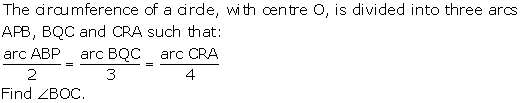Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Circle
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 17 Circle
Exercise 17(A)1.A chord of length 6 cm is drawn in a circle of radius 5 cm. Calculate its distance from the centre of the circle.
Solution 1:
2.A chord of length 8 cm is drawn at a distance of 3 cm from the centre of the circle. Calculate the radius of the circle.
Solution 2:
3.The radius of a circle is 17.0 cm and the length of perpendicular drawn from its centre to a chord is 8.0 cm. Calculate the length of the chord.
Solution 3:
4.A chord of length 24 cm is at a distance of 5 cm from the centre of the circle. Find the length of the chord of the same circle which is at a distance of 12 cm from the centre.
Solution 4:
5.In the following figure, AD is a straight line,
Solution 5:
6.In a circle of radius 17 cm, two parallel chords of lengths 30 cm and 16 cm are drawn. Find the distance between the chords, if both the chords are:
(i) on the opposite sides of the centre;
(ii) on the same side of the centre.
Solution 6:
Let O be the centre of the circle and AB and CD be the two parallel chords of length 30 cm and 16 cm respectively.
Drop OE and OF perpendicular on AB and CD from the centre O.
7.Two parallel chords are drawn in a circle of diameter 30.0 cm. The length of one chord is 24.0 cm and the distance between the two chords is 21.0 cm; find the length of another chord.
Solution 7:
Since the distance between the chords is greater than the radius of the circle (15 cm), so the chords will be on the opposite sides of the centre.
8.A chord CD of a circle whose centre is O, is bisected at P by a diameter AB. Given OA = OB = 15 cm and OP = 9 cm. Calculate the lengths of:
(i) CD ; (ii) AD ; (iii) CB.
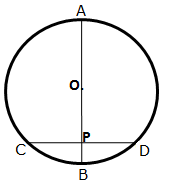
Solution 8:
9.The figure given below shows a circle with centre O in which diameter AB bisects the chord CD at point E. If CE = ED = 8 cm and EB = 4 cm, find the radius of the circle.
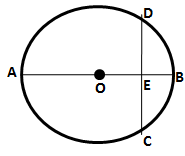
Solution 9:
10.In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. AB and CD are two chords of the circle. OM is perpendicular to AB and ON is perpendicular to CD. AB = 24 cm, OM = 5 cm, ON = 12 cm, Find the :
(i) radius of the circle
(ii) length of chord CD
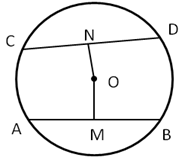
Solution 10:
Exercise 17(B)
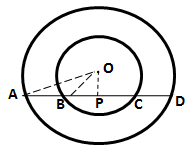
1.The figure shows two concentric circles and AD is a chord of larger circle. Prove that: AB = CD.
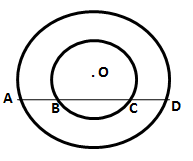
Solution 1:
2.A straight line is drawn cutting two equal circles and passing through the mid-point M of the line joining their centres O and O'. Prove that the chords AB and CD, which are intercepted by the two circles, are equal.
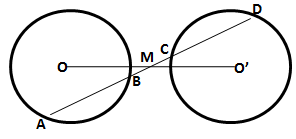
Solution 2:
3.M and N are the mid-points of two equal chords AB and CD respectively of a circle with centre O. Prove that:
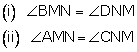
Solution 3:
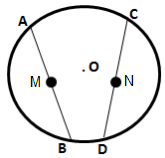
4.In the following figure; P and Q are the points of intersection of two circles with centres O and O'. If straight lines APB and CQD are parallel to OO'; prove that:
Solution 4:
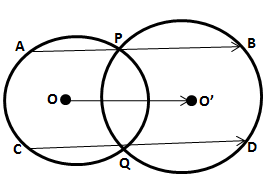
5.Two equal chords AB and CD of a circle with centre O, intersect each other at point P inside the circle. Prove that:
(i) AP = CP ; (ii) BP = DP
Solution 5:
6.In the following figure, OABC is a square. A circle is drawn with O as centre which meets OC at P and OA at Q. Prove that:
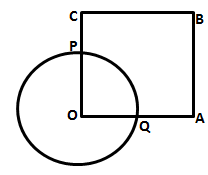
Solution 6:
7.The length of the common chord of two intersecting circles is 30 cm. If the diameters of these two circles be 50 cm and 34 cm, calculate the distance between their centres.
Solution 7:
8.The line joining the midpoints of two chords of a circle passes through its centre. Prove that the chords are parallel.
Solution 8:
9.In the following figure, the line ABCD is perpendicular to PQ; where P and Q are the centres of the circles. Show that:
(i) AB = CD ;
(ii) AC = BD.
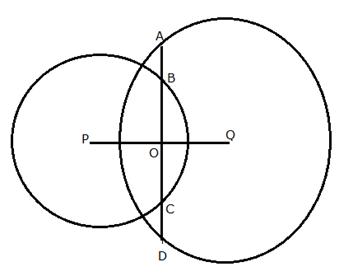
Solution 9:
10.AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle with centre O which intersect each other at right angle at point P. If OM
Solution 10:
Exercise 17(C)
1.In the given figure, an equilateral triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle with centre O.
Find: (i) ∠BOC (ii) ∠OBC
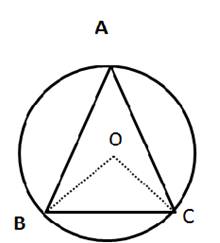
Solution 1:
2.In the given figure, a square is inscribed in a circle with centre O. Find:
(i) ∠BOC
(ii) ∠OCB
(iii) ∠COD
(iv) ∠BOD
Is BD a diameter of the circle?
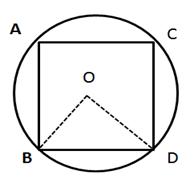
Solution 2:
3.In the given figure, AB is a side of regular pentagon and BC is a side of regular hexagon.
(i) ∠AOB
(ii) ∠BOC
(iii) ∠AOC
(iv) ∠OBA
(v) ∠OBC
(vi) ∠ABC
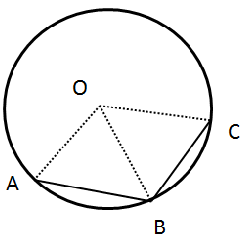
Solution 3:
As given that AB is the side of a pentagon the angle subtended by each arm of the pentagon at
4.In the given figure, arc AB and arc BC are equal in length.
If ∠AOB = 48°, find:
(i) ∠BOC
(ii) ∠OBC
(iii) ∠AOC
(iv) ∠OAC
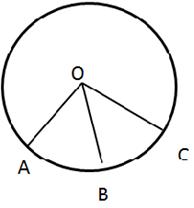
Solution 4:
5.In the given figure, the lengths of arcs AB and BC are in the ratio 3:2.
If ∠AOB = 96°, find:
(i) ∠BOC
(ii) ∠ABC
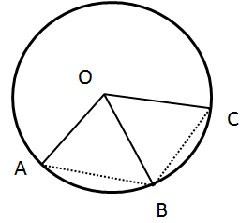
Solution 5:
6.In the given figure, AB = BC = DC and ∠AOB = 50°.
(i) ∠AOC
(ii) ∠AOD
(iii) ∠BOD
(iv) ∠OAC
(v) ∠ODA
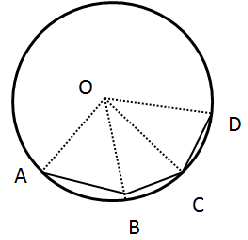
Solution 6:
7.In the given figure, AB is a side of a regular hexagon and AC is a side of a regular eight sided polygon. Find:
(i) ∠AOB
(ii) ∠AOC
(iii) ∠BOC
(iv) ∠OBC
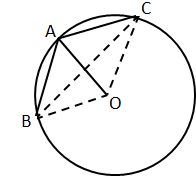
Solution 7:
8.In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle and the length of arc AB is twice the is twice the length of arc BC.
If ∠AOB = 100°, find:
(i) ∠BOC
(ii) ∠OAC
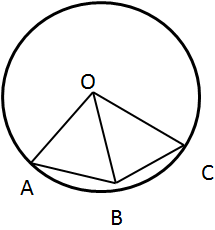
Solution 8:
Exercise 17(D)
1.The radius of a circle is 13 cm and the length of one of its chords is 24 cm. Find the distance of the chord from the centre.
Solution 1:
2.Prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centre.
Solution 2:
3.Draw two circles of different radii. How many points these circles can have in common? What is the maximum number of common points?
Solution 3:
4.Suppose you are given a circle. Describe a method by which you can find the centre of this circle.
Solution 4:
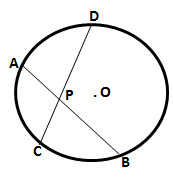
5.Given two equal chords AB and CD of a circle with centre O, intersecting each other at point P. Prove that:
(i) AP = CP
(ii) BP = DP
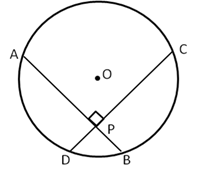
Solution 5:
6.In a circle of radius 10 cm, AB and CD are two parallel chords of lengths 16 cm and 12 cm respectively. Calculate the distance between the chords, if they are on:
(i) the same side of the centre.
(ii) the opposite sides of the centre.
Solution 6:
7.In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle with radius 20 cm and OD is perpendicular to AB.
If AB = 32 cm, find the length of CD
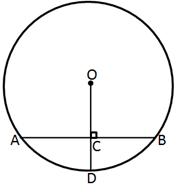
Solution 7:
8.In the given figure, AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle, with centre O.
If P is the mid-point of chord AB, Q is the mid-point of chord CD and ∠POQ = 150°, find ∠APQ.
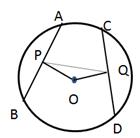
Solution 8:
9.In the given figure, AOC is the diameter of the circle, with centre O.
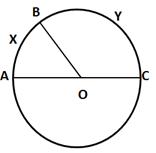
If arc AXB is half of arc BYC, find ∠BOC.
Solution 9:
10.