Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Co-ordinate Geometry
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 26 Co-ordinate Geometry
Exercise 26(A)
1. For each equation given below; name the dependent and independent variables.
(i) y = 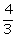 x -7
x -7
(ii) x = 9y + 4
(iii) x = 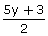
(iv) y = 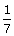 (6x + 5)
(6x + 5)
Solution 1:
2.Plot the following points on the same graph paper:
(i) (8, 7)(ii) (3, 6)
(iii) (0, 4)(iv) (0, -4)
(v) (3, -2)(vi) (-2, 5)
(vii) (-3, 0)(viii) (5, 0)
(ix) (-4, -3)
Solution 2:
On the graph paper, let us draw the co-ordinate axes XOX’ and YOY’ intersecting at the origin O. With proper scale, mark the numbers on the two co-ordinate axes.
Now for the point A(8,7)
Step I
Starting from origin O, move 8 units along the positive direction of X axis, to the right of the origin O
Step II
Now from there, move 7 units up and place a dot at the point reached. Label this point as A(8,7)
Similarly plotting the other points
3.Find the values of x and y if:
(i) (x - 1, y + 3) = (4, 4,)
(ii) (3x + 1, 2y - 7) = (9, - 9)
(iii) (5x - 3y, y - 3x) = (4, -4)
Solution 3:
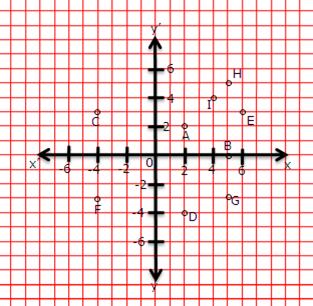
4.Use the graph given alongside, to find the coordinates of point (s) satisfying the given condition:
(i) The abscissa is 2.
(ii)The ordinate is 0.
(iii) The ordinate is 3.
(iv) The ordinate is -4.
(v) The abscissa is 5.
(vi) The abscissa is equal to the ordinate.
(vii) The ordinate is half of the abscissa.
Solution 4:
(i) The abscissa is 2
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point A is given by (2,2)
(ii) The ordinate is 0
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point B is given by (5,0)
(iii) The ordinate is 3
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point C and E is given by (-4,3)& (6,3)
(iv) The ordinate is -4
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point D is given by (2,-4)
(v) The abscissa is 5
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point H, B and G is given by (5,5) ,(5,0) & (5,-3)
(vi)The abscissa is equal to the ordinate.
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point I,A & H is given by (4,4),(2,2) & (5,5)
(vii)The ordinate is half of the abscissa
Now using the given graph the co-ordinate of the given point E is given by (6,3)
5.State, true or false:
(i) The ordinate of a point is its x-co-ordinate.
(ii) The origin is in the first quadrant.
(iii) The y-axis is the vertical number line.
(iv) Every point is located in one of the four quadrants.
(v) If the ordinate of a point is equal to its abscissa; the point lies either in the first quadrant or in the second quadrant.
(vi) The origin (0, 0) lies on the x-axis.
(vii) The point (a, b) lies on the y-axis if b = 0.
Solution 5:
(i)The ordinate of a point is its x-co-ordinate.
False.
(ii)The origin is in the first quadrant.
False.
(iii)The y-axis is the vertical number line.
True.
(iv)Every point is located in one of the four quadrants.
True.
(v)If the ordinate of a point is equal to its abscissa; the point lies either in the first quadrant or in the second quadrant.
False.
(vi)The origin (0,0) lies on the x-axis.
True.
(vii)The point (a,b) lies on the y-axis if b=0.
False
6.In each of the following, find the co-ordinates of the point whose abscissa is the solution of the first equation and ordinate is the solution of the second equation:
(i) 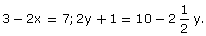
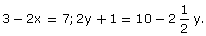
(ii) 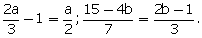
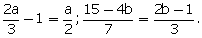
(iii) 

Solution 6:
7.In each of the following, the co-ordinates of the three vertices of a rectangle ABCD are given. By plotting the given points; find, in each case, the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex:
(i) A(2, 0), B(8, 0) and C(8, 4).
(ii) A (4, 2), B(-2, 2) and D(4, -2).
(iii) A (-4, -6), C(6, 0) and D(-4, 0).
(iv) B (10, 4), C(0, 4) and D(0, -2).
Solution 7:
After plotting the given points A(2,0), B(8,0) and C(8,4) on a graph paper; joining A with B and B with C. From the graph it is clear that the vertical distance between the points B(8,0) and C(8,4) is 4 units, therefore the vertical distance between the points A(2,0) and D must be 4 units. Now complete the rectangle ABCD
As is clear from the graph D(2,4)
(ii)A(4,2), B(-2,-2) and D(4,-2)
After plotting the given points A(4,2), B(-2,2) and D(4,-2) on a graph paper; joining A with B and A with D. From the graph it is clear that the vertical distance between the points A(4,2) and D(4,-2) is 4 units and the horizontal distance between the points A(4,2) and B(-2,2) is 6 units , therefore the vertical distance between the points B(-2,2)and C must be 4 units and the horizontal distance between the points B(-2,2) and C must be 6 units. Now complete the rectangle ABCD
As is clear from the graph C(-2,2)
8.A (-2, 2), B(8, 2) and C(4, -4) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD. By plotting the given points on a graph paper; find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex D.
Also, form the same graph, state the co-ordinates of the mid-points of the sides AB and CD.
Solution 8:
After plotting the given points A(2,-2), B(8,2) and C(4,-4) on a graph paper; joining B with C and B with A . Now complete the parallelogram ABCD.
As is clear from the graph D(-6,4)
Now from the graph we can find the mid points of the sides AB and CD.
Therefore the co-ordinates of the mid-point of AB is E(3,2) and the co-ordinates of the mid-point of CD is F(-1,-4)
9.A (-2, 4), C(4, 10) and D(-2, 10) are the vertices of a square ABCD. Use the graphical method to find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex B. Also, find:
(i) The co-ordinates of the mid-point of BC;
(ii) The co-ordinates of the mid-point of CD and
(iii) The co-ordinates of the point of intersection of the diagonals of the square ABCD.
Solution 9:
10.By plotting the following points on the same graph paper. Check whether they are collinear or not:
(i) (3, 5), (1, 1) and (0, -1)
(ii) (-2, -1), (-1, -4) and (-4, 1)
Solution 10:
11.Plot the point A(5, -7). From point A, draw AM perpendicular to x-axis and AN perpendicular to y-axis. Write the co-ordinates of points M and N.
Solution 11:

12.In square ABCD; A = (3, 4), B = (-2, 4) and C = (-2, -1). By plotting these points on a graph paper, find the co-ordinates of vertex D. Also, find the area of the square.
Solution 12:
After plotting the given points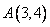 ,
,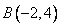 and
and 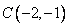 on a graph paper; joining
on a graph paper; joining  with
with 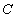 and
and 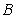 with
with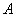 . From the graph it is clear that the vertical distance between the points
. From the graph it is clear that the vertical distance between the points 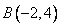 and
and 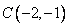 is
is 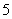 units and the horizontal distance between the points
units and the horizontal distance between the points 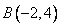 and
and 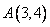 is
is 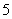 units , therefore the vertical distance between the points
units , therefore the vertical distance between the points 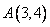 and
and  must be
must be 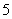 units and the horizontal distance between the points
units and the horizontal distance between the points 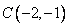 and
and 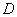 must be
must be 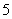 units. Now complete the square
units. Now complete the square 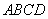
As is clear from the graph 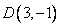
Now the area of the square  is given by
is given by
13.In rectangle OABC; point O is the origin, OA = 10 units along x-axis and AB = 8 units. Find the co-ordinates of vertices A, B and C.
Solution 13:
Exercise 26(B)
1.Draw the graph for each linear equation given below:
(i) x = 3(ii) x + 3 = 0
(iii) x - 5 = 0(iv) 2x - 7 = 0
(v) y = 4(vi) y + 6 = 0
(vii) y -2 = 0(viii) 3y + 5 = 0
(ix) 2y - 5 = 0(x) y = 0
(xi) x = 0
Solution 1:
2.Draw the graph for each linear equation given below:
(i) y = 3x
(ii) y = -x
(iii) y = -2x
(iv) y = x
(v) 5x+ y = 0
(vi) x+2y = 0
(vii) 4x - y = 0
(viii) 3x+2y = 0
(ix) x = -2y
Solution 2:
3.Draw the graph for the each linear equation given below:
(i) y = 2x + 3
(ii) 

(iii) y = -x + 4
(iv) 

(v) 

(vi) 2x - 3y = 4
(vii) 

(viii) 

(ix) x + 5y + 2 =0
Solution 3:
4.Draw the graph for each equation given below:
(i) 3x +2y = 6
(ii) 2x - 5y = 10
(iii) 
(iv) 
In each case, find the co-ordinates of the points where the graph (line ) drawn meets the co-ordinates axes.
Solution 4:
5.For each linear equation, given above, draw the graph and then use the graph drawn (in each case) to find the area of a triangle enclosed by the graph and the co-ordinates axes:
(i) 3x - (5 - y) = 7
(ii) 7 - 3 (1 - y) = -5 + 2x.
Solution 5:
6.For each pair of linear equations given below, draw graphs and then state, whether the lines drawn are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
(i) y = 3x - 1
y = 3x + 2
(ii) y = x - 3
y = -x + 5
(iii) 2x - 3y = 6
(iv) 3x + 4y = 24
Solution 6:
7.On the same graph paper, plot the graph of y = x - 2, y = 2x + 1 and y = 4 from x= -4 to 3.
Solution 7:
8.On the same graph paper, plot the graphs of y = 2x - 1, y = 2x and y = 2x + 1 from x = -2 to x = 4. Are the graphs (lines) drawn parallel to each other?
Solution 8:
9.The graph of 3x + 2y = 6 meets the x=axis at point P and the y-axis at point Q. Use the graphical method to find the co-ordinates of points P and Q.
Solution 9:
10.Draw the graph of equation x + 2y - 3 = 0. From the graph, find:
(i) x1, the value of x, when y = 3
(ii) x2, the value of x, when y = -2.
Solution 10:
11.Draw the graph of the equation 3x - 4y = 12.
Use the graph drawn to find:
(i) y1, the value of y, when x = 4.
(ii) y2, the value of y, when x = 0.
Solution 11:
12.Draw the graph of equation
(i) x1, the value of x, when y = 10
(ii) y1, the value of y, when x = 8.
Solution 12:
13.Use the graphical method to show that the straight lines given by the equations x + y = 2, x - 2y = 5 and
Solution 13:
Exercise 26(C)
1.In each of the following, find the inclination of line AB:
(i)
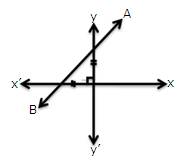
(ii)
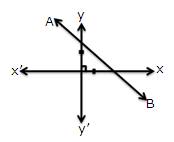
(iii)
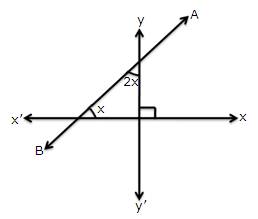
Solution 1:
The angle which a straight line makes with the positive direction of x-axis (measured in anticlockwise direction) is called inclination o the line.
The inclination of a line is usually denoted by θ
(i)The inclination is θ = 45°
(ii) The inclination is θ = 135°
(iii) The inclination is θ = 30°
2.Write the inclination of a line which is:
(i) Parallel to x-axis.
(ii) Perpendicular to x-axis.
(iii) Parallel to y-axis.
(iv) Perpendicular to y-axis.
Solution 2:
(i)The inclination of a line parallel to x-axis is θ = 0°
(ii)The inclination of a line perpendicular to x-axis is θ = 90°
(iii) The inclination of a line parallel to y-axis is θ = 90°
(iv) The inclination of a line perpendicular to y-axis is θ = 0°
3.Write the slope of the line whose inclination is:
(i) 0o(ii) 30o (iii) 45o(iv) 60o
Solution 3:
4.Find the inclination of the line whose slope is:
(i) 0(ii) 1(iii)  (iv)
(iv) 
 (iv)
(iv) 
Solution 4:
5.Write the slope of the line which is:
(i) Parallel to x-axis.
(ii) Perpendicular to x-axis.
(iii) Parallel to y-axis.
(iv) Perpendicular to y-axis.
Solution 5:
6.For each of the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
(i) x + 3y + 5 = 0
(ii) 3x - y - 8 = 0
(iii) 5x = 4y + 7
(iv) x= 5y - 4
(v) y = 7x - 2
(vi) 3y = 7
(vii) 4y + 9 = 0
Solution 6:
7.Find the equation of the line whose:
(i) Slope = 2 and y-intercept = 3
(ii) Slope = 5 and y-intercept = -8
(iii) slope = -4 and y-intercept = 2
(iv) slope = -3 and y-intercept = -1
(v) slope = 0 and y-intercept = -5
(vi) slope = 0 and y-intercept = 0
Solution 7:
8.Draw the line 3x + 4y = 12 on a graph paper. From the graph paper. Read the y-intercept of the line.
Solution 8:
Given line is 3x + 4y = 12
The graph of the given line is shown below.
Clearly from the graph we can find the y-intercept.The required y-intercept is 3.
9.Draw the line 2x - 3y - 18 = 0 on a graph paper. From the graph paper read the y-intercept of the line?
Solution 9:
Given line is
2x – 3y – 18 = 0
The graph of the given line is shown below.
Clearly from the graph we can find the y-intercept.
The required y-intercept is -6
10.Draw the graph of line x + y = 5. Use the graph paper drawn to find the inclination and the y-intercept of the line.
Solution 10:
Given line is
x + y = 5
The graph of the given line is shown below.
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry











































































