Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Construction of Polygons
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of Polygons (Using ruler and compass only)
Exercise 15
1.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
AB = 3.2 cm, BC = 5.2 cm, CD = 6.2 cm, DA = 4.2 cm and BD = 5.2 cm.
2.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
AB = 7.2 cm, BC = 5.8 cm, CD = 6.3 cm, AD = 4.3 cm and angle A = 75o.
Solution 2:
3.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
Angle A = 90o, AB = 4.6 cm, BD = 6.4 cm, AC = 6.0 cm and CD = 4.2 cm.
Solution 3:
4.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
AB = 3.8 cm, AC = 4.8 cm, AD = 2.8 cm, angle A = 105o and angle B = 60o.
Solution 4:
5.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
BC = 7.5 cm AC = 5.8 cm, AD = 3.6 cm, CD = 4.2 cm and angle A = 120o.
Solution 5:
6.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
AD = AB = 4 cm, BC = 2.8 cm, CD = 2.5 cm and angle BAD = 45o.
Solution 6:
7.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when:
AB = 6.3 cm, BC = CD=4.2 cm and  ABC =
ABC =  BCD = 90o.
BCD = 90o.
Solution 7:
8.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
AB = 4.4 cm, AD = 6.2 cm and AC = 4.8 cm.
Solution 8:
9.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
Diagonal AC = 6.4 cm, diagonals BD = 8.2 cm and angle between the diagonals = 60o.
Solution 9:
10.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
AB = 5.8 cm, diagonal AC = 8.2 cm and diagonal BD = 6.2 cm.
Solution 10:
11.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
AB = 6.0 cm, AD = 5.0 cm and  A = 45o.
A = 45o.
Solution 11:
12.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
Base AB = 6.5 cm, BC = 4 cm and the altitude corresponding to AB = 3.1 cm.
Solution 12:
13.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
AB = 4.5 cm,  B = 120o and the distance between AB and DC = 3.0 cm.
B = 120o and the distance between AB and DC = 3.0 cm.
Solution 13:
14.Construct a parallelogram ABCD, when:
Base BC = 5.6 cm, diagonal BD = 6.5 cm and altitude = 3.2 cm.
Solution 14:
15.Construct a rectangle ABCD, when:
Its sides are 6.0 cm and 7.2 cm.
Solution 15:
16.Construct a rectangle ABCD, when:
One side = 4 cm and one diagonal is 5 cm. Measure the length of other side.
Solution 16:
17.Construct a rectangle ABCD, when:
One diagonal = 6.0 cm and the acute angle between the diagonals = 45o.
Solution 17:
18.Construct a rectangle ABCD, when:
Area = 24 cm2 and base = 4.8 cm2.
Solution 18:
19.Construct a rectangle ABCD, when:
Area = 36 cm2 and height = 4.5 cm.
Solution 19:
20.Construct a trapezium ABCD, when:
AB = 4.8 cm, BC = 6.8 cm, CD = 5.4 cm, angle B = 60o and AD // BC.
Solution 20:
21.Construct a trapezium ABCD, when:
AB = CD = 3.2 cm, BC = 6.0 cm, AD = 4.4 cm and AD // BC.
Solution 21:
22.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
Its one side = 6 cm and  A = 60o.
A = 60o.
Solution 22:
23.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
One side = 5.4 cm and one diagonals is 7.0 cm.
Solution 23:
Steps:
We construct the segment AC = 7cm.
With A as a centre and radius 5.4 cm , we draw an arc extending on both sides of AC.
With C as centre and same radius as in step 2, we draw an arc extending on both sides of AC to cut the first arc at B and D.
Join AB,BC,CD and DA.
ABCD is the required rhombus.
24.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
Diagonal AC = 6.3 cm and diagonal BD = 5.8 cm.
Solution 24:
25.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
One side = 5.0 cm and height = 2.6 cm.
Solution 25:
26.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
Solution 26:
27.Construct a rhombus ABCD, when:
Diagonal AC = 6.0 cm and height = 3.5 cm.
Solution 27:
28.Construct a square ABCD, when:
One side = 4.5 cm.
Solution 28:
29.Construct a square ABCD, when:
One diagonal = 5.4 cm.
Solution 29:
30.Construct a square ABCD, when:
Perimeter = 24 cm.
Solution 30:
31.Construct a rhombus, having given one side = 4.8 cm and one angle = 75o.
Solution 31:
32.Using ruler and compasses only, construct a rectangle each of whose diagonals measure 6 cm and the diagonals interest at an angle of 45o.
Solution 32:
33.Using ruler and compasses only, construct the quadrilateral ABCD, having given AB = 5 cm, BC = 2.5 cm, CD = 6 cm. angle BAD = 90o and the diagonal AC = 5.5 cm.
Solution 33:
34.Using ruler and compasses only, construct a trapezium ABCD, in which the parallel sides AB and DC are 3.3 cm apart; AB = 4.5 cm, angle A = 120o BC = 3.6 cm and angle B is obtuse.
Solution 34:
35.Using ruler and compasses only, construct the quadrilateral ABCD, having given AB = 5 cm, BC = 2.5 cm CD = 6 cm, Selina Solutions Icse Class 9 Mathematics Chapter - Construction Of Polygons Using Ruler And Compass OnlyBAD = 90o and diagonal BD = 5.5 cm.
Solution 35:
36.Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD using the following data: AB = 6 cm, AD = 3 cm and
Solution 36:
37.The perpendicular distance between the pair of opposite sides of a parallelogram are 3 cm and 4 cm, and one of its angles measures 60oo. Using ruler and compasses only, construct the parallelogram.
Solution 37:
Steps:
Draw a base line AQ.
From A take some random distance in compass and draw one are below and above the line. Now without changing the distance in compass draw one are below and above the line. These arcs intersect each other above and below the line.
Draw the line passing through these intersecting points, you will get a perpendicular to the line AQ.
Take distance of 4 cm in compass and mark an arc on the perpendicular above the line. Draw a line parallel to line AQ passing through through this arc.
From point A measure an angle of 60 degree and draw the line which intersect above drawn line at some point label it as D.
Using the procedure given in step 2 again draw a perpendicular to line AD.
Take distance of 3 cm in compass and mark an arc on the perpendicular above the line. Draw a line parallel to line AD passing through through this arc which intersect the line AQ at some point label it as B and to other line at point C.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
38.Draw parallelogram ABCD with the following data:
AB = 6 cm, AD = 5 cm and  DAB = 45o.
DAB = 45o.
Let AC and DB meet in O and let E be the mid-point of BC. Join OE. Prove that:
(i) OE // AB(ii) OE = 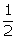 AB.
AB.
Solution 38:
To draw the parallelogram follows the steps:
- First draw a line AB of measure 6cm. Then draw an angle of measure 450 at point A such that ∠DAB = 450 and AD = 5cm.
- Now draw a line CD parallel to the line AB of measure 6cm. Then join BC to construct the parallelogram as shown below:
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chapter 15 - Construction of Polygons







































