Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Heights and Distances
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Chapter 22 Heights and Distances
Heights and Distances Exercise 22A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
The height of a tree is √3 times the length of its shadow. Find the angle of elevation of the sun.
Solution:
Question 2.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground and at a distance of 160 m from its foot, is found to be 60o. Find the height of the tower.
Solution:
Question 3.
A ladder is placed along a wall such that its upper end is resting against a vertical wall. The foot of the ladder is 2.4 m from the wall and the ladder is making an angle of 68o with the ground. Find the height, upto which the ladder reaches.
Solution:
Question 4.
Two persons are standing on the opposite sides of a tower. They observe the angles of elevation of the top of the tower to be 30o and 38o respectively. Find the distance between them, if the height of the tower is 50 m.
Solution:
Question 5.
A kite is attached to a string. Find the length of the string, when the height of the kite is 60 m and the string makes an angle 30o with the ground.
Solution:
Question 6.
A boy, 1.6 m tall, is 20 m away from a tower and observes the angle of elevation of the top of the tower to be (i) 45o, (ii) 60o. Find the height of the tower in each case.
Solution:
Question 7.
The upper part of a tree, broken over by the wind, makes an angle of 45o with the ground and the distance from the root to the point where the top of the tree touches the ground is 15 m. What was the height of the tree before it was broken?
Solution:
Question 8.
The angle of elevation of the top of an unfinished tower at a point distance 80 m from its base is 30o. How much higher must the tower be raised so that its angle of elevation at the same point may be 60o?
Solution:
Question 9.
At a particular time, when the sun’s altitude is 30o, the length of the shadow of a vertical tower is 45 m. Calculate
(i) the length of the tower.
(ii) the length of the shadow of the same tower, when the sun’s altitude is
(a) 45o (b) 60o
Solution:Question 10.
Two vertical poles are on either side of a road. A 30 m long ladder is placed between the two poles. When the ladder rests against one pole, it makes angle 32o24′ with the pole and when it is turned to rest against another pole, it makes angle 32o24′ with the road. Calculate the width of the road.
Solution:
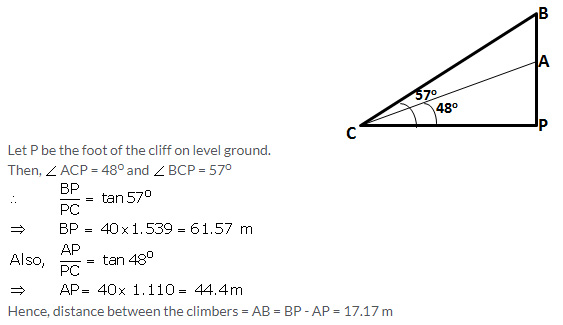
Question 11.
Two climbers are at points A and B on a vertical cliff face. To an observer C, 40m from the foot of the cliff, on the level ground, A is at an elevation of 48o and B of 57o. What is the distance between the climbers?
Solution:
Question 12.
A man stands 9 m away from a flag-pole. He observes that angle of elevation of the top of the pole is 28o and the angle of depression of the bottom of the pole is 13o. Calculate the height of the pole.
Solution:
Question 13.
From the top of a cliff 92 m high, the angle of depression of a buoy is 20o. Calculate, to the nearest metre, the distance of the buoy from the foot of the cliff.
Solution:
Heights and Distances Exercise 22B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Solution:
Question 2.
Find the height of a tree when it is found that on walking away from it 20 m, in a horizontal line through its base, the elevation of its top changes from 60o to 30o.
Solution:
Question 3.
Find the height of a building, when it is found that on walking towards it 40 m in a horizontal line through its base the angular elevation of its top changes from 30o to 45o.
Solution:
Question 4.
From the top of a light house 100 m high, the angles of depression of two ships are observed as 48o and 36o respectively. Find the distance between the two ships(in the nearest metre) if:
(i) the ships are on the same side of the light house.
(ii) the ships are on the opposite sides of the light house.
Solution:Question 5.
Two pillars of equal heights stand on either side of a roadway, which is 150 m wide. At a point in the roadway between the pillars the elevations of the tops of the pillars are 60o and 30o ; find the height of the pillars and the position of the point.
Solution:
Question 6.
Solution:
Question 7.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower is observed to be 60o. At a point, 30 m vertically above the first point of observation, the elevation is found to be 45o. Find:
(i) the height of the tower,
(ii) its horizontal distance from the points of observation.
Solution:Question 8.
From the top of a cliff, 60 metres high, the angles of depression of the top and bottom of a tower are observed to be 30o and 60o. Find the height of the tower.
Solution:
Question 9.
A man on a cliff observes a boat, at an angle of depression 30o, which is sailing towards the shore to the point immediately beneath him. Three minutes later, the angle of depression of the boat is found to be 60o. Assuming that the boat sails at a uniform speed, determine:
(i) how much more time it will take to reach the shore.
(ii) the speed of the boat in metre per second, if the height of the cliff is 500 m.
Solution:Question 10.
A man in a boat rowing away from a lighthouse 150 m high, takes 2 minutes to change the angle of elevation of the top of the lighthouse from 60o to 45o. Find the speed of the boat.
Solution:
Question 11.
A person standing on the bank of a river observes that the angle of elevation of the top of a tree standing on the opposite bank is 60o. When he moves 40 m away from the bank, he finds the angle of elevation to be 30o. Find:
(i) the height of the tree, correct to 2 decimal places,
(ii) the width of the river.
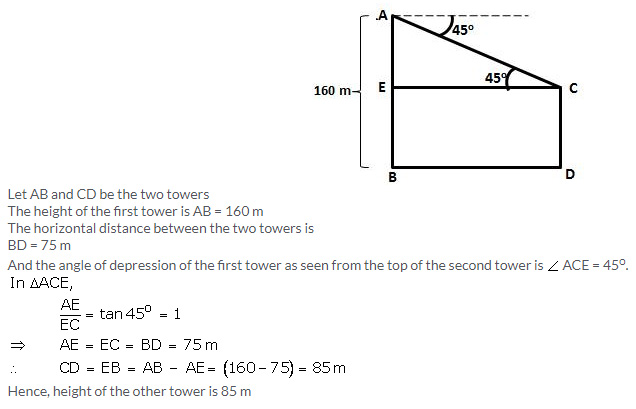
Solution:Question 12.
The horizontal distance between two towers is 75 m and the angular depression of the top of the first tower as seen from the top of the second, which is 160 m high, is 45o. Find the height of the first tower.
Solution:Question 13.
The length of the shadow of a tower standing on level plane is found to be 2y metres longer when the sun’s altitude is 30o than when it was 45o. Prove that the height of the tower is y(√3 + 1) metres.
Solution:
Question 14.
An aeroplane flying horizontally 1 km above the ground and going away from the observer is observed at an elevation of 60o. After 10 seconds, its elevation is observed to be 30o; find the uniform speed of the aeroplane in km per hour.
Solution:
Question 15.
From the top of a hill, the angles of depression of two consecutive kilometer stones, due east, are found to be 30o and 45o respectively. Find the distances of the two stones from the foot of the hill.
Solution:
Heights and Distances Exercise 22C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.Solution:
Question 2.
Solution:
Question 3.
Solution:
Question 4.
Solution:
Question 5.
The radius of a circle is given as 15 cm and chord AB subtends an angle of 131o at the centre C of the circle. Using trigonometry, calculate:
(i) the length of AB;
(ii) the distance of AB from the centre C.
Solution:Question 6.
At a point on level ground, the angle of elevation of a vertical tower is found to be such that its tangent is 5/12. On walking 192 metres towards the tower, the tangent of the angle is found to be 3/4. Find the height of the tower.
Solution:
Question 7.
Solution:
Question 8.
With reference to the given figure, a man stands on the ground at point A, which is on the same horizontal plane as B, the foot of the vertical pole BC. The height of the pole is 10 m. The man’s eye s 2 m above the ground. He observes the angle of elevation of C, the top of the pole, as xo , where tan xo = 2/5. Calculate:
(i) the distance AB in metres;
(ii) angle of elevation of the top of the pole when he is standing 15 metres from the pole. Give your answer to the nearest degree.
Solution:Question 9.
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points on the ground at distances a and b metres from the base of the tower and in the same line are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is √ab metre.
Solution:Question 10.
Solution:
Question 11.
A vertical tower is 20 m high. A man standing at some distance from the tower knows that the cosine of the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 0.53. How far is he standing from the foot of the tower?
Solution:
Question 12.
A man standing on the bank of a river observes that the angle of elevation of a tree on the opposite bank is 60o. When he moves 50 m away from the bank, he finds the angle of elevation to be 30o. Calculate:
(i) the width of the river;
(ii) the height of the tree.Solution:
Question 13.
A 20 m high vertical pole and a vertical tower are on the same level ground in such a way that the angle of elevation of the top of the tower, as seen from the foot of the pole is 60o and the angle of elevation of the top of the pole, as seen from the foot of the tower is 30o. Find:
(i) the height of the tower ;
(ii) the horizontal distance between the pole and the tower.
Solution:Question 14.
A vertical pole and a vertical tower are on the same level ground in such a way that from the top of the pole, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 60o and the angle of depression of the bottom of the tower is 30o. Find:
(i) the height of the tower, if the height of the pole is 20 m;
(ii) the height of the pole, if the height of the tower is 75 m.
Solution:Question 15.
From a point, 36 m above the surface of a lake, the angle of elevation of a bird is observed to be 30o and the angle of depression of its image in the water of the lake is observed to be 60o. Find the actual height of the bird above the surface of the lake.
Solution:
Question 16.
A man observes the angle of elevation of the top of a building to be 30o. He walks towards it in a horizontal line through its base. On covering 60 m, the angle of elevation changes to 60o. Find the height of the building correct to the nearest metre.
Solution:
Question 17.
As observed from the top of a 80 m tall lighthouse, the angles of depression of two ships, on the same side of a light house in a horizontal line with its base, are 30° and 40° respectively. Find the distance between the two ships. Give your answer corrected to the nearest metre.
Solution:
Question 18.
Solution:
Question 19.
An aeroplane, at an altitude of 250 m, observes the angles of depression of two boats on the opposite banks of a river to be 45° and 60° respectively. Find the width of the river. Write the answer correct to the nearest whole number.
Solution:
Question 20.
Solution:
Question 21.
The angles of depression of two ships A and B as observed from the top of a light house 60m high, are 60° and 45° respectively. If the two ships are on the opposite sides of the light house, find the distance between the two ships. Give your answer correct to the nearest whole number.
Solution: