm; find x.
9 cm. If the length of the longest rod that can be placed in this box is 17 cm; find x.
4.The internal length, breadth and height of a box are 30 cm, 24 cm, and 15 cm. Find the largest number of cubes which can be placed inside this box if the edge of each cube is
(i) 3 cm(ii) 4 cm(iii) 5 cm
Solution 4:
5.A rectangular field is 112 m long and 62 m broad. A cubical tank of edge 6 m is dug at each of the four corners of the field and the earth so removed is evenly spread on the remaining field. Find the rise in level.
Solution 5:
6.When length of each side of a cube is increased by 3 cm, its volume is increased by 2457 cm3. Find its side. How much will its volume decrease, if length of each side of it is reduced by 20%?
Solution 6:
7.A rectangular tank 30 cm × 20 cm × 12 cm contains water to a depth of 6 cm. A metal cube of side 10 cm is placed in the tank with its one face resting on the bottom of the tank. Find the volume of water, in litres, that must be poured in the tank so that the metal cube is just submerged in the water.
Solution 7:
8.The dimensions of a solid metallic cuboid are 72 cm × 30 cm × 75 cm. It is melted and recast into identical solid metal cubes with each of edge 6 cm. Find the number of cubes formed.
Also, find the cost of polishing the surfaces of all the cubes formed at the rate Rs. 150 per sq. m.
Solution 8:
9.The dimensions of a car petrol tank are 50 cm × 32 cm × 24 cm, which is full of petrol. If car's average consumption is 15 km per litre, find the maximum distance that can be covered by the car.
Solution 9:
10.The dimensions of a rectangular box are in the ratio 4 : 2 : 3. The difference between cost of covering it with paper at Rs. 12 per m2 and with paper at the rate of 13.50 per m2 is Rs. 1,248. Find the dimensions of the box.
Solution 10:
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiDNBpX7gTSjLYJJdi35mVG0KxWm2rBWzgpaMDbE3MP_AjQbxkfmlJg2zGgzbENU35RLGFVE6PzjgoNS_kBebExknvj3awVM22_7rBk_0ScnpqpFOauArVNo0TiXhT30TGGTOs_zyL-KeLE/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids.jpg)

![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh0oxZYdRtiBwCSalvuZJEWBWnrqcrM7rHCAFSxnLxx3YGX_QmXlLIfC0AQtqHhM0bnEVLIx_R8JQlQcmjoovBFC0IrhCtdkNPhKTFvEQhCwLtzt8dkez7HP7KnTzkVNQEWLHgQpgqP_NZk/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+2.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhIeeS3NAjHUr0J1qc_g6lmZnAG334IoFFnWsEjtMlKq9y9cALpTLocLUUqLqhRJV0ZzE2aoOfs3YoFvhPCmfP9ra_HWpnMHxdBaYPKY-mYlBgmYZN-Hilct5a1H_kuo3HNIvF3TNXMHA_a/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+3.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgyeUT-EeIaSaiROD3vCJQai2R1F-svyovnnFpSk2FwIf6yFXLreCeZiWIoh8uHpPcHBA_Eq0EXD0HHqecK-bw_oePDrH-OGBKrxyk76rKXJUQcboLmrSQVEdy8LB89wxY4oD7wchJEPYEz/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+4.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhK79p3B7L-NjP_c6fxPft5FLfji9e8O3qt19cAl7750MUdb3oo1O8-Zd0ftlJQbItje7GwDR34c-0VKy0jlcbOXjJp6lgZ8n3an-hRmU8TYdlDkkurN0fTSRHyYjCXf0gLN5EoDVqO_B6x/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+5.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgXpPlbGdg2NTLv4pFrLAQQsHTu21cbpVT5B7O6bJEV73Mmn7fMbbwmah3NEM9a5asJuZkZZFyI3SV-s00GEtEzO7dnKB_VXU_5PQhR2gMNj0dKUCJlyVSDcEM6usWxS55A5ZzJ3Aag7FdJ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+6.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjmafiOeuk2yOUkql0Spsslqdh1HiPKVx-LXfDbm67pOJZOSfLT9s1Pv6vf6iACBNXHW2ObT74QWmS3iWWTrIqKInQRyHaDmQVjW1VAzRml8L8VvXh3-4a4SjAdDeM08XwePbI_9KpgOhQr/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+7.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhS2m_3T4s72pbUKWfBj2bKYxTR7ngHvJImAGsuCScJ7QxNySYrI2mPihmhbhqc-TgD8NErlx8jgM746RIfMAxBzMvwUffKs8Y9gxhOAp_AsEOqVgJ-Eu7122ACvcm3b95VatcE7hZpFLeV/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+8.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgkZBQaiB9KAji_8UekU1p7wwuUKNxU2d_kKifgGiRwXeSkXfE3kccld-cVY9bhsH6oa4ujhhtpCd2o18JTDUL8n7SvbQguYsq1Qj47HBP6toHVopfZqme4xwogoitW4_fCTYxBN6rcvq2Z/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+9.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEipJISo2qKp-c6qPs6o9TL7djVkARXPiXHtegNaQB3iERy636Zi9q92mVsMgCLzIKFEo9HN1sn6TIEoAMAzMOhzdZLnjbjjrqRYH2QV5nGVaYvrAT7vlvax4klN-tEcEEbKE10IFdFTPAgY/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+10.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEigoXyxDHszeJEK1YBZxW803TBYXz2KdnR3ICbpwJWHb7Tlm_x-1tsX2M2Xj4jyDqL8LROlvLyYBoDndpABeMVz6U0Zxva9jeA_MzSZDiXcddlNajVZRx0SnSOwz0O_yfRMuiGzq6SGsILB/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+11.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEghVNCYXkHERMF69BvQS_OAD8qLyd1d3J6Hd064bpOX2Ixw-bi12__R2aIHQIVJp3TxgshKQN9o7rEg7pu5JPqfOsKEcrFPTjjvdcyRB6Ce0pV_evhToBy_QdXnf8H5X7WcE9QtEaOEDIaQ/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+12.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhk3n-4p0fnq0P-rUrZKNSR2dap3g13fyfluw6p8bNAtHlQq986SF6htKhsbgbRMWrw8V97nQNsJdyybq9q0b5dYwcvUk0AUcC51nLx2rbJuD8z8m7DjJZaFZxxVzCSXMyTxVPW0rdN0q5L/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+13.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhy7bh5reeSYtAP7w7Gpi472MANNM4ovsNRzFSIwbX9gmp8GLH7mdVixsdU1FmyTgZmUJ9GhzwqIiurvnvjc5t41cf4UDr6hhyZLsUlSn6GS1pXd4tgOBEBV-vuRb0oy9e5CARIGamNPuZh/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+14.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjih58hvq0mAf9bb7SyUAHy9ecpuV-9KG-ybBGnQAO78uAh6z25ies82pLaUGYJO-OP1eh_oyAhhCagLwRiCyusy4udRXS7TDhSdQGBEwr6GYtJs5n2pmxfNqNFbExvsO3gDAp0St0_vTJz/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+15.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh7EhAMnUx7GPfWlmsi0iQPyLOeAo2-HTBu6C3ONLXj1RwlR-3UdJljHkjqwFR3HLJj8_NSL43f_j1912qeSHtHRBLir_WOlM1nye8op4DEnlF1QF1jPXMxNL9bTeBqGq9S4zu6Vtstj7tf/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+16.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhMI1AWx6J2I6jQ1KdpVf8_JPtP0LflBxy4mtN1m30oZuLa7v10EkhcnRnaeFO82immZP_O9YxDJtTBeEqjf26Apn9qbnVit2oBTuVVqbJSQ2nIfYFlv7hB_oPTbKWcR1ieWKbHlgKBgv0A/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+17.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhAh-dZDaN0Po5bzYY9yIn4grA9q-5JS7VpH02GX-h4ZrCi2ywztYuMn5feC5EwLnXQRu6HsuJVL7oHYybuoZ_1zjd8e7PHHvJdAKfg89JpCz31ZnRdshlR0VJRxz5SZehWjFTaPgj3NrIs/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+18.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhTn_K-HgSLKfuOmZYehDXXUBcVrZB9FupIPu5pPDYW7WtLJzU293bT6IYpDcsAFSLjQPilOpArUYF1XZxpud6Xn1R_YUgElp6l4pl23_AoRCPpPRhc9Cr1zHA7OiOdEinTQJfxRKGVgDK_/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+19.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhvHiISKuq45rPvGU34voliUZmJFOl1HifrUJVMQLqOo3ZuvwALh1sqxjwjZLpvsl6hyphenhyphenG6OGrbqXbMq-xMVg769HWP8HhVGe23K1yTXJy2SWPe9BLcwh2CWmao9Y6otlLJZhofiBbKc9RBO/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+20.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhrGVGrfHrvEgKSZ3Ye9ymYiHSIPcKcIEd54blONOZesvnq22HsBjWELI7htJNw0RESqM-aDRwNLsylnUTlcaQyKtY9fQJ0sZGXfsruYqdDJW4oNzB76LU84atg9A1U86glzJqrVfolw8YN/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+21.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEisBE_X34g7FfjEtIeQ0IWaFglzHe2KXhXfQA1CQiYLI3KAg2ouoNCZrNlrMjeN9b46akBEE1wEXpyXxpsIXkcA9HHzH5Bt2tuyG-CBo1mec9UeqeRdWGHhsTmPNuan8mb45MOhICjQvE4R/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+22.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiY8Ps8SRfh7bkTbE-T5xcL7CTCXMV15NliYJ1hbHnKsjzonf8l0bPblQBNAc3TyUOm_E5KMr38Eyx9BXdbJlNs0fROXLCmRVUmB1L7Z-M9ifYAJwaoTK-wBXty-CXkAw_QN0lqYBPxDCVY/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+23.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEghIossI4ziWsBMTvxgUqBc96TDs8UhHvY4LX3I7Om0mju43lqcVM5dAkxjRlCvHP62EYdRpTCQJW1IjzQvtLI67SZ8CXHxNT4hUDXOImH4dbYzYtTb2jkx24saHKlTdGD9O3FC6cQM5Bpj/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+24.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjbPhaXHyMjEJqVTrSUlIo0VmaClfYG3mVV2kpjCrK1lVqXd8349vnZdLnRs07nbr5WwUOGCc3Rwobg8q5yeFyOFbBsYQdtEdKItB9CezCABi411380Bmms6E1M_pgFfBqdpQezKikVNtkG/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+25.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjShEzXo9Ja2GPBlBhhKFmKt1EONT0ujH_0dpXNyudI6bGguyyRnzbUG1ChDWRqwdHUCOlAoaFVTqDb_kK3maS9_g4TjmOaHc2YXaM5CzQI9sk4ZBDrHTDAdRaSSgq3rEXmSwXftO4oW2vA/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+26.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhbldE1HhjJjwuAULTbbhMPTEWSteP5Q5Wurdz2hak_9EVAdRrOB2nKSDBWh60GaCfNWnsYbhDiSSv5GAIVtc7rJocJ12VsEnBrziKH96umF2secdLH9WLtrCU3rpAD-8OOexn6ePRY7wVc/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+27.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEha1Hv8D1kMHXSYiQTv4IEx2Y_8J2jVkqT-cA23oQHx-q2bwbfyFdmyd8-reKlr8m6teSvRWS_vCwkekCp2zbfixC5kXdRNRS92IUmXgHg1gZ89vriuudhRBBmlQsJ-2UM2CUDybff-gO0X/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+28.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjJEEUaH6cpGnaVrux4ge7bWGxnG_LQS2Qe6D0FACv1E3RZw2o9e8-jmHv69yPfCaljZFufM_RLyqJb4QQ9NsRPlUawcj7YbxGhaP47qFC_uW5Ag8XCJRfyxJXqe9cHYW7Lehyphenhyphen-bPPW6lCl/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+29.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgDCNgVGp3k4IZjxqxFvLxAS18o3ea8tOUaFr66NK0zvVYFabCQUKDicDSyGfNTk38s9X3nwzxf2DbFiebGUqHMEkx5WxUgkpTh9IXl8Afcvs-2e7Kw9eWbXdaHuQdKRuure57oQc9sqtiX/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+30.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjAC_HnuyQWLmW6vs4ayOZ04-zjeNGqosYPbb8hGAilkJUdx0JIjPwM6WKo_yNnUbTRZLdVhsyvzLXp6ofa__UnV_CpuTsxbmv-hB65e3LOxCg6j8jkiO5H6GOlPB-toRF9NdDGi3OrNkZs/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+31.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgU2lue6cyjZowhVSxEkOKc0vz-vlyNfLypAU_TeGW_Heg-tkWH2YqA9MTOE30dmImzxQnhSFTyzDyjO_mLt9kLoNtBuh1UZ7n1LdLIjY_EAQKYNLMp9MZp05XzIqdzo_ZeJllc8eNQ6CO3/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+38.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhVsmtLc-0cJ4snUv2Xp1a1-BwlNeGHvC21KnilwE8QdclDl-_eWZXFDWUyrn0BET3kU_VXh7ZRaAcHmVZ69M4z9BaBGLocNiIc5p8hMVFI7w8J2N76l3OPVPMTJPkXpl8RlJZ8iypwNyEv/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+32.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiRQC2Ssw63DrEntWeR2qmmTYCkFI3WbUrggitgXxGJwI68C3BHL3wwVlzF_ji9xE9HoYJQtJPIHe9cCkRUsgv-Pk71EwvOsSRSYZAnj_ItYC-8ekn65H8Kvj17SaZNcBzLN7Gm_YdSoR_D/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+33.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj_ExkdnV-Vw70E9fVW2TgtoH-U51Ido3CDJe9nwFYM8n4EM_HKg3cTwTroYsnVScKXk6TKQo-CZ_W3AhlO4MTjBqCYlue8ucmdOekY8_DaCb6ftfUTV0kK5eTp0ifAiG918nx58oH6UO8H/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+34.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhjYjJ-fzV0grnyEKGTN_DTJKdkcnTLYbTX8bbzzO17ShEm-QU3ukWs4Aj8QTvawnXAJ738ptUVYVBM9dF9J9G2rr1qpM70KCs3lYCeCmGb6aylEZrt1Z2Yfk66KykQJcpMSmaFOzfwTtlL/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+35.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgtHe3l-rpILqJsDmNfw7tmwyCEgXm2B_dQ2wYP18-WiLEssB6QnewGgpp0xENSUR_ZRgkv2b9gHH5fw2Ba7sA4JFZndnArdCXWAgApvK6evWtLcESmtzAGmbapQQUy1GqOx1H7opZLx4Fx/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+36.jpg)
![Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids] Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 21 - Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgJ-yVs3Dbh2d_Lnl-16LACpPoKiPcbc6NAF8nT81jT6jhTUAOhfUnpXyNHgVWEjjRIf51sRng9nWC1Vf2d5JuZUD1wc0Oy-PFRzF1P8UUbaH2gd0Kq7HLamaz8Ftuhbk1zcxjbcT5i5Wub/s1600/selina-concise-mathematics-class-9-icse-solutions-solids-surface-area-and-volume-of-3-d-solids+37.jpg)