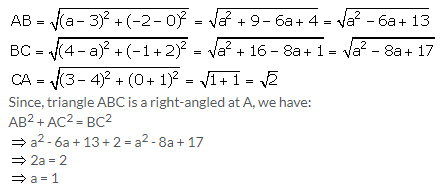Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Distance Formula
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 28 Distance Formula
Exercise 28(A)1.Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(i) (-3, 6) and (2, -6)
(ii) (-a, -b) and (a, b)
(iii) 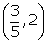 and
and 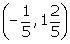
(iv) 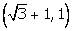 and
and 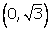
Solution 1:
2.Find the distance between the origin and the point:
(i) (-8, 6) (ii) (-5, -12) (iii) (8, -15)
Solution 2:
3.The distance between the points (3, 1) and (0, x) is 5. Find x.
Solution 3:
4.Find the co-ordinates of points on the x-axis which are at a distance of 17 units from the point (11, -8).
Solution 4:
5.Find the co-ordinates of the points on the y-axis, which are at a distance of 10 units from the point (-8, 4).
Solution 5:
6.A point A is at a distance of 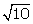 unit from the point (4, 3). Find the co-ordinates of point A, if its ordinate is twice its abscissa.
unit from the point (4, 3). Find the co-ordinates of point A, if its ordinate is twice its abscissa.
Solution 6:
7.A point P (2, -1) is equidistant from the points (a, 7) and (-3, a). Find a.
Solution 7:
8.What point on the x-axis is equidistant from the points (7, 6) and (-3, 4)?
Solution 8:
9.Find a point on the y-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, 2) and (-4, 3).
Solution 9:
10.A point P lies on the x-axis and another point Q lies on the y-axis.
(i) Write the ordinate of point P.
(ii) Write the abscissa of point Q.
(iii) If the abscissa of point P is -12 and the ordinate of point Q is -16; calculate the length of line segment PQ.
Solution 10:
11.Show that the points P (0, 5), Q (5, 10) and R (6, 3) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Solution 11:
12.Prove that the points P(0, -4), Q(6, 2), R(3, 5) and S(-3, -1) are the vertices of a rectangle PQRS.
Solution 12:
13.Prove that the points A (1, -3), B (-3, 0) and C (4, 1) are the vertices of an isosceles right-angled triangle. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution 13:
14.Show that the points A (5, 6), B (1, 5), C (2, 1) and D (6, 2) are the vertices of a square ABCD.
Solution 14:
15.Show that (-3, 2), (-5, -5), (2, -3) and (4, 4) are the vertices of a rhombus.
Solution 15:
16.Points A (-3, -2), B (-6, a), C (-3, -4) and D (0, -1) are the vertices of quadrilateral ABCD; find a if 'a' is negative and AB = CD.
Solution 16:
17.The vertices of a triangle are (5, 1), (11, 1) and (11, 9). Find the co-ordinates of the circumcentre of the triangle.
Solution 17:
18.Given A = (3, 1) and B = (0, y - 1). Find y if AB = 5.
Solution 18:
19.Given A = (x + 2, -2) and B (11, 6). Find x if AB = 17.
Solution 19:
20.The centre of a circle is (2x - 1, 3x + 1). Find x if the circle passes through (-3, -1) and the length of its diameter is 20 unit.
Solution 20:
21.The length of line PQ is 10 units and the co-ordinates of P are (2, -3); calculate the co-ordinates of point Q, if its abscissa is 10.
Solution 21:
22.Point P (2, -7) is the centre of a circle with radius 13 unit, PT is perpendicular to chord AB and T = (-2, -4); calculate the length of:
(i) AT (ii) AB.
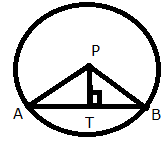
Solution 22:
23.Calculate the distance between the points P (2, 2) and Q (5, 4) correct to three significant figures.
Solution 23:
24.Calculate the distance between A (7, 3) and B on the x-axis whose abscissa is 11.
Solution 24:
25.Calculate the distance between A (5, -3) and B on the y-axis whose ordinate is 9.
Solution 25:
26.Find the point on y-axis whose distances from the points A (6, 7) and B (4, -3) are in the ratio 1: 2.
Solution 26:
27.The distances of point P (x, y) from the points A (1, -3) and B (-2, 2) are in the ratio 2: 3. Show that: 5x2 + 5y2 - 34x + 70y + 58 = 0
Solution 27:
28.The points A (3, 0), B (a, -2) and C (4, -1) are the vertices of triangle ABC right angled at vertex A. Find the value of a.
Solution 28:
Selina Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 28 - Distance Formula